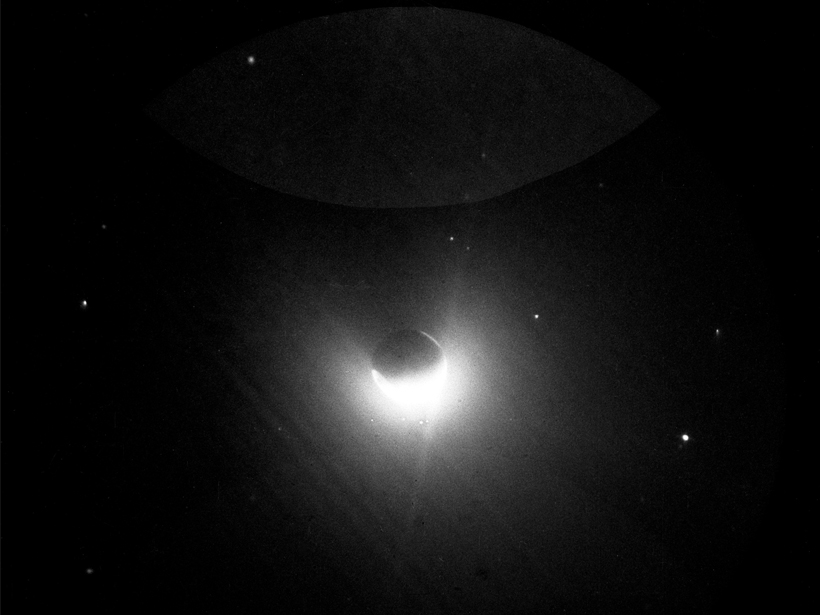
Data from the Cassini spacecraft show that the cusp regions of Saturn’s magnetic field—where it connects to the Sun’s magnetic field—have similarities to Earth’s and also intriguing differences.
magnetic fields & magnetism
O. Walter Lennartsson (1943–2017)
A pioneering leader in unraveling the complex plasma interactions that drive the dynamics of Earth’s magnetosphere and other space plasma environments.
Testing Models of Near-Space Electrical Currents
Modeling Earth’s near-space environment and its electrical currents is challenging. A new study compares how four different models stack up against observations.
How Geomagnetic Storms Light Up the Geocorona
After geomagnetic storms, Earth’s corona abruptly increases in hydrogen density. For the first time, serendipitous observations have allowed researchers to investigate why.
Where Are the Electrical Currents in the Enceladus Plume?
A plume of water ice that escapes Saturn’s moon Enceladus should be coursing with electrical currents, but data are mixed. Now simulations suggest that a sticky dust cloud may shield signals.
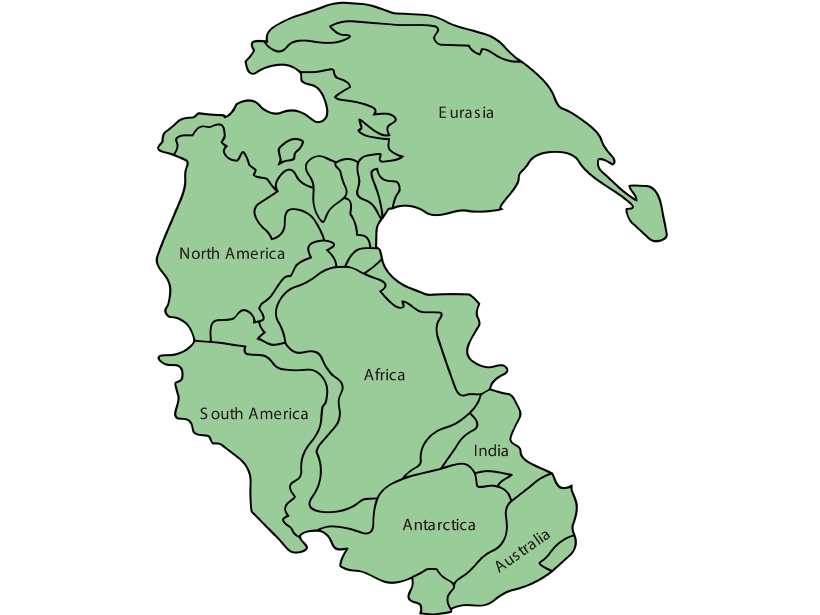
Paleomagnetic Data Hint at Link from Earth’s Core to Continents
Earth’s magnetic field waxes and wanes as supercontinents form and break up, suggests a new study postulating a direct connection between our planet’s crust and its core.
Can Ocean Tides Be Powerful Indicators of Climate Change?
A new study simulates how ocean warming due to climate change will affect the electromagnetic signal emitted by ocean tides over the next century.
Close Encounter with Jupiter
First results from the Juno mission shed new light on Jupiter’s atmosphere, gravity, magnetic field, aurora, history, and more.
David S. Evans (1936–2016)
Evans, a pioneer of auroral physics, changed the way scientists thought about the aurora and magnetic fields and guided a new generation of researchers.
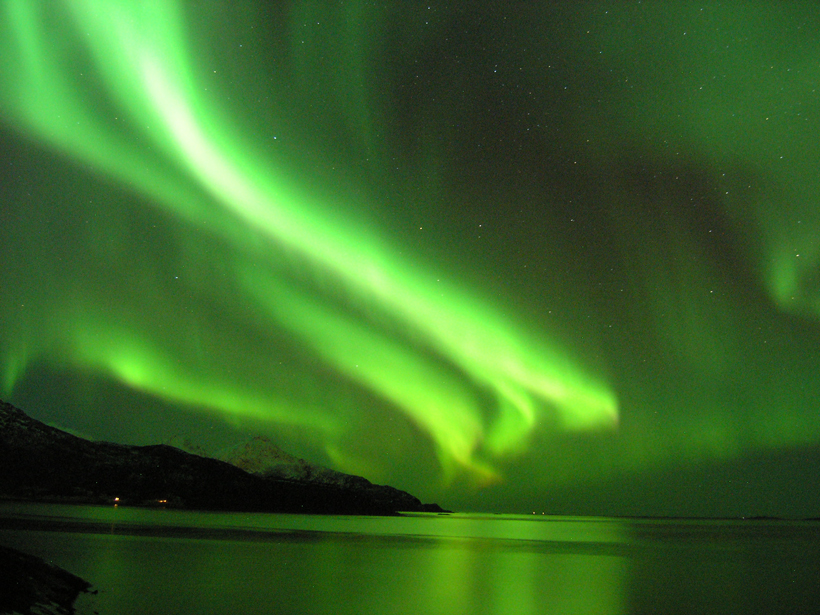
Mining Ancient Texts Reveals Clues to Space Weather of Yore
Low-latitude sightings of colorful hues in the sky likely to have been auroras indicate powerful geomagnetic storms buffeted Earth when some old chronicles were written, researchers report.