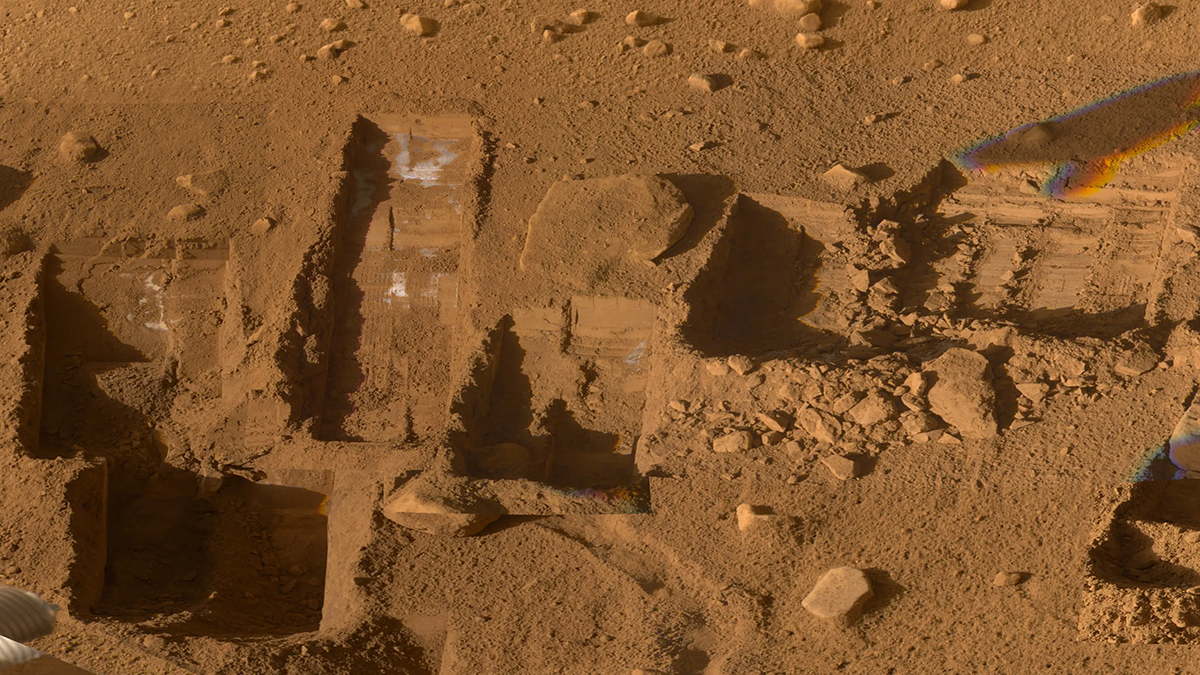
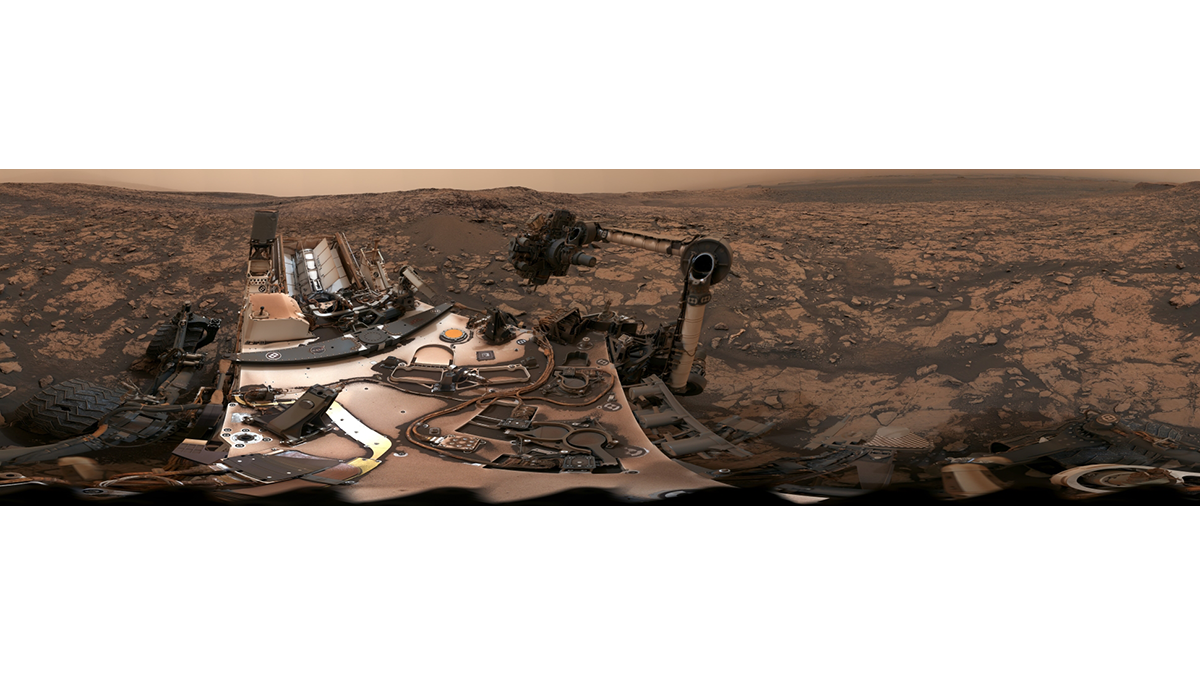
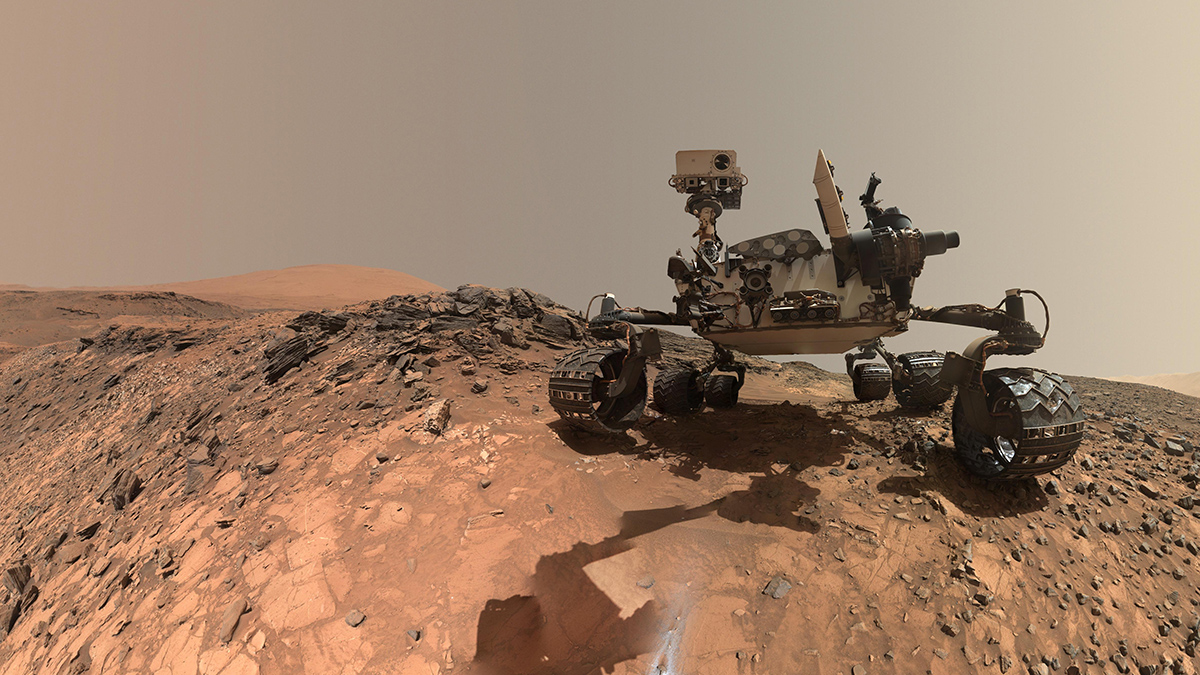
Global detections of oxychlorine salts reveal a complex, 4-billion-year chemical cycle on Mars. They can act as de-icing agents, oxidants, a hazard and a vital resource for future human exploration.
Mars Curiosity Rover
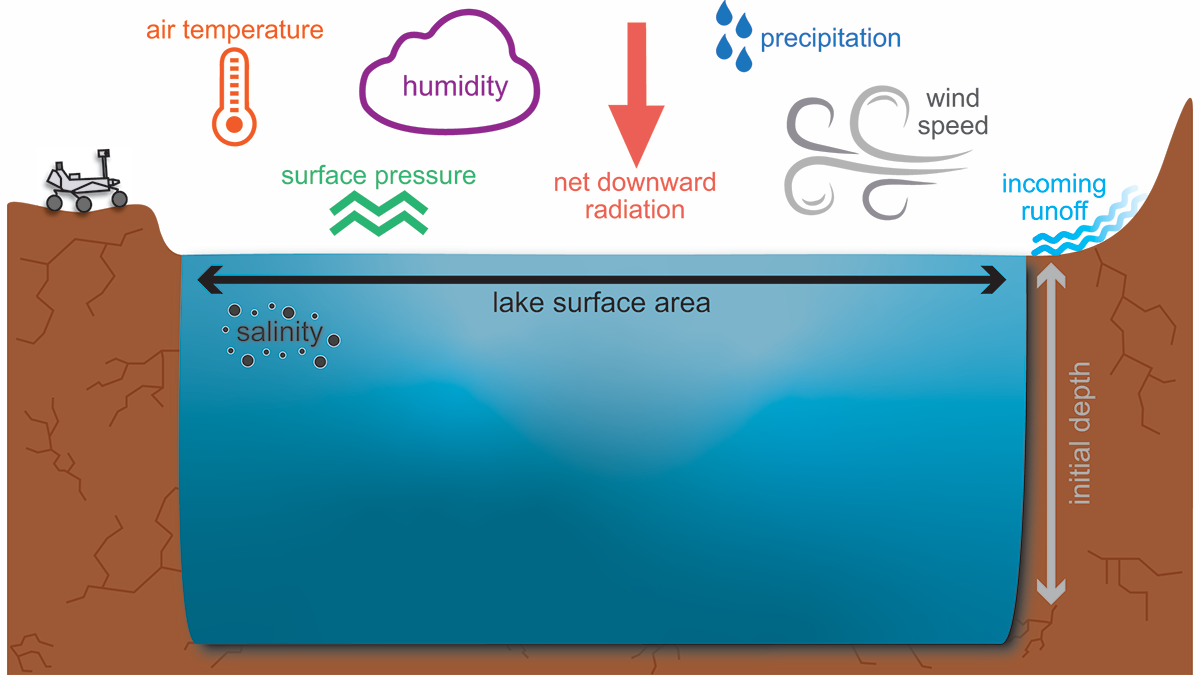
Successful Liquid Lake Conditions in a Cold Martian Paleoclimate
Simulations from a new lake model explain how liquid water could have been maintained over Mars in a cold climate, thus resolving a critical scientific gap in our understanding of Mars’ early history.
Sediments Hint at Large Ancient Martian Moon
Regular, alternating layers in Gale Crater may have been deposited as the result of tides raised by a moon at least 18 times the mass of Phobos, a study says.
Tanya Harrison: Roving on Mars
This planetary geologist has worked on nearly every Mars rover while connecting government, universities, the private sector, and the public.
Proposed Experiment Could Clarify Origin of Martian Methane
Curiosity’s detection of the gas, if atmospheric, could be an indicator of life on the Red Planet. But skeptics say further work is needed to rule out the rover itself as the source of the methane.
Curiosity Digs Up Evidence of a Cold, Wet Martian Past
Amorphous materials, which are rarely studied on Earth, yield insights into the history of Gale Crater and the early Martian environment.
Salty Soil May Release Methane on Mars
Through roving and drilling, Mars Curiosity Rover may be breaking up the ground’s salty, hardened soils that seal methane, possibly causing a temporal, local methane spike.
Scientists Turn Back Time to Track Methane Emissions on Mars
Period spikes of methane on Mars could originate inside Gale crater, where NASA’s Curiosity rover is currently exploring.s
Machine Learning Algorithms Help Scientists Explore Mars
Researchers applied machine learning algorithms to several distinct chemical compositions of Mars and suggest that these algorithms could be a powerful tool to map the planet’s surface on a large scale.
Curiosity Solves the Mystery of Gale Crater’s Hematite Ridge
A new special issue of JGR: Planets details the water-rich history of a distinctive geomorphic feature on Mars dubbed Vera Rubin ridge, as investigated by the Curiosity rover.