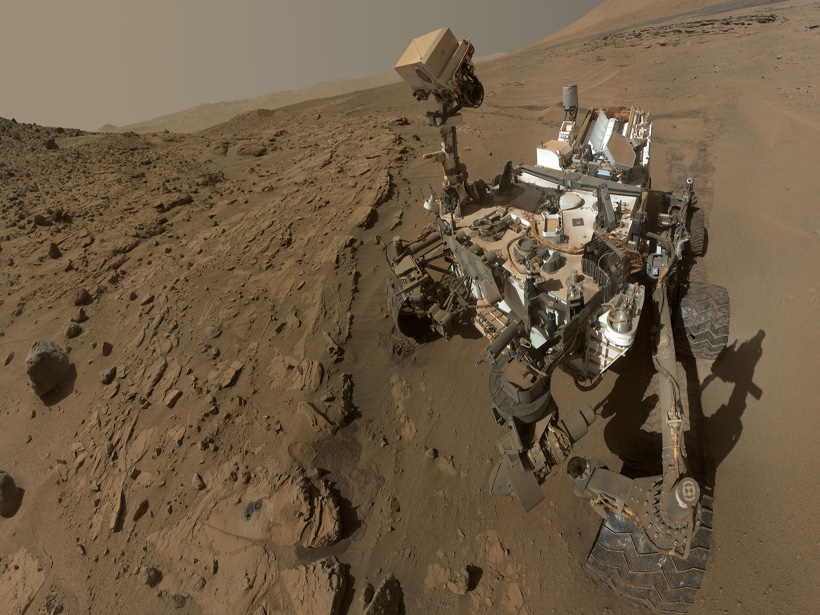
Since the 1970s, no surface platform had made meteorological measurements of a global dust storm on Mars, but last summer NASA’s Curiosity rover witnessed one of these rare events.
Mars Curiosity Rover
Rover and Lasers Unlock Clues to Early Martian Atmosphere
Sediments from the Curiosity rover and experiments using tanks of gas and laser beams helped reveal how water continued to flow on Mars after the planet lost its atmospheric carbon dioxide.
A Rover’s Eye View of Moving Martian Dunes
A new special issue of JGR: Planets presents findings on sand motion, morphology, and mineralogy from the Curiosity rover’s traverse of the active Bagnold dune field in Gale crater.
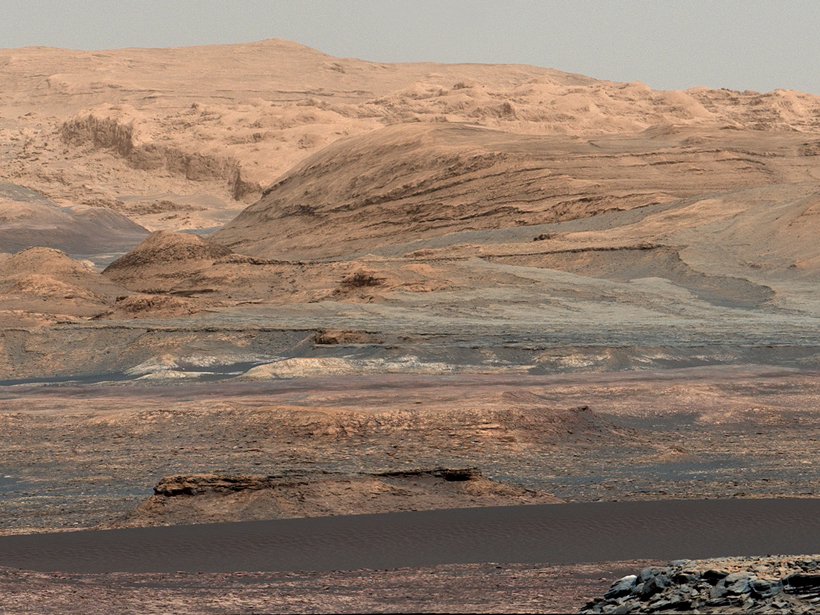
Insights into the Habitability of Mars
NASA’s Curiosity rover explored the Kimberley region of Mars to search for signs that the planet was once habitable.
Curiosity Sends Curious Water Data from Mars
The rover's neutron spectroscopy instrument hints at an unexpected trend: The upper soil levels in the layers of Gale Crater's Kimberley formation seem to hold more water-associated hydrogen.
How on Earth to Decide Where on Mars to Land?
The Public Lecture at AGU's 2016 Fall Meeting will feature three experts—including one still in high school—to discuss landing site selection for the Mars 2020 rover.
Where Curiosity Has Taken Us
The Curiosity rover, one of NASA's flagship missions, analyzes Martian geology, geochemistry, climatology, and radiation to assess whether Mars could have supported microbial life.
Curiosity Rover Finds Organic Molecules on Martian Surface
Scientists assess the present and past habitability of Mars from organic compounds detected at Gale Crater.
Future Mars Rovers: The Next Places to Direct Our Curiosity
Where will the next Mars rovers will land? Think of the selection process as the science fair to end all science fairs, where participating scientists get first looks at the newest Mars data.