A close look at everyday decisions—whether or not to wear a bike helmet or cheat on bus fare—helps students learn about assessing natural hazards, mitigating risks, and setting political priorities.
Modeling
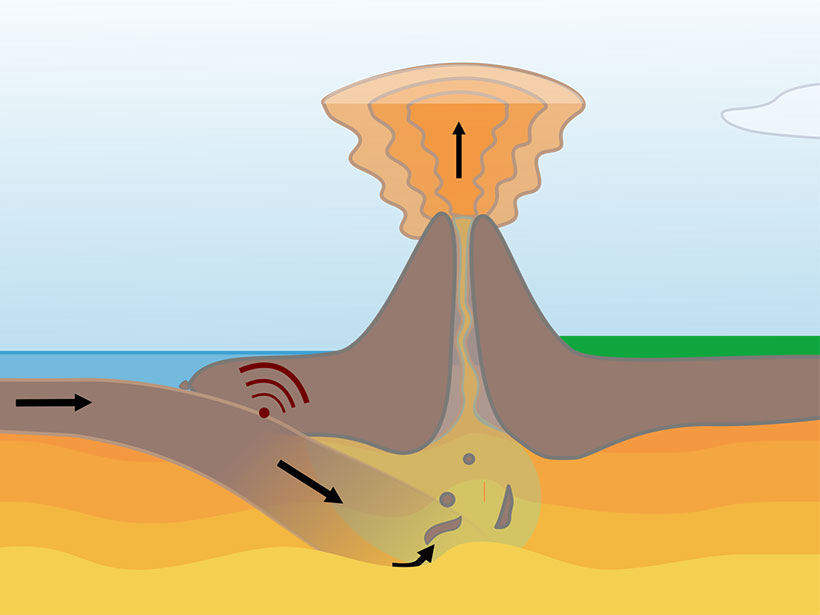
Overriding Plate's Properties Affect Subduction
The properties of the plate that does not sink may strongly control subduction zone dynamics.
As Forests Age, Their Climate Effects Shift
The amount of moisture transpired from leaves increases for some tree species but drops on average.
Observing and Modeling the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
2014 U.S. AMOC Science Team Meeting;
Seattle, Washington, 9–11 September 2014
Seismic Stress Modeling Puts Istanbul in the Crosshairs
Twenty years of ground motion observations show that seismic strain is accumulating south of Istanbul.
Changing Patterns in U.S. Air Quality
Over the northeast United States, ground-level ozone will peak in the winter rather than the summer thanks to continued reductions of regional nitrogen oxide emissions from smokestacks and tailpipes.
How a River Gets Its Width
A new model of deposition and erosion on river banks allows scientists to study how the banks control their stream’s width.
Tracking Down a Subduction Zone Earthquake
Researchers use computer simulations to find the date and earthquake source of an ancient tsunami that deposited sediment in a Hawaii sinkhole.
Bank Materials Strongly Influence River Valley Evolution
Models suggest that the shape of river valleys depends strongly on how meandering rivers interact with the sediment and bedrock of the banks.
Can Scientists Boost Solar Modeling Despite a Lack of Data?
Researchers show that a data processing technique could salvage useful information from raw solar observations, opening the door to improved understanding of the solar dynamo.