Scenario Planning for Climate Adaptation Decision Making; Tucson, Arizona, 31 March to 1 April 2015
Modeling
A Cooler Climate Would Trigger More Tropical Cyclones
New model reveals tropical cyclones could form at lower sea surface temperatures than previously thought.
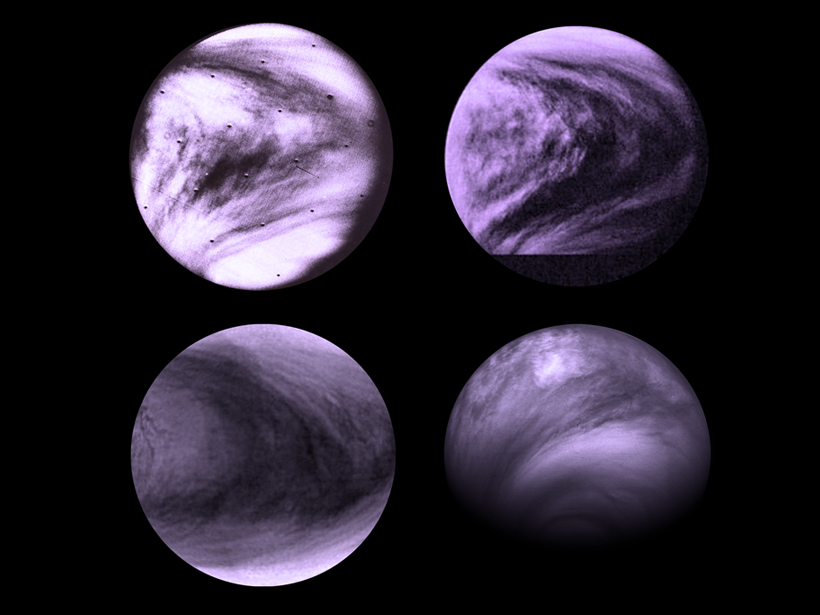
New Atmospheric Wave May Shape Venus's Clouds
A novel model suggests that a new wave may be responsible for Venus's iconic Y pattern.
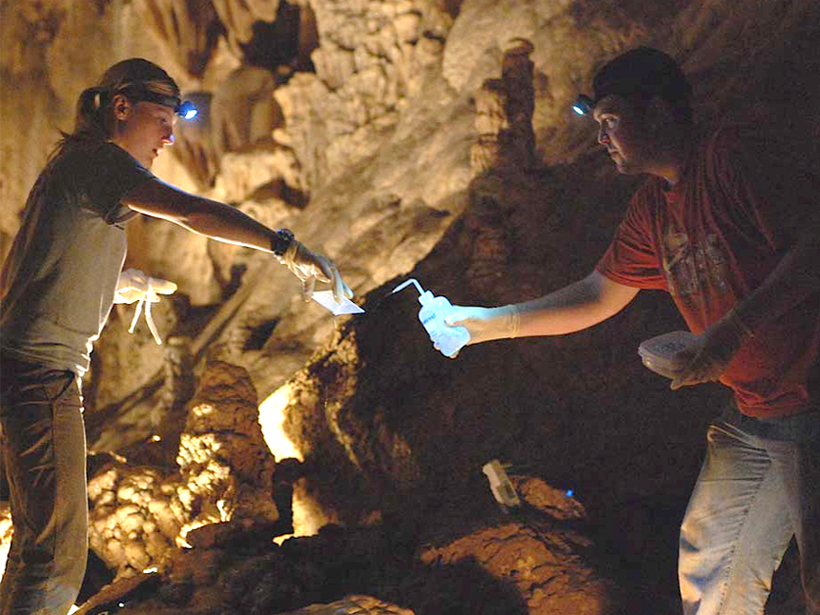
Cave "Breathing" Affects Mineral Growth and Climate Clues
A new global model suggests how and where air flow in caves affects the growth of cave mineral deposits that scientists use to reconstruct ancient climates.
To Help Fix the Hole in the Ozone Layer, Just Add Ice
Computer simulations show that adding tiny droplets of ice to the atmosphere during the spring could help eliminate chlorofluorocarbons and repair the hole in the ozone layer.
Predicting Space Weather on a Satellite Superhighway
Scientists combined 82 satellite years of data to create a more comprehensive model of how plasma behaves in a region of Earth's magnetosphere with heavy spacecraft traffic.
Surface Climate Processes Keep Earth's Energy Balance in Check
Models show that an abrupt increase in carbon dioxide emissions would trigger feedback processes that would change Earth's hydrological cycle.
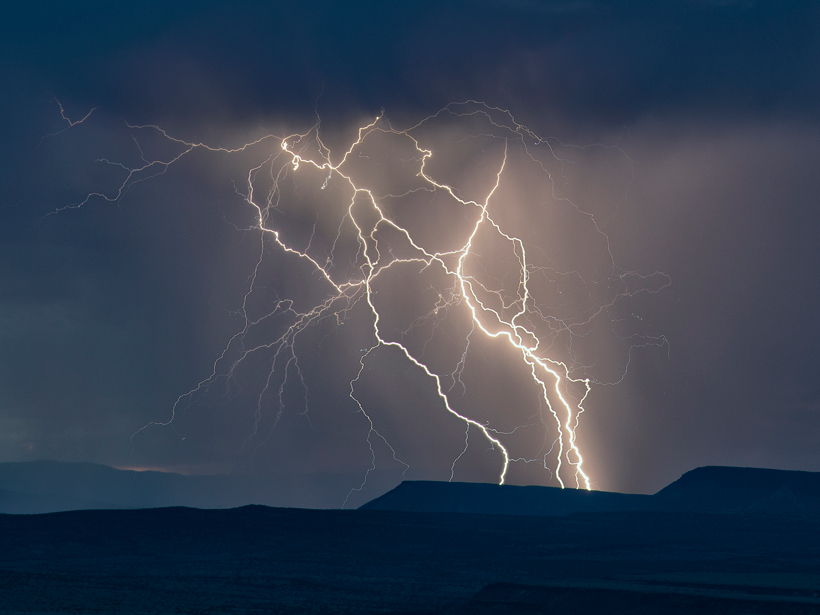
Lightning "Impulses" Improve Models of Global Electrical Circuit
New simulations of how thunderstorms drive electrical currents through the Earth's atmosphere combine precision with computational speed.
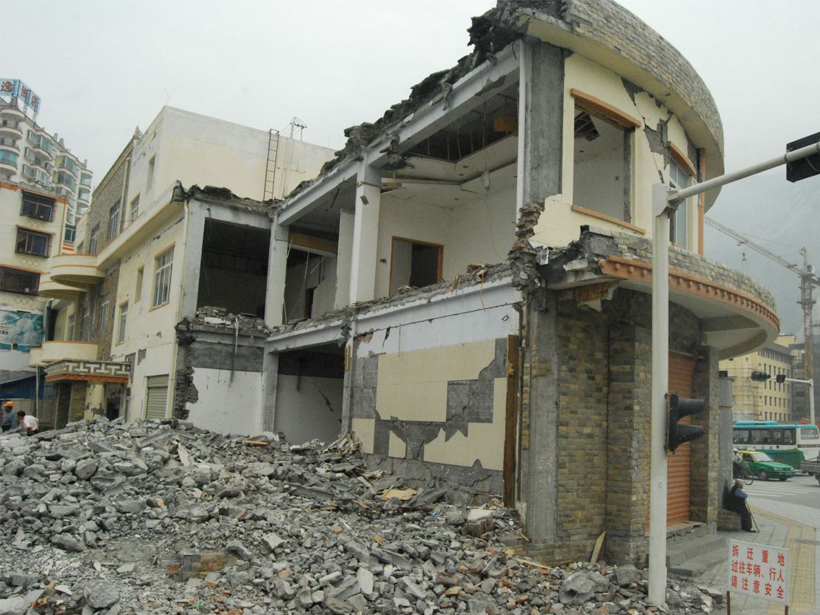
New Models Explain Unexpected Magnitude of China's Wenchuan Quake
The 2008 earthquake surprised scientists, but the inclusion of new variables reveals that Earth's crust under the Sichuan Province was under more strain than previously thought.
On the Rebound: Modeling Earth's Ever-Changing Shape
A new modeling tool easily computes the elastic response of changes in loading on Earth's surface to high resolution. Scientists test this tool using finely detailed data on glaciers' mass changes.