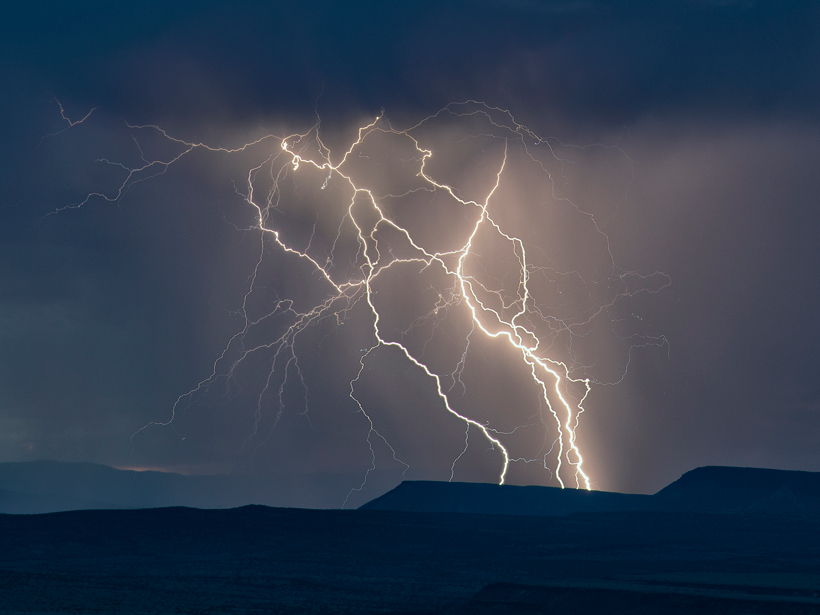
New simulations of how thunderstorms drive electrical currents through the Earth's atmosphere combine precision with computational speed.
Modeling
New Models Explain Unexpected Magnitude of China's Wenchuan Quake
The 2008 earthquake surprised scientists, but the inclusion of new variables reveals that Earth's crust under the Sichuan Province was under more strain than previously thought.
On the Rebound: Modeling Earth's Ever-Changing Shape
A new modeling tool easily computes the elastic response of changes in loading on Earth's surface to high resolution. Scientists test this tool using finely detailed data on glaciers' mass changes.
Reality Check: Seismic Hazard Models You Can Trust
Probabilistic hazard assessments, even the most recent models, routinely underestimate earthquake effects. A neodeterministic approach comes closer to observed data.
Dispelling Clouds of Uncertainty
How do you build a climate model that accounts for cloud physics and the transitions between cloud regimes? Use MAGIC.
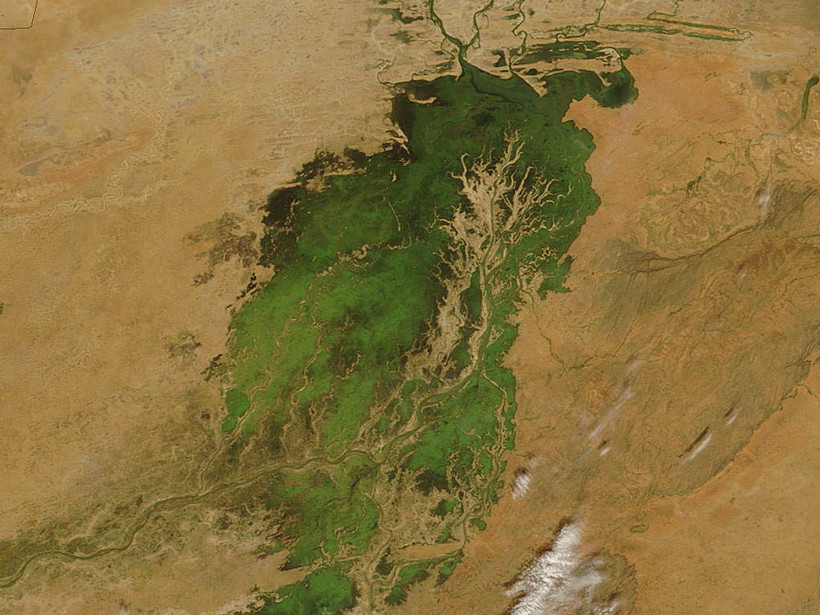
Satellite Measurements May Help Real-Time Water Management
Upper Niger River study shows that satellite altimetry could help resource managers optimize reservoir releases even on ungauged rivers.
Building Sandbars in the Grand Canyon
Annual controlled floods from one of America's largest dams are rebuilding the sandbars of the iconic Colorado River.
Inflexibility of Some Hydrological Models Limits Accuracy
Reducing the number of fixed assumptions may improve the accuracy of complex process-based models.
Global Atmospheric Model Simulates Fine Details of Gravity Waves
Whole-atmosphere general circulation model captures many aspects of mesoscale gravity wave structures—down to the tens of kilometers—and resulting temperatures and tides.
Surface Folds Hint at Magnitude of Slip Along Thrust Faults
The shape of deformed sediments at the surface may allow researchers to estimate the cumulative slip along thrust faults such as the Chelungpu fault in Taiwan.