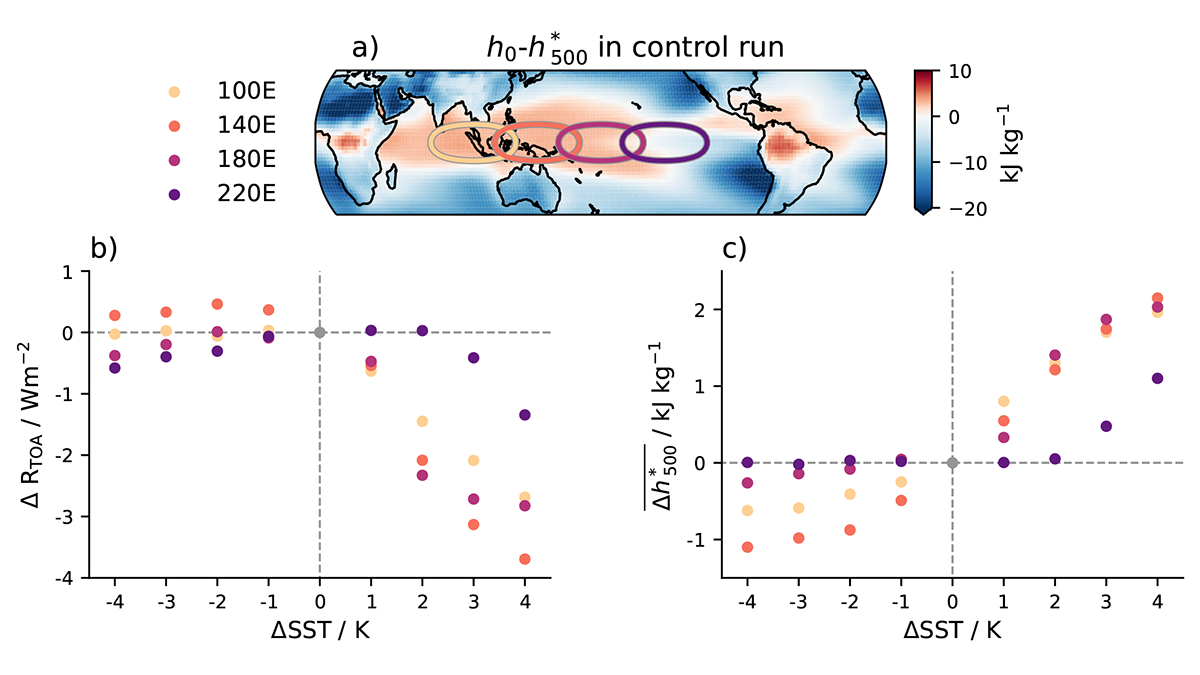
A new study shows the importance of considering non-linear responses to isolated sea surface temperature (SST) changes and the implications for the linear frameworks used to quantify the SST pattern effect.
Modeling
Climate Models Aren’t Dusty Enough
Mineral dust aloft in the atmosphere has a cooling effect not accounted for in current climate models.
Gulf Stream Closes the Valve of the Labrador Current
Virtual particles released in the Labrador Current revealed that the westward penetration of the current into the shelf seas is inhibited by warm core rings emanating from the Gulf Stream.
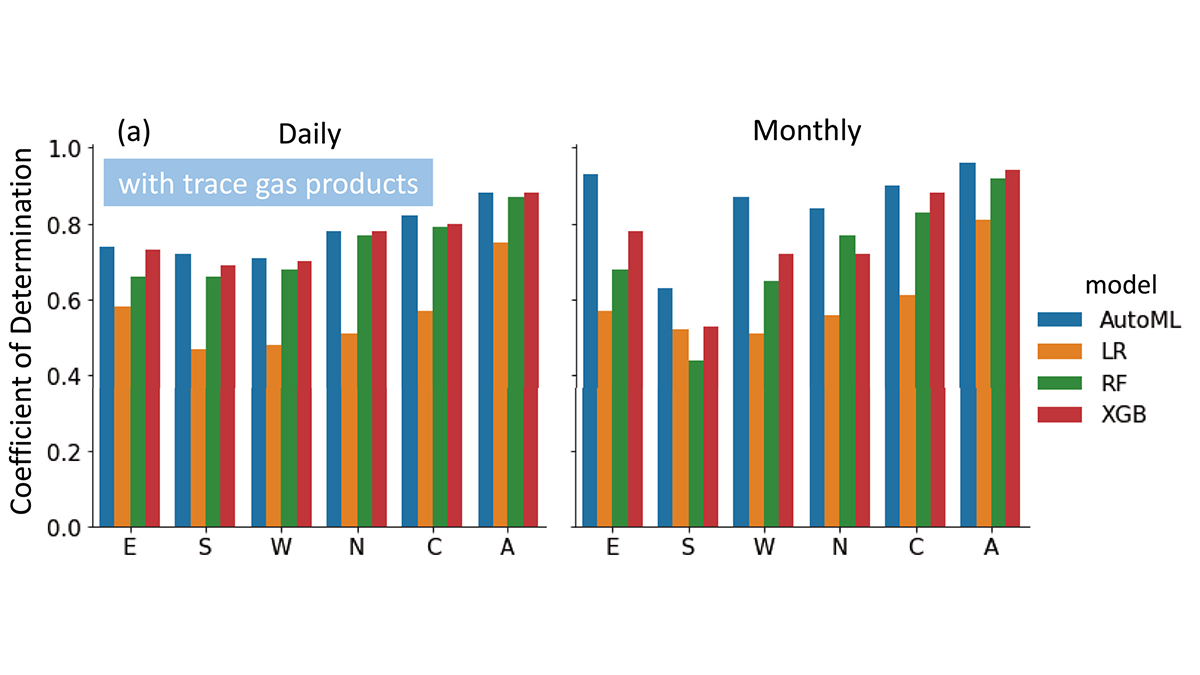
Unleashing the Power of AutoML for Atmospheric Research
Automated Machine Learning liberates domain scientists from selecting learners and hyperparameters and discovers the importance of atmospheric trace gases for improving surface PM2.5 estimates.
El dióxido de carbono antropogénico es rastreado hacia el océano
Con ayuda de un modelo de circulación oceánica, un equipo de investigadores logró etiquetar y rastrear el carbono emitido antropogénicamente para determinar si su destino es la atmósfera o el océano.
Conserving Biodiversity Could Alter Crop Production
Researchers examined the land use trade-offs that could come with protecting at-risk species. But some scientists question what should be prioritized.
How Kicked-Up Dust Forms Cirrus Clouds
Dust lifted into the air by cyclones provides anchor points for cloud-forming ice.
Better Resolution Might Unlock the Mystery of Storms
Climate models have many persistent and systematic biases, but a new study shows that allowing for a physical rather than statistical representation of energy transport reduces one of them.
A New Approach to Spinning-Up Passive Tracers in Ocean Models
A new computational method enables finding steady-state distributions of tracers in ocean circulation models, opening opportunities for physical and biogeochemical insight.
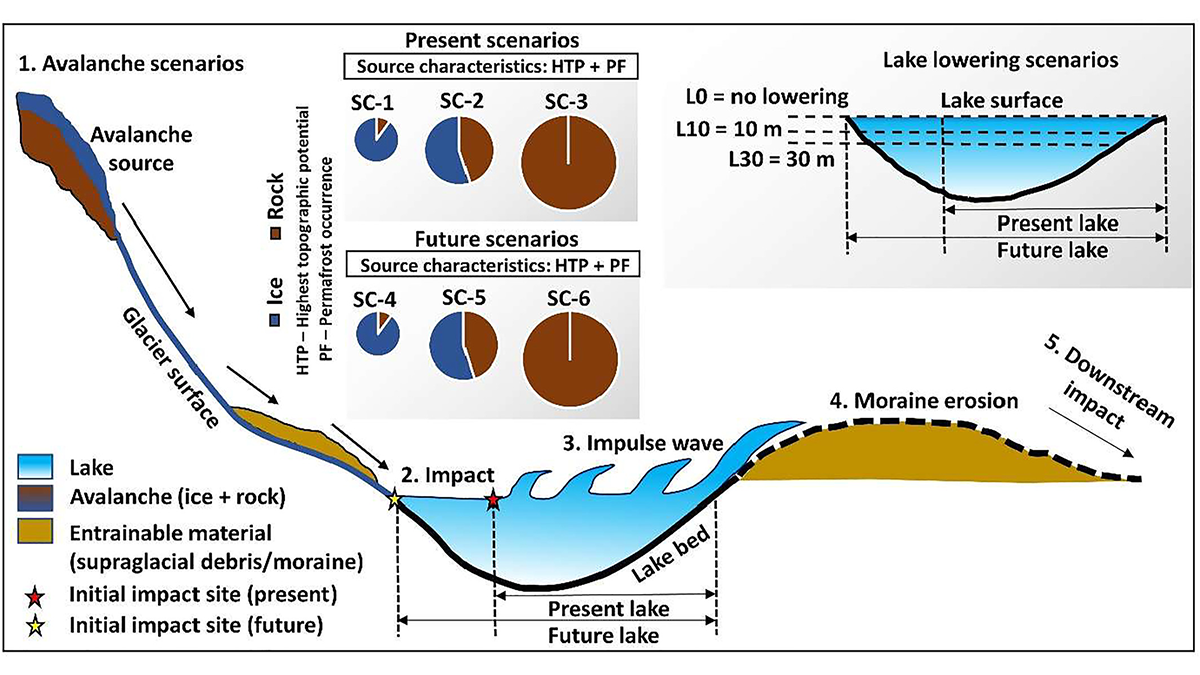
Artificial Lake-Level Lowering Alleviates Floods in the Himalayas
A new model combining future permafrost degradation and related avalanches demonstrates that artificial lake-lowering could significantly reduce the risk of glacial lake outburst floods.