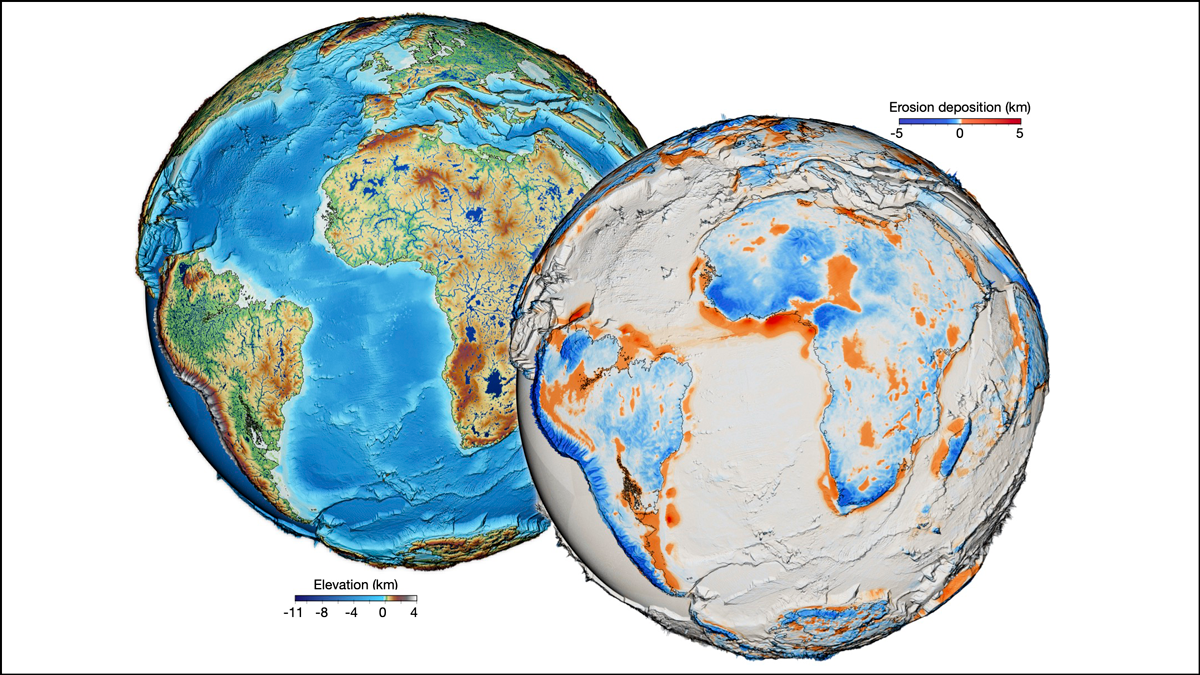
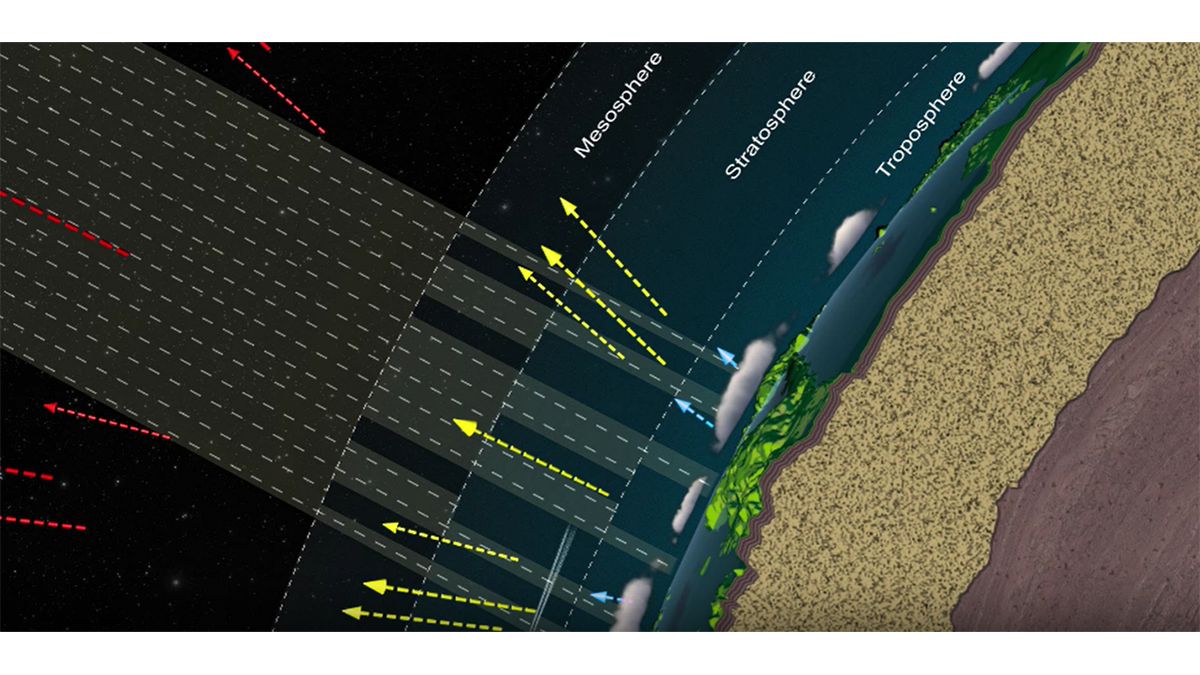
For the first time, scientists have forged a nearly all-encompassing model of Earth’s surface evolution over the past 100 million years.
Modeling
Meshless Methods Tell Us What Lurks Beneath the Surface
Limitations with resolving complex underground targets with sufficiently fine resolution may be alleviated through the adoption of meshless electromagnetic methods.
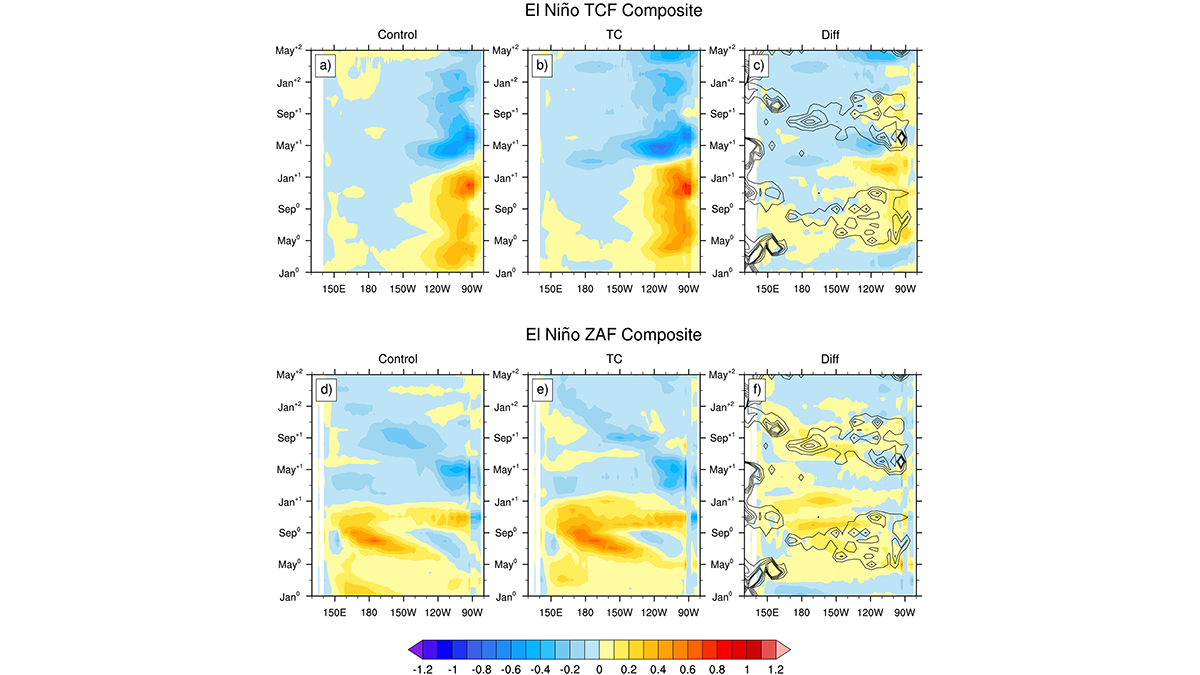
Impact of Tropical Cyclones on El Niño-Southern Oscillation
A suite of Earth Systems model experiments is used to explore how tropical cyclones influence the frequency, magnitude, and timing of El Niño-Southern Oscillation events.
Taking Cloud Microphysics Experiments to the Next Level
Experiments in a cloud chamber have provided valuable insights into microphysical processes and will get more realistic as the height of the chamber increases.
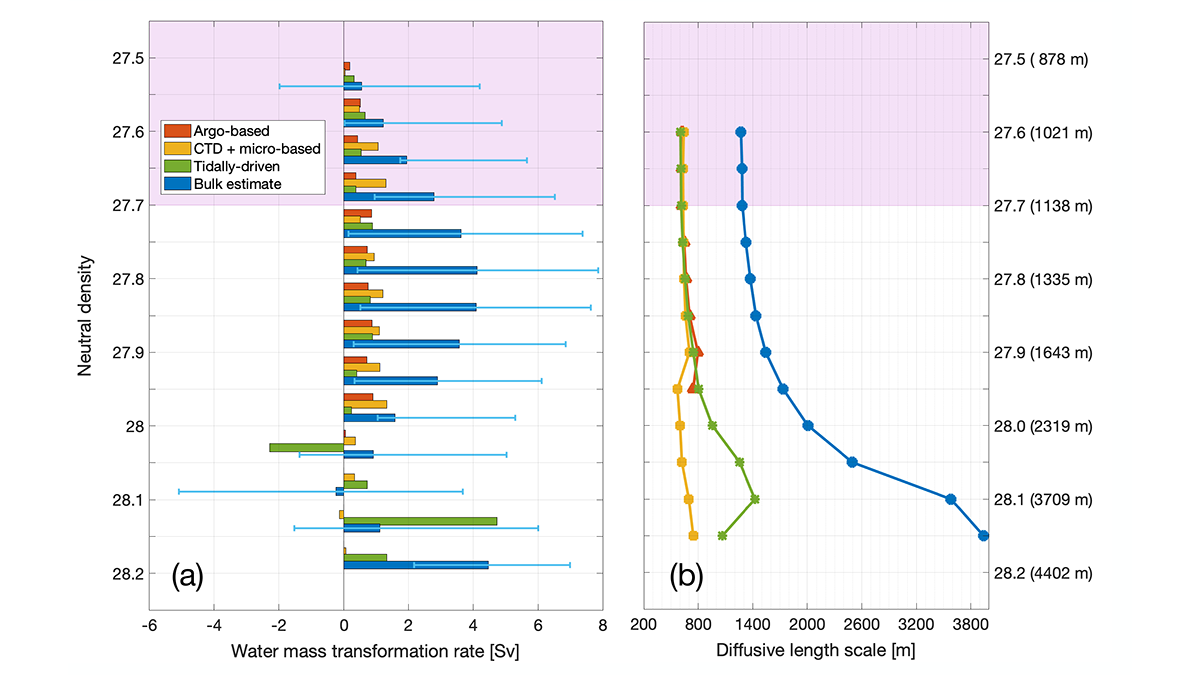
Diapycnal Mixing and the Atlantic Ocean Overturning Circulation
Quantitative observation-based estimates highlight the contribution of diapycnal mixing to the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, water mass formation, and tracer transfers and pathways.
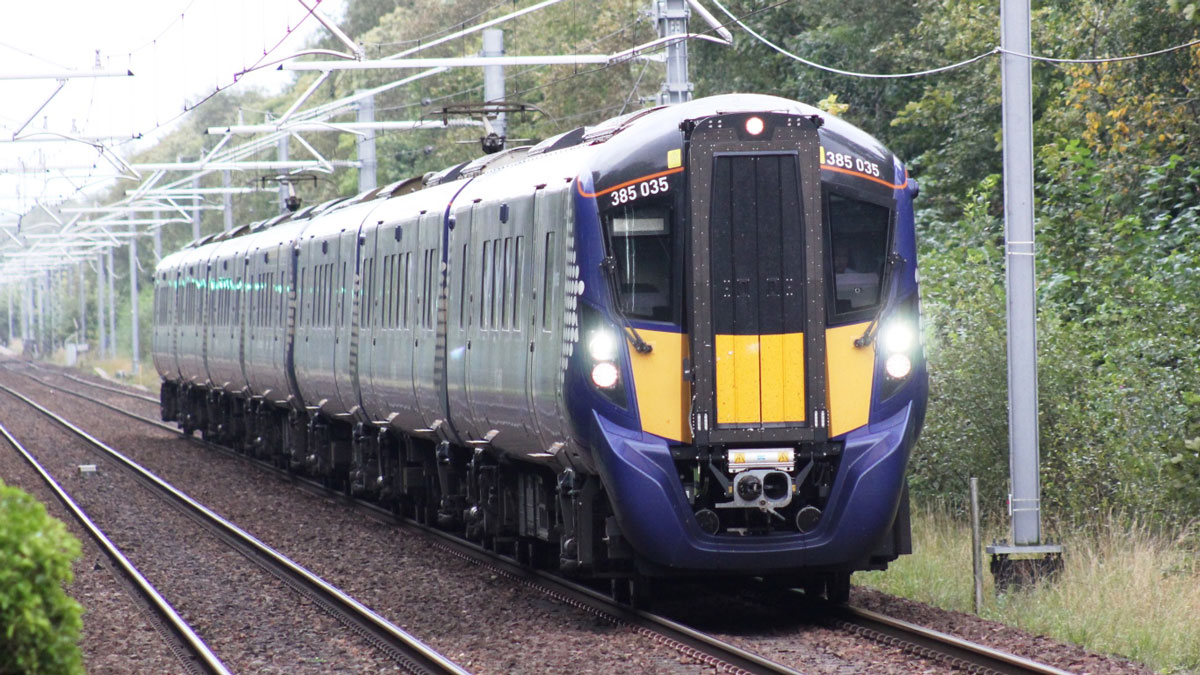
How Space Storms Miscue Train Signals
Geomagnetic storms could significantly disrupt electrified train operations in the United Kingdom once every few decades, according to a new study.
Updated Reference Standard for Total Solar Irradiance
Version 2 of the Total and Spectral Solar Irradiance Sensor-1 Hybrid Solar Reference Spectrum captures a spectral resolution spanning 0.115-200 micrometers and integrates nearly 100% of the TSI energy.
How Big Data is Helping Environmental and Climate Research
A new special collection invites papers focusing on the processing, modeling, and analysis of all types of big datasets in the Earth and space sciences, including the influence of solar forcing on Earth’s climate.
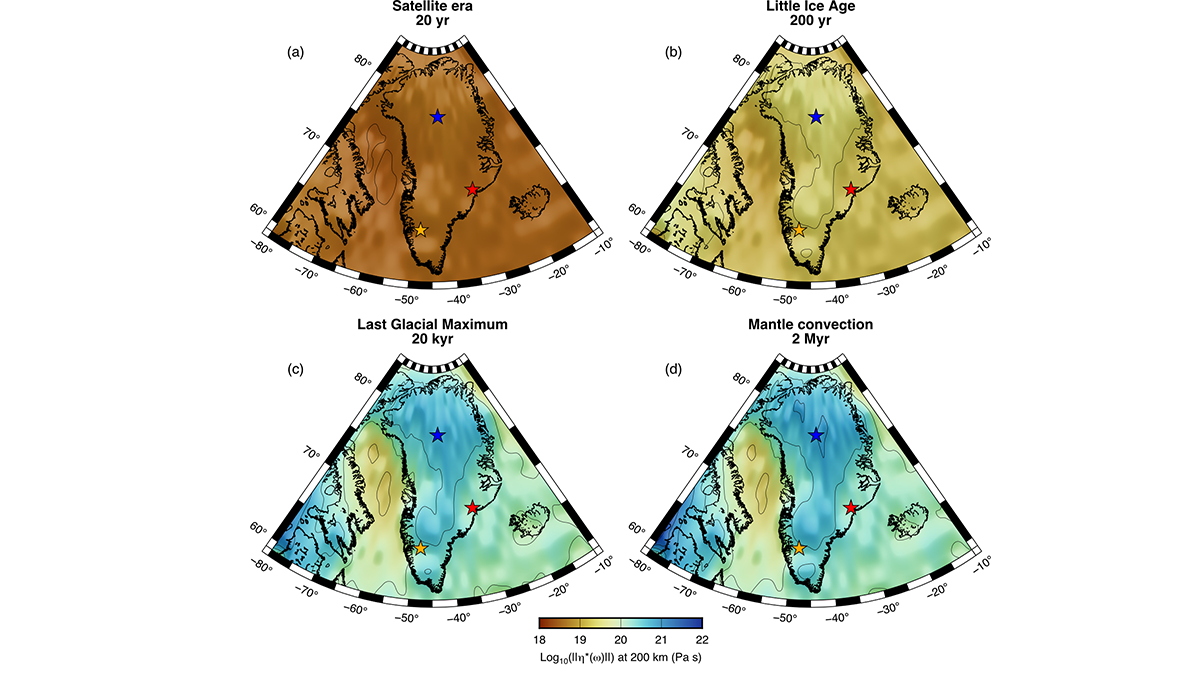
4D Viscosity Constraints from Greenland
The mantle’s resistance to flow appears different for glacial and plate tectonic timescales but this behavior can be reconciled with new thermo-mechanical models of the asthenosphere.
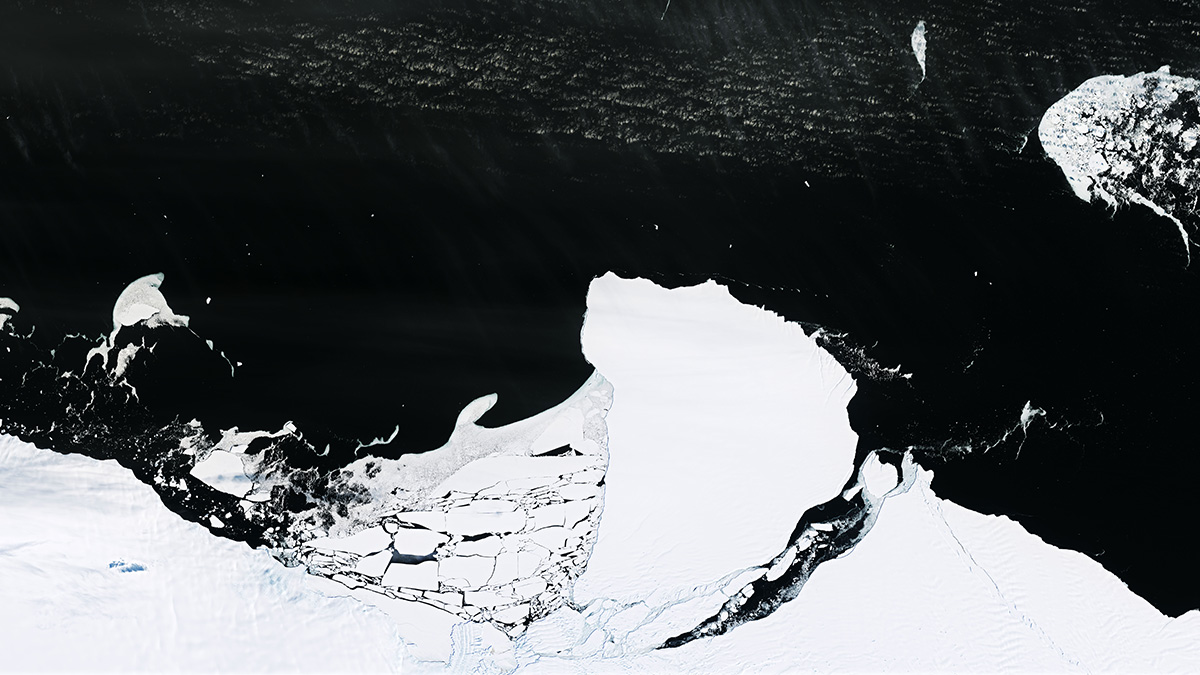
Supercharged El Niño Could Speed Up Southern Ocean Warming
Projected changes to El Niño will likely accelerate warming of the deep oceans around the Antarctic, supplying heat that could drive ice loss and sea level rise.