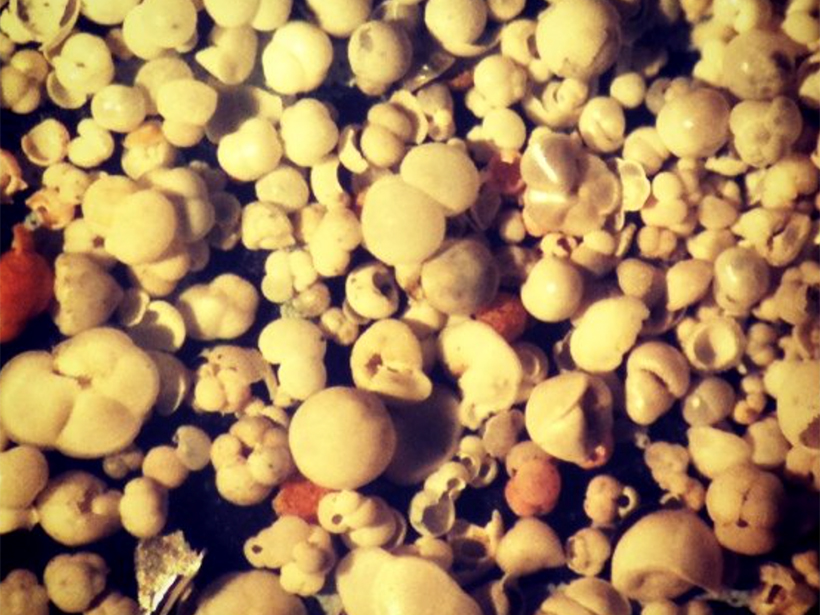
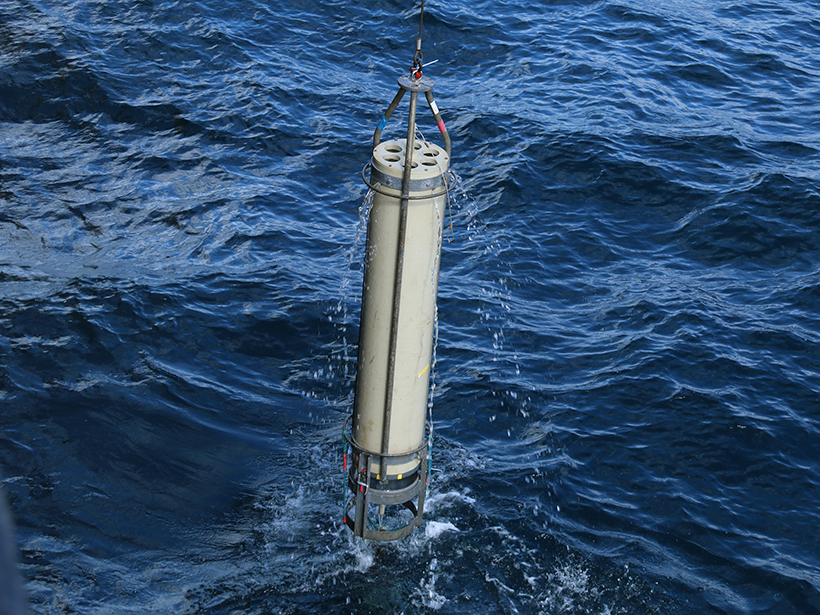
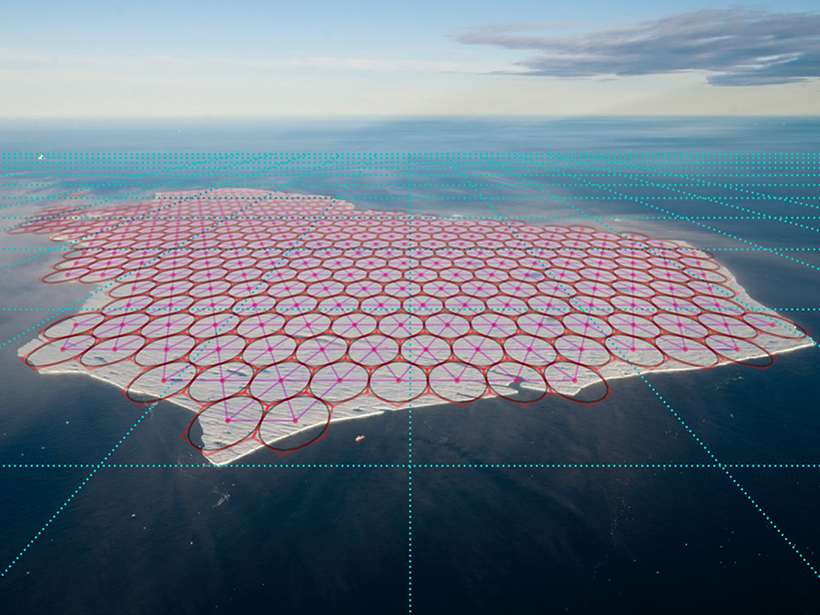
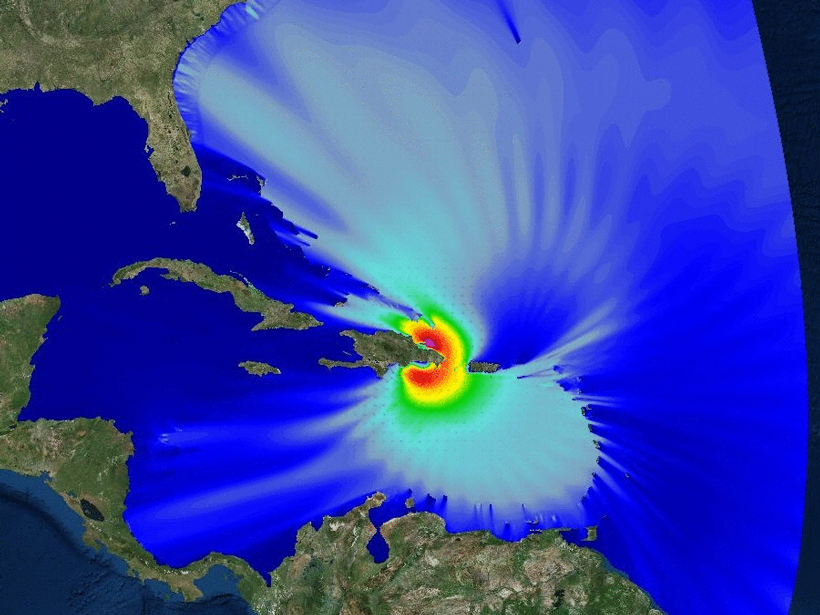
Small, slow-sinking organic particles may play a bigger role than previously thought in the transport of carbon below the surface ocean.
Modeling
Peering into the Cracks
A recent article in Reviews of Geophysics combined mathematical modeling, fracture mechanics theory and engineering research data to provide new insights into a critical geological process.
Improving Our Understanding of El Niño in a Warm Climate
A new study seeks to bring together the strongest features of proxy data and climate models to reduce uncertainties in reconstructions of past El Niño behavior.
Simulations Give New View of Global Auroral Storms
New computer models capture the movement of the strongest auroral storms as they sweep across Earth at night, challenging scientists’ views of what drives them.
How to Find an Iceberg’s Breaking Point
Researchers develop a mathematical method of modeling tabular icebergs, like the one that broke away from an Antarctic ice shelf earlier this year.
A Test Bed for Coastal and Ocean Modeling
An ocean modeling program is improving our ability to predict circulation along the U.S. West Coast, dead zones and other coastal ecosystem responses, and storm surges in island environments.
A Promising New Tool for Forecasting Volcanic Hazards
A new model that simulates the behavior of surging ash clouds may help scientists to better predict the hazards associated with the deadliest type of volcanic flows.
A New Model for River Meanders
A river’s twists and turns are shaped by its past flood events.
Follow Earthworm Tracks to Better Simulate Water Flow in Soils
Incorporating paths carved by the critters and by tree roots helps scientists align simulations of tropical soils more closely with real-world data.
The Competing Climate Effects of Elevation and Albedo
Variations in surface reflectivity are as important as surface elevation changes in determining regional climate at nonpolar latitudes, according to a new modeling study.