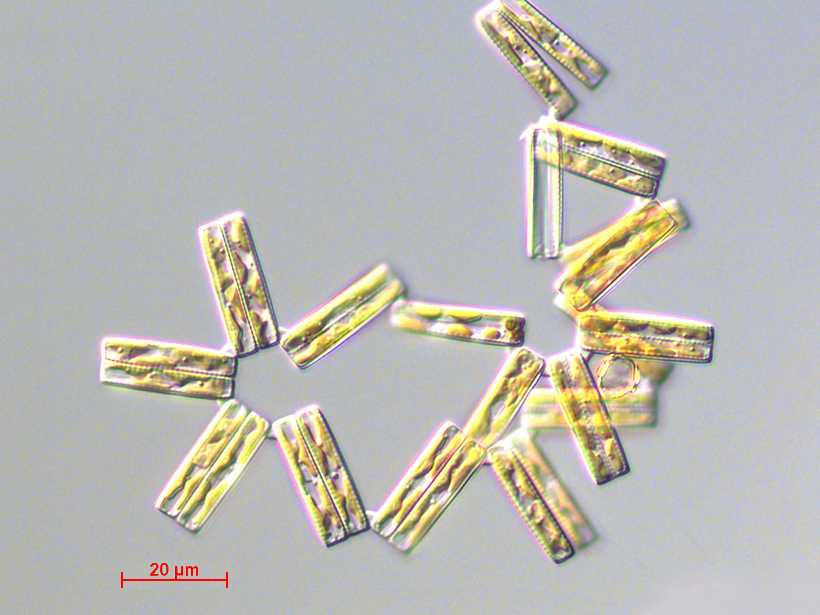
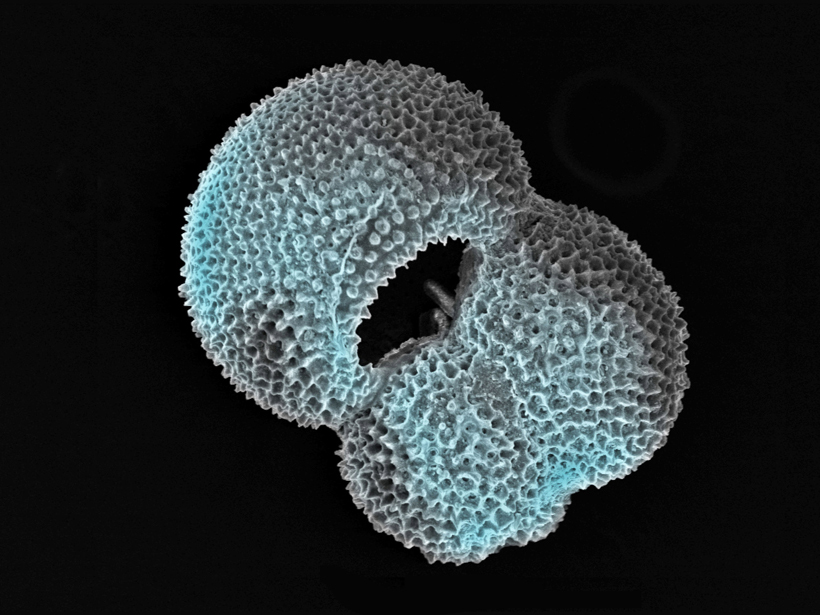
Varying amounts of glacial debris in a core of ancient sediment show the ice cover grew and shrank until airborne carbon dioxide levels fell below 600 parts per million, spurring steady growth.
paleoclimatology & paleoceanography
Characterizing Interglacial Periods over the Past 800,000 Years
Researchers identified 11 different interglacial periods over the past 800,000 years, but the interglacial period we are experiencing now may last an exceptionally long time.
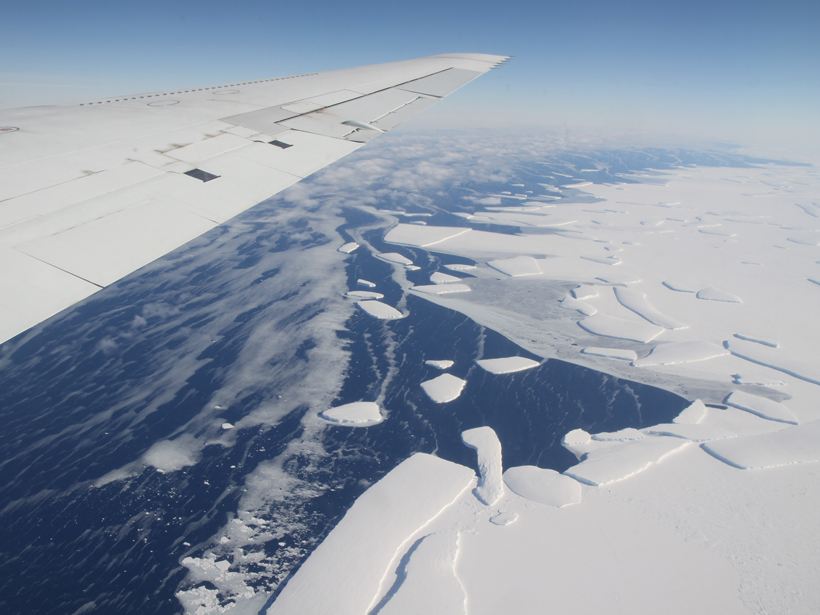
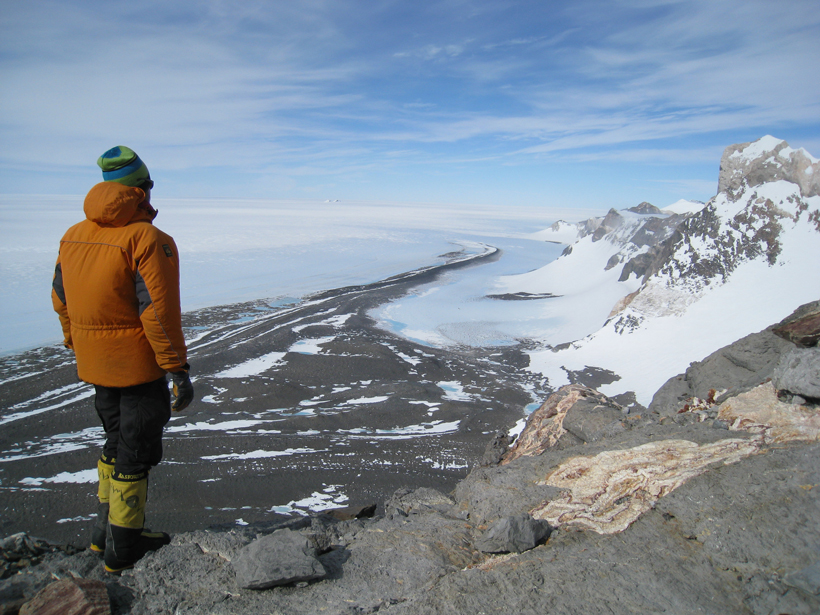
Pleistocene Rocks Tell Tale of Past Ice Sheet Melting
Researchers examine evidence from a past interglacial period to predict sea level rise in the future.
Deep-Sea Microbes Can Leave Records of the Past
Researchers use carbon signatures within sea sediments to identify microbial activity and also to date earthquakes.
Sea Level and Ice Sheet Changes During Past Warm Periods
PALSEA2 2015 Workshop; Tokyo, Japan, 22–24 July 2015
Ancient Start of Animal Evolution Wasn't Delayed by Low Oxygen
New research finds that Earth had sufficient oxygen 1.4 billion years ago for animals to evolve. Therefore, low oxygen levels probably didn't hold back evolution, as scientists have long thought.
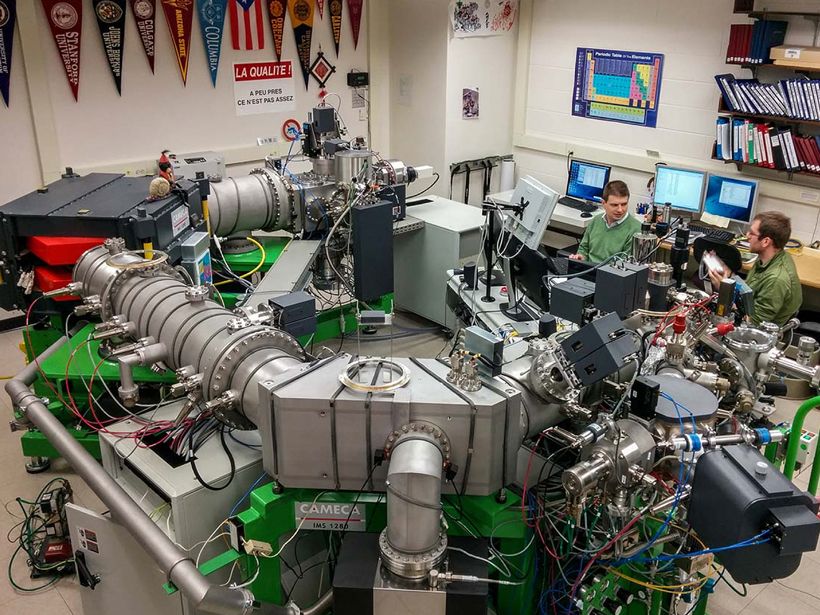
Plankton Reveal New Secrets About Ancient CO2 Levels
An analysis of phytoplankton shells doubles previous estimates of the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere 11 million years ago.
High-Resolution Tools Advance Study of Paleoclimate Archives
HiRes2015: High Resolution Proxies of Paleoclimate; Madison, Wisconsin, 31 May to 3 June 2015
Correlating Monsoon Strength with Boron Isotopes
Scientists tell the story of the past monsoon by measuring boron isotopes in organisms in the Arabian Sea.
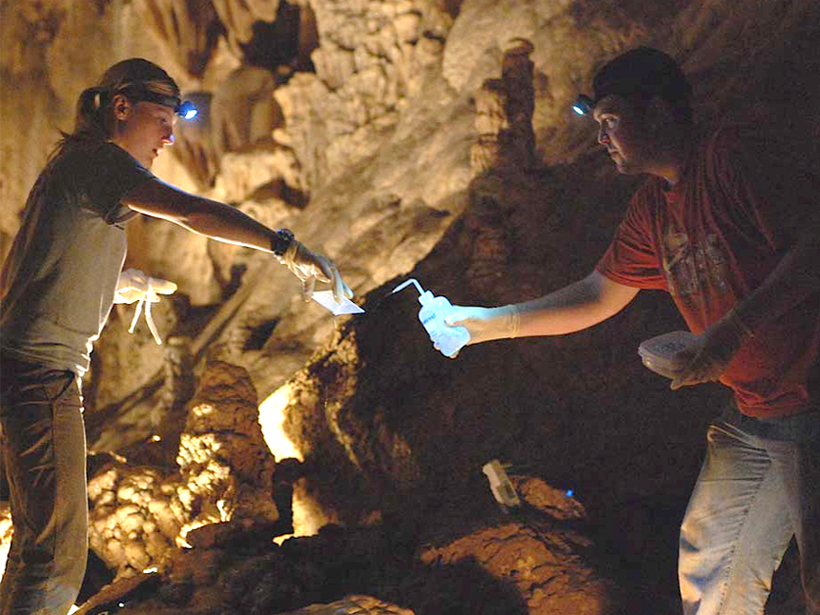
Cave "Breathing" Affects Mineral Growth and Climate Clues
A new global model suggests how and where air flow in caves affects the growth of cave mineral deposits that scientists use to reconstruct ancient climates.