High-resolution imagery of newly discovered paleolakes shows a period of consistent liquid water flow.
paleoclimatology & paleoceanography
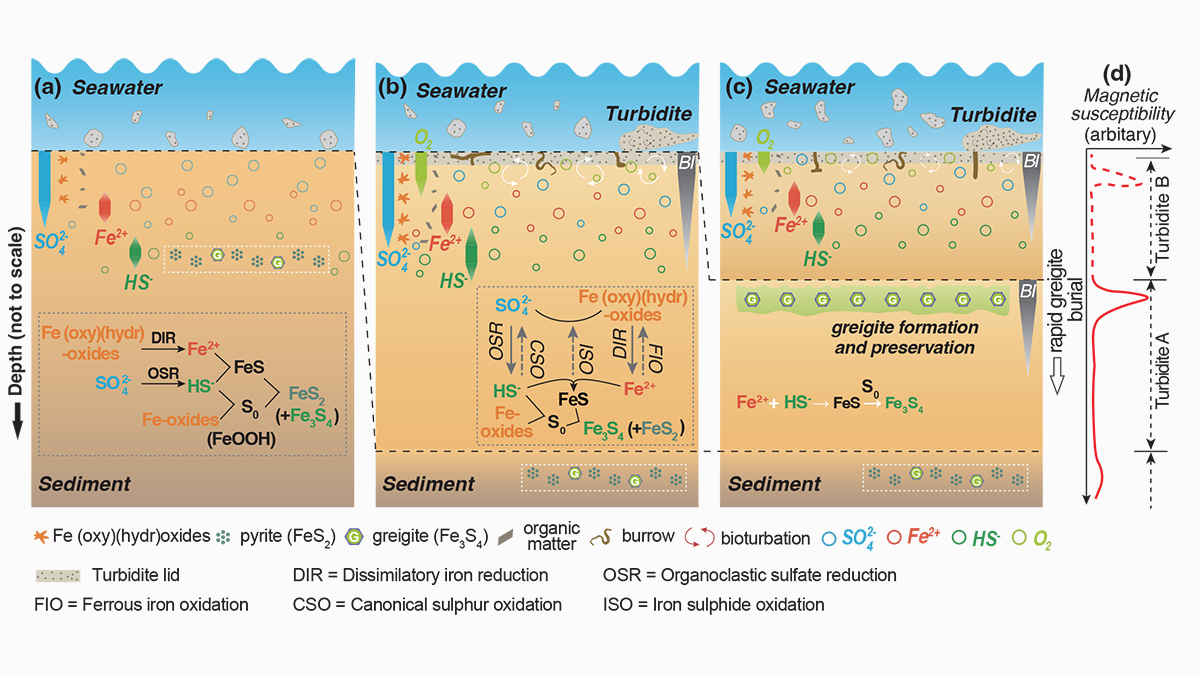
New Mechanism for “Giant” Greigite Growth in Deep-Sea Sediments
Understanding greigite formation pathways in sediments is a prerequisite for assessing the marine iron-sulfur-carbon cycle and yield reliable near-syn-sedimentary paleomagnetic records.
Did a Chaotic Climate Drive Human Evolution?
A new 620,000-year climate record from East Africa reveals dramatic swings between wet and dry conditions that may have influenced human evolution.
A Mysterious Dome Reveals Clues to Australia’s Miocene History
The Nullarbor Plain has been relatively untouched by geological forces, leaving traces of the continent’s deep past.
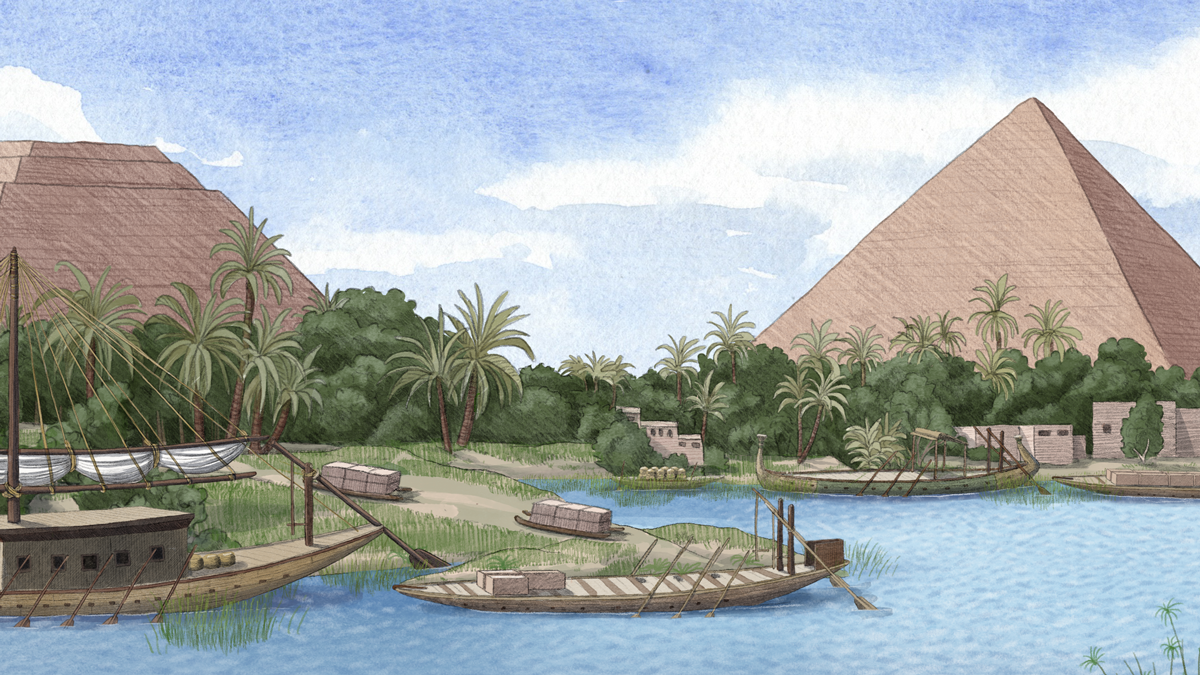
Ancient Nile Tributary May Have Aided Pyramid Construction
Pollen from sediment cores shows that a now dry channel cutting through Giza was once a flowing waterway that Egyptian pyramid builders could have used to transport supplies.
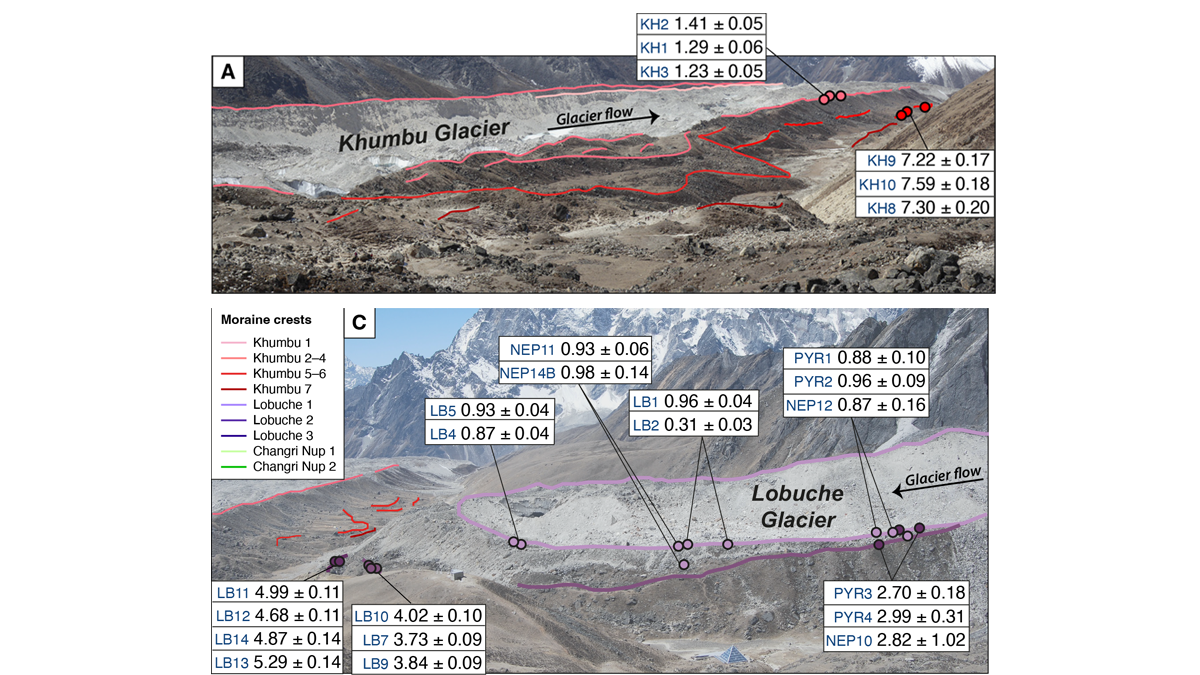
Glacier Advance and Retreat: Insights From the Top of the World
New dating of glacial features reveals predictable glacier behavior in response to climate warming and cooling in the Everest region in the past 8,000 years.
A Post-Impact Deep Freeze for Dinosaurs
New research supports the hypothesis that dinosaurs were done in by climate change after an asteroid impact kicked up a massive plume of sulfur gases that circled the globe for several decades.
Volcanic Winters Ushered in the Jurassic Reign of the Dinosaurs
Sediment cores from northwestern China reveal freezing conditions during the Late Triassic killed off many forms of life—but not dinosaurs.
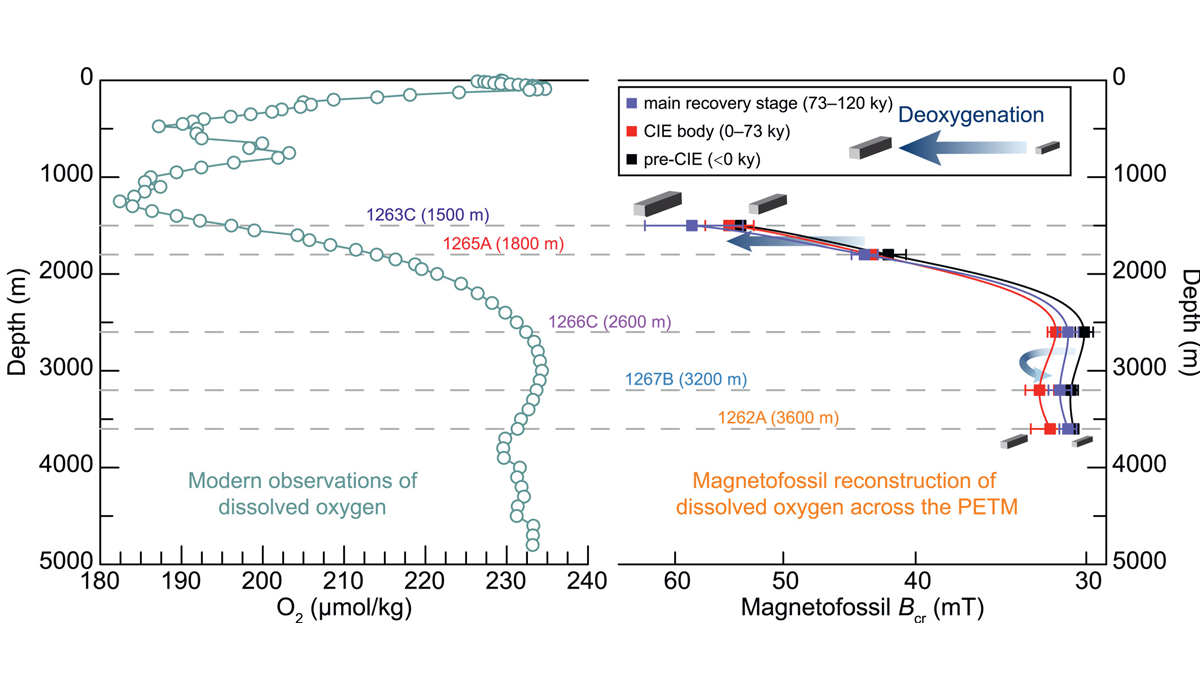
Magnetofossils Unveil Paleoredox Conditions in Extreme Climate
The Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum, a thermal pulse about 56 million years ago, is an analog for future global warming. A new magnetofossil study shows progressive ocean deoxygenation.
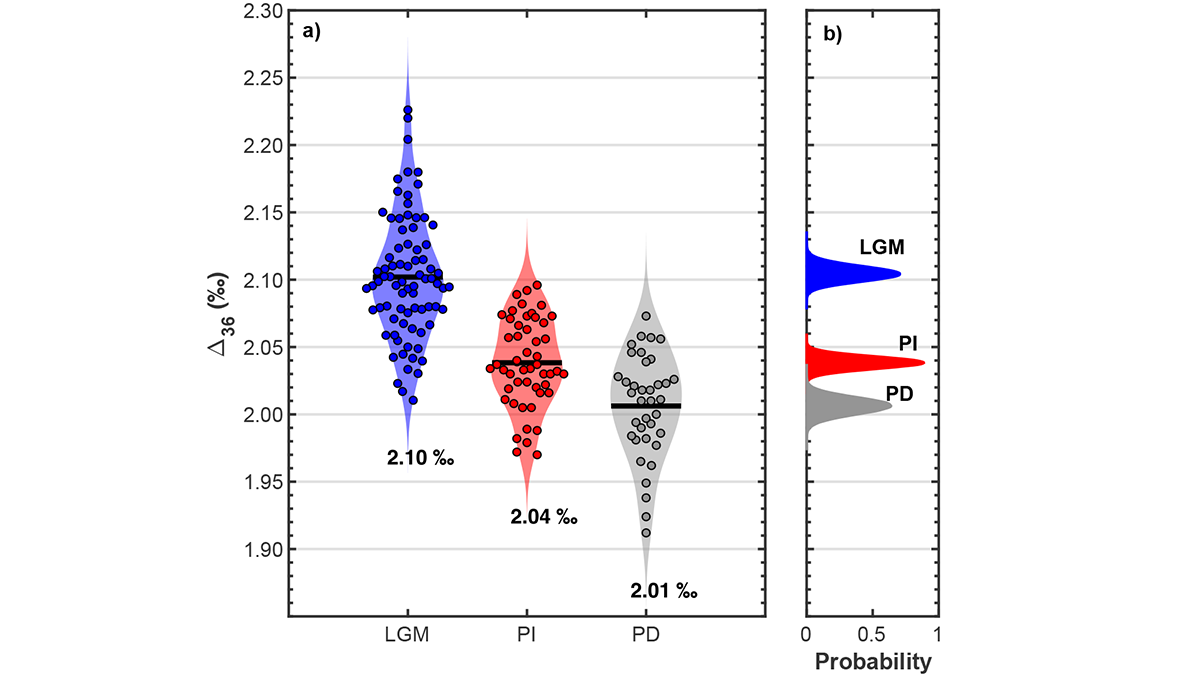
New Tool to Decipher Past Upper Troposphere Temperatures
Small variations in clumped O2 isotopes reflect temperatures in the upper troposphere. Bubbles measured in polar ice cores show the global lapse-rate appears to steepen during the Last Glacial Maximum.