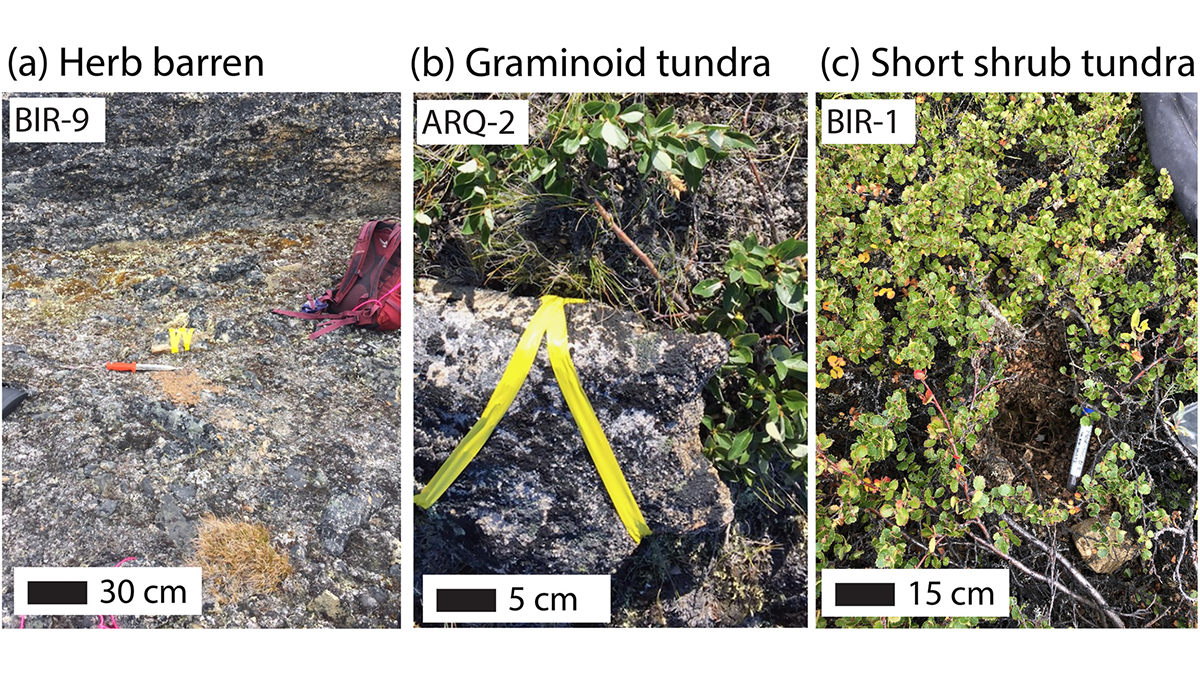
Extensive ground temperature measurements complicate our understanding of how vegetation cover, snow duration, and microtopography influence the pace of permafrost thaw in a changing climate.
permafrost
Groundwater Flow May Contribute to Submarine Permafrost Thaw
New, detailed surveys from the Beaufort Sea reveal a seafloor depression the size of a city block associated with permafrost thaw and likely influenced by the movement of groundwater below.
Why is Permafrost Groundwater Surfacing?
Hydrogeological properties of degrading permafrost come to fruition with a new 3-D modeling study that highlights the increasing role of groundwater in the water cycle of high-latitude areas.
More Fires, More Problems
Increasing incidents of wildfires in the Arctic are not only thawing permafrost but changing the entire underlying structure of the region.
Hot Lakes in a Cold Climate
Arctic warming may release less carbon dioxide from high latitude lakes but increase their climate impact by releasing more methane.
Projection: $110 Billion in Repairs for Russian Pipelines on Permafrost
Permafrost thaw is a major threat to pipelines in the Russian Arctic, particularly those carrying natural gas.
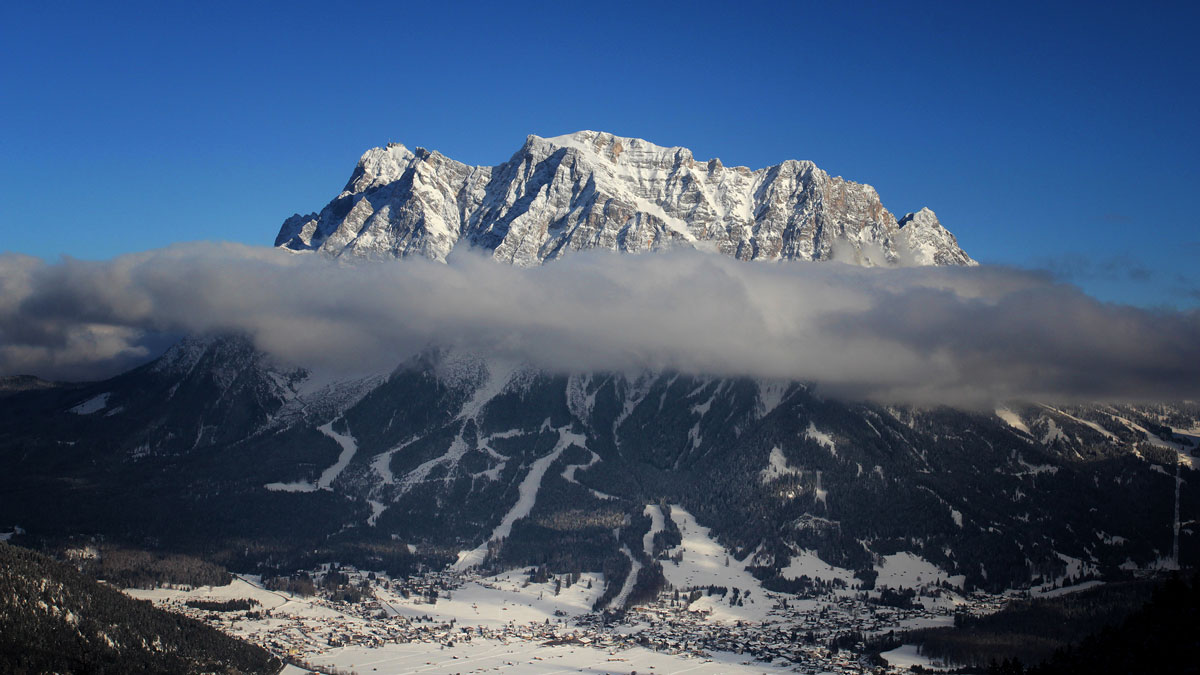
Seismology: A Promising Tool for Monitoring Permafrost
Passive seismic data from a station atop Germany’s highest peak reveal a 15-year record of permafrost degradation, suggesting that this technique could be used for long-term environmental monitoring.
Minimal Evidence of Permafrost Carbon in Siberia’s Kolyma River
New research finds that Arctic rivers currently transport limited permafrost-derived dissolved organic carbon, which has implications for understanding the region’s changing carbon cycle—and its potential to accelerate climate change.
Ice Lenses May Cause Many Arctic Landslides
When permafrost thaw reaches concentrations of ice underneath the surface, it may trigger local soil instability.
Chile’s Glacier Protection Law Needs Grounding in Sound Science
In the works for more than a decade, proposed legislation to protect glacial and permafrost environments in Chile suffers from uncertainties and omissions that could sow conflict instead of solutions.


![A 3-D image of the study area of Liu et al. [2022] in Kuuguluk River at Salluit, Nunavik (Quebec), Canada. The image shows the locations of A-A’ and B-B’ and lines C1-5.](https://eos.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/2021WR031630-Figure-4.png)






