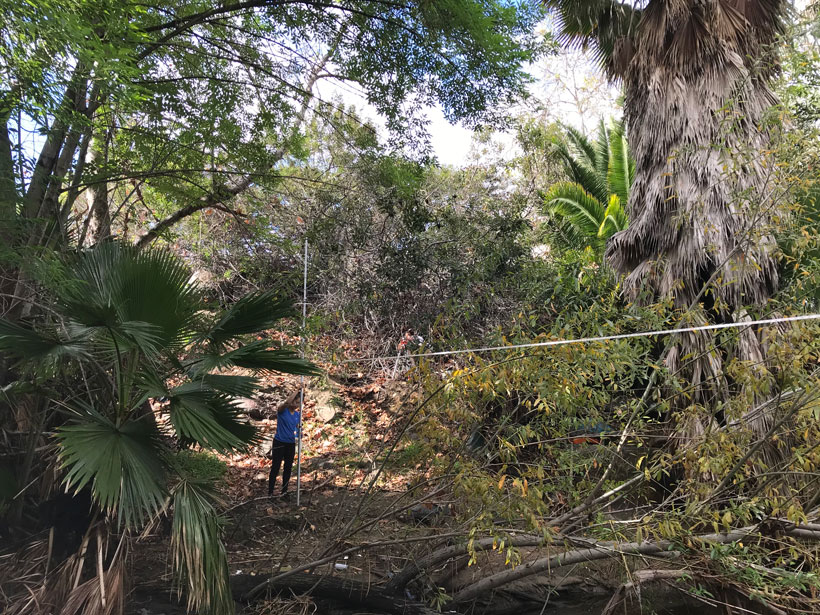
As fires burn across Southern California, researchers examine what role nonnative vegetation plays.
plants
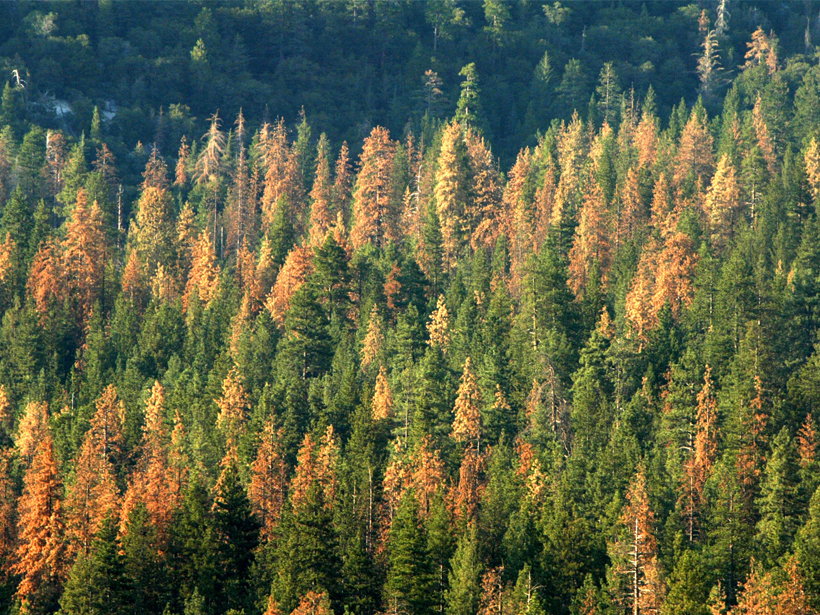
Foretelling Forest Death from Above
A satellite-based early-warning signal may spot the start of a forest’s decline and give forest managers more time to save its life.
600 Years of Grape Harvests Document 20th Century Climate Change
A 664-year record of grape harvest dates from Burgundy, France, reveals significantly warmer temperatures since 1988.
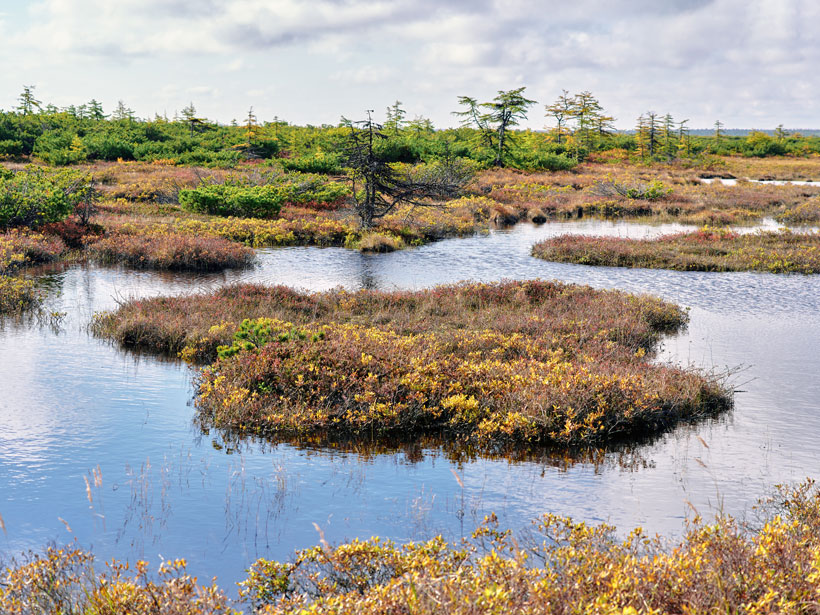
Turning the Arctic Brown
For a generation, the tundra has seen an increasing growth of vegetation, a process known as Arctic greening. A more accurate term might be “Arctic browning.”
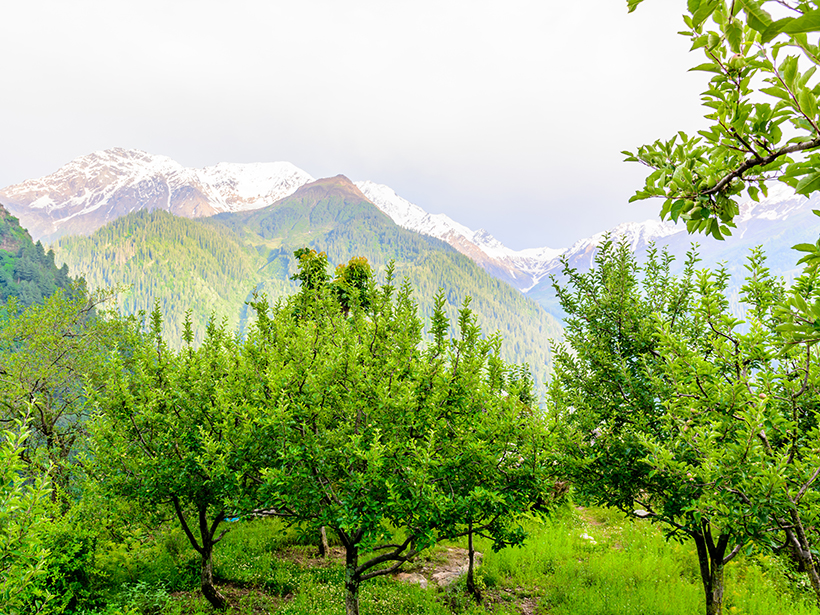
As Climate Changes, So Does the Apple as Rising Temperatures Push Growers Higher Into Himalayas
Climatic factors have wreaked havoc on India’s apple crops by disrupting natural flowering seasons and pollination systems. The shape, size, and quality of Himalayan apples have changed.
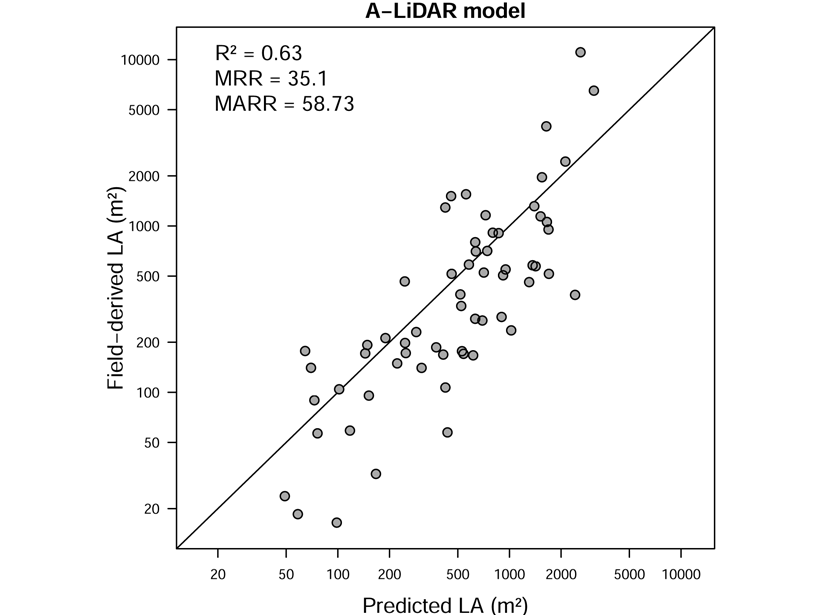
Tropical Forests May Have More Canopy Than Previously Thought
A rare attempt to directly estimate leaf area in a tropical African broadleaved forest suggests that there may be more tree foliage than previously estimated.
Organic Gases Released and Taken Up by Soil Lack Quantification
Soils both emit and take up different biogenic volatile organic compounds, altering the chemical composition of the atmosphere and influencing local, regional, and global climate.
The Flickering Sky Islands
In the Andes, islands in the sky flicker, and evolution kicks into high gear.
Restoring Natural Fire Regimes Can Yield More Water Downstream
Research in Yosemite National Park offers a new benchmark for understanding water balance changes in a mountainous basin 4 decades after its natural wildfire regime was reestablished.
North Carolina Bald Cypress Tree Is at Least 2,674 Years Old
Researchers say it’s the oldest-known living tree in eastern North America. If it hadn’t been protected, it could have ended up as garden mulch.