A first-of-its-kind study suggests that isotope analysis could be used to pinpoint sources and sinks of atmospheric methyl chloride.
plants
Harpy Eagles Concentrate Precious Nutrients in the Amazon
Amazon soils are usually low in the nutrients that plants covet, but harpy eagles can create local hot spots with their poop and prey.
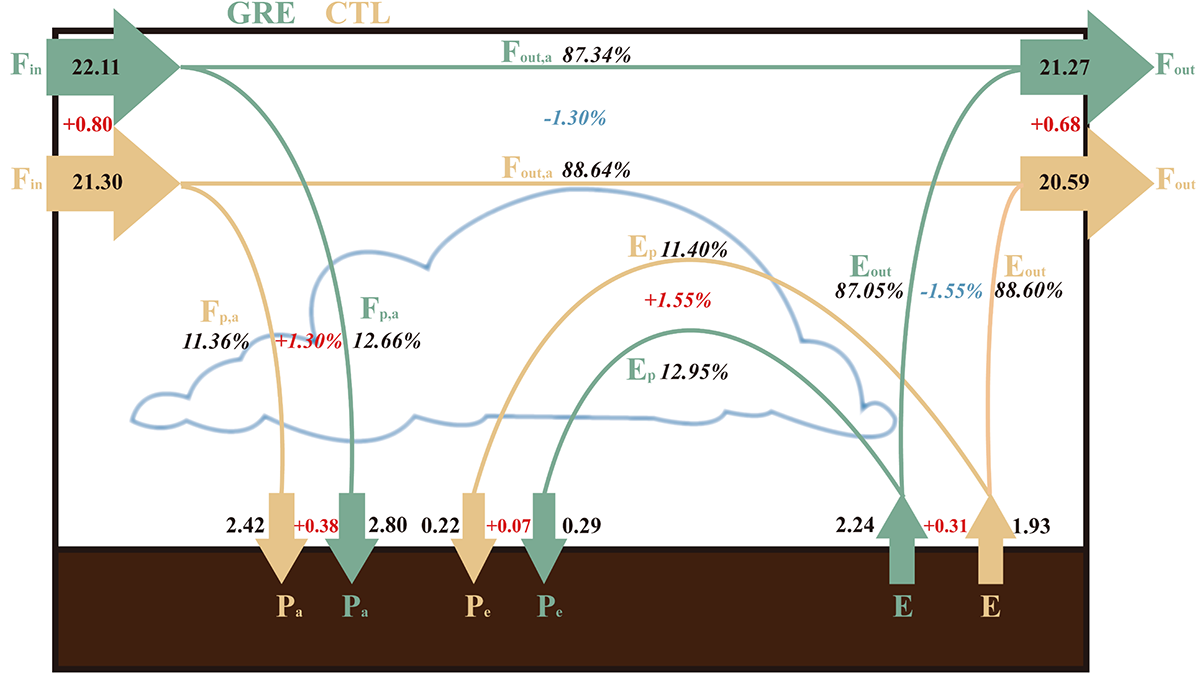
Greening of Loess Plateau Increases Water Yield
Vegetation restoration over the Chinese Loess Plateau can enhance atmospheric moisture convergence, increasing the precipitation enough to compensate for the vegetation water consumption.
Carbon Sink Models Need Nitrogen
If terrestrial biosphere models don’t include nitrogen, they will overestimate carbon sequestration.
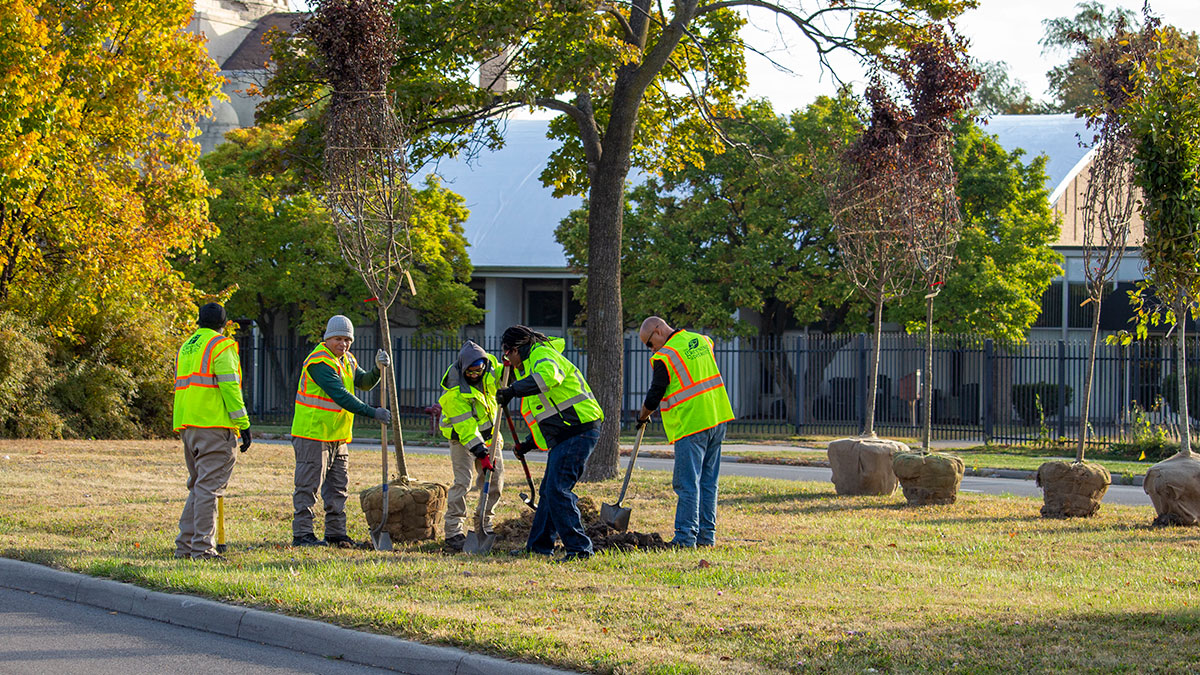
Cities Are Rethinking What Kinds of Trees They’re Planting
U.S. cities are losing some 36 million trees every year, but hardier species can restore their canopies.
As the Arctic Warms, These Rivers Are Slowing Down
The Arctic is warming up, but instead of large rivers migrating faster, they’re actually slowing down because of shrubification.
Gardens Are Good for the Neighborhood
A new study highlights the benefits of urban gardens for their human caretakers and local ecosystems.
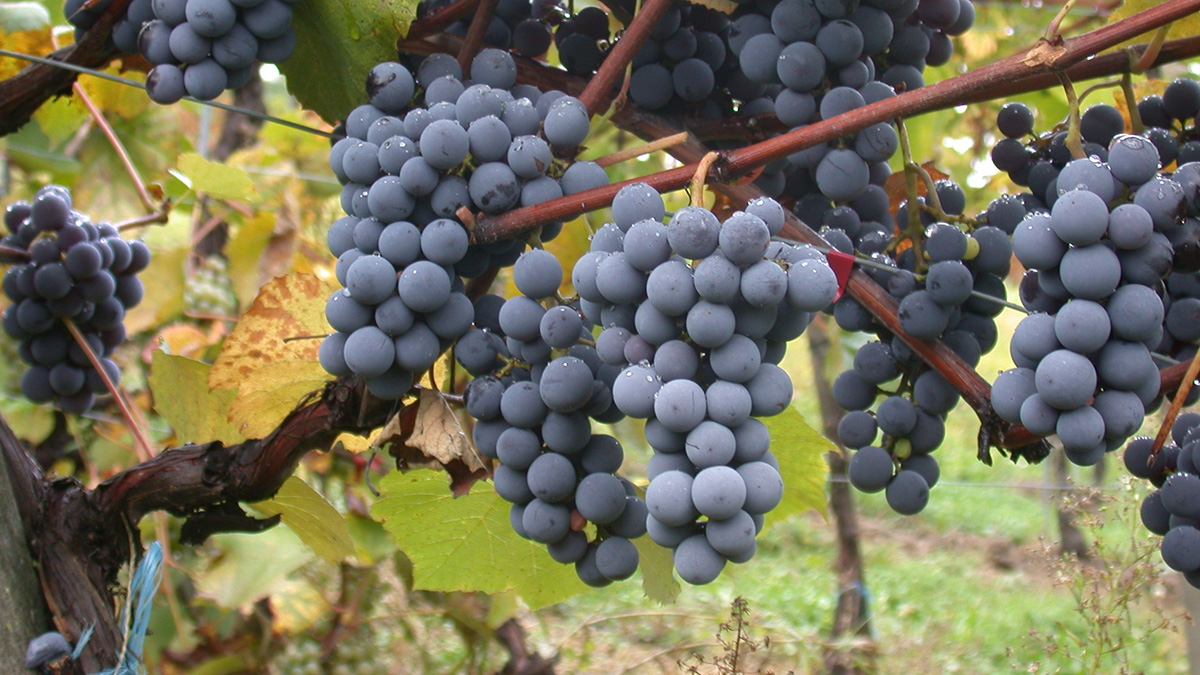
Cómo el Último Máximo Glacial influenció en el origen del vino
El severo clima de la era de hielo influenció el cultivo de la vid durante el nacimiento de la agricultura.
Native Plants Are Hiding Up High, but Invaders Are Catching Up
Far from pristine outposts of nature, mountains across the world are being rapidly colonized by non-native plants that spread uphill along roads.
How Wine’s Origin Was Shaped by the Last Glacial Maximum
The harsh climate of the ice age influenced grapevine cultivation at the dawn of agriculture.