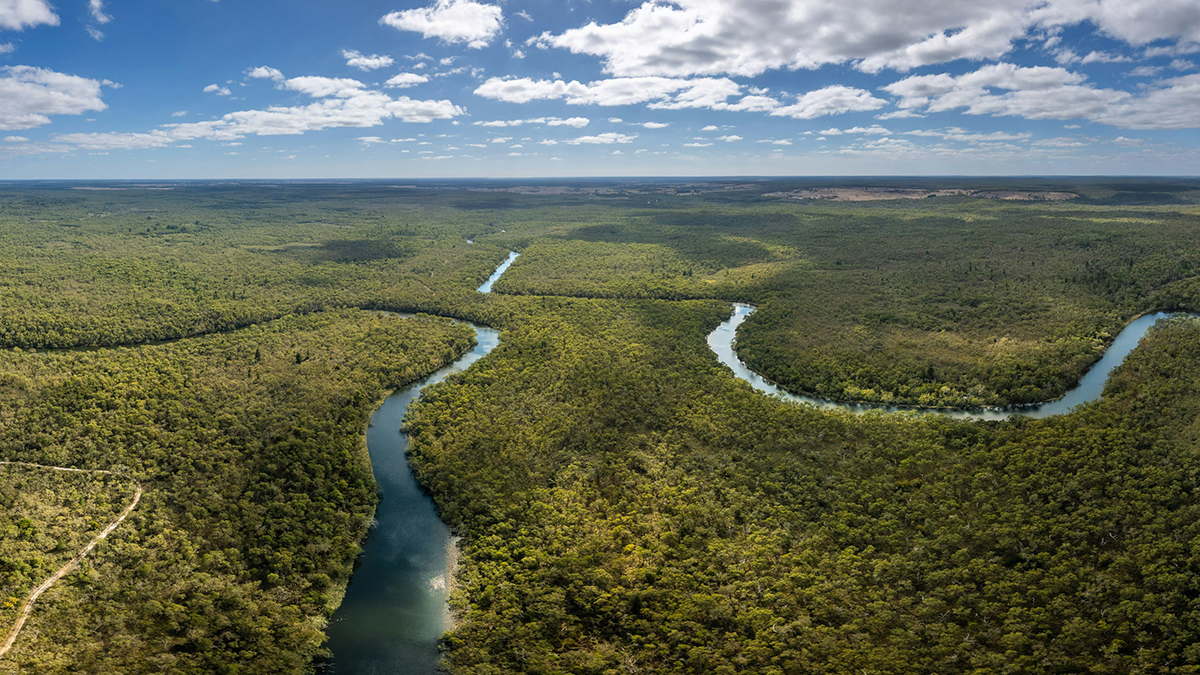
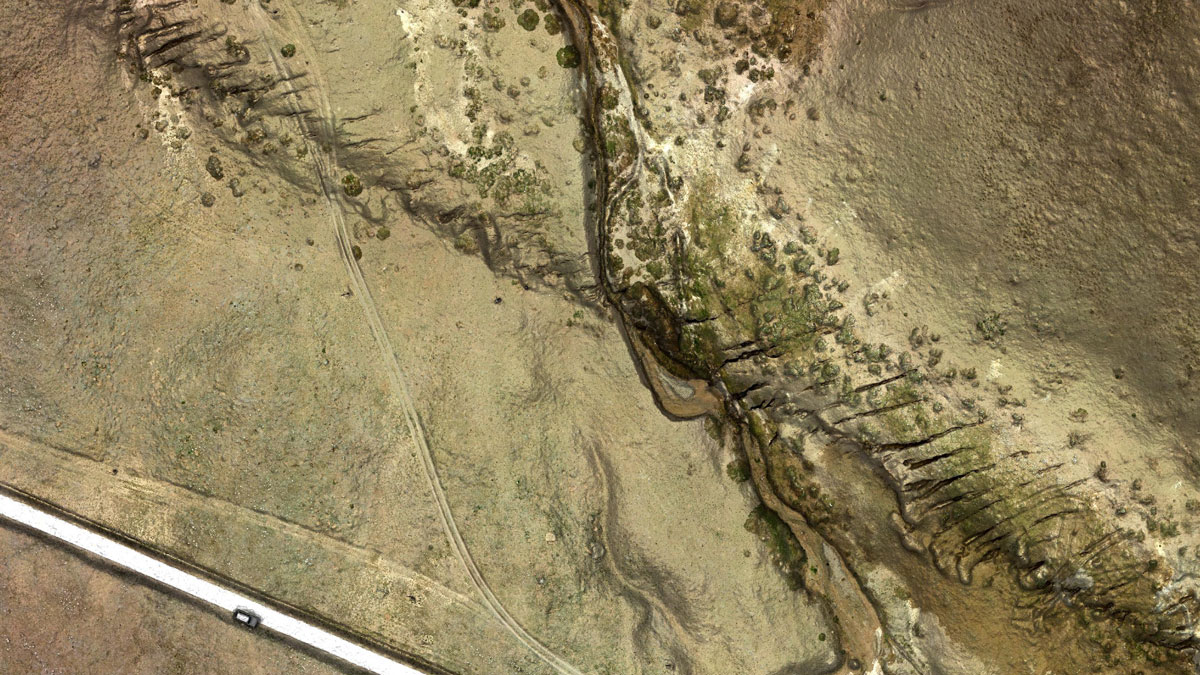
Scientists thought two factors influencing river avulsion were unrelated, but new research suggests they may be working in tandem. The findings could help predict new river pathways and improve disaster preparedness.
remote sensing
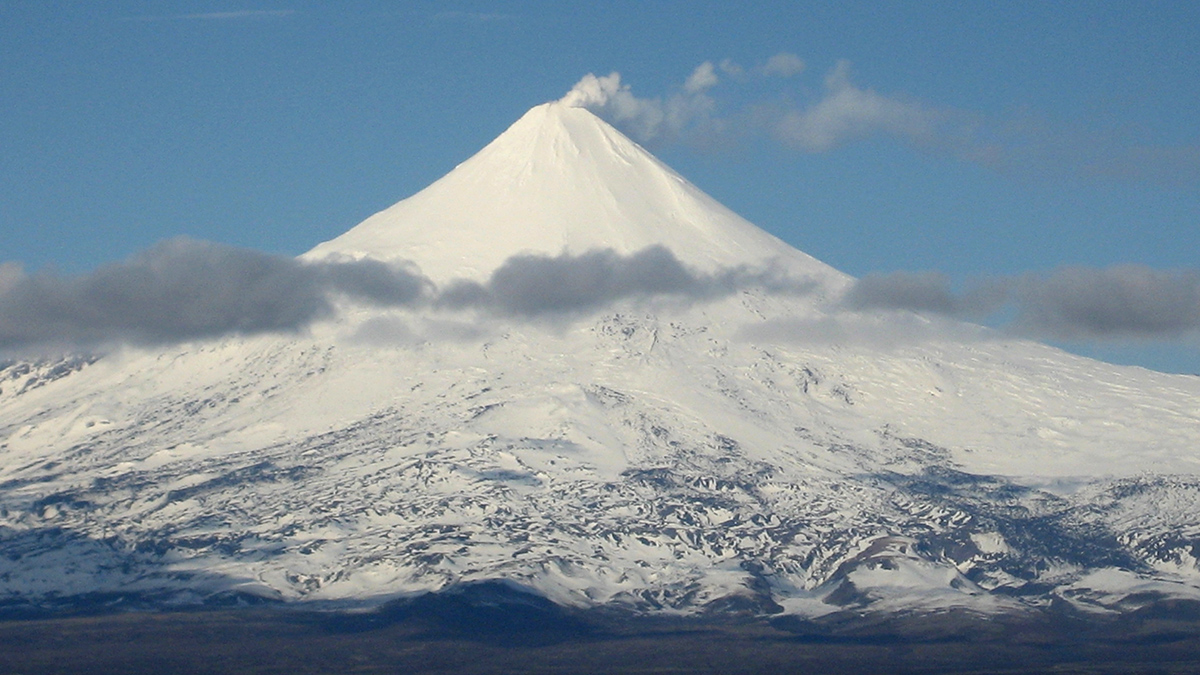
Glaciers near Active Volcanoes Flow Faster
Monitoring glacier velocity could help predict volcanic activity, a study of more than 210,000 glaciers suggests.
O Legado Rico em Nutrientes nas Terras Pretas da Amazônia
Os solos férteis de terra preta foram criados através de séculos de uso da terra cuidadosamente administrado. Os cientistas estão colhendo referências desses solos para remover o carbono e melhorar o solo para a agricultura.
Unlocking the Power of Synthetic Aperture Radar for Geosciences
Due to its unique ability to monitor Earth’s surface, Synthetic Aperture Radar plays a pivotal role in revolutionizing the geosciences.
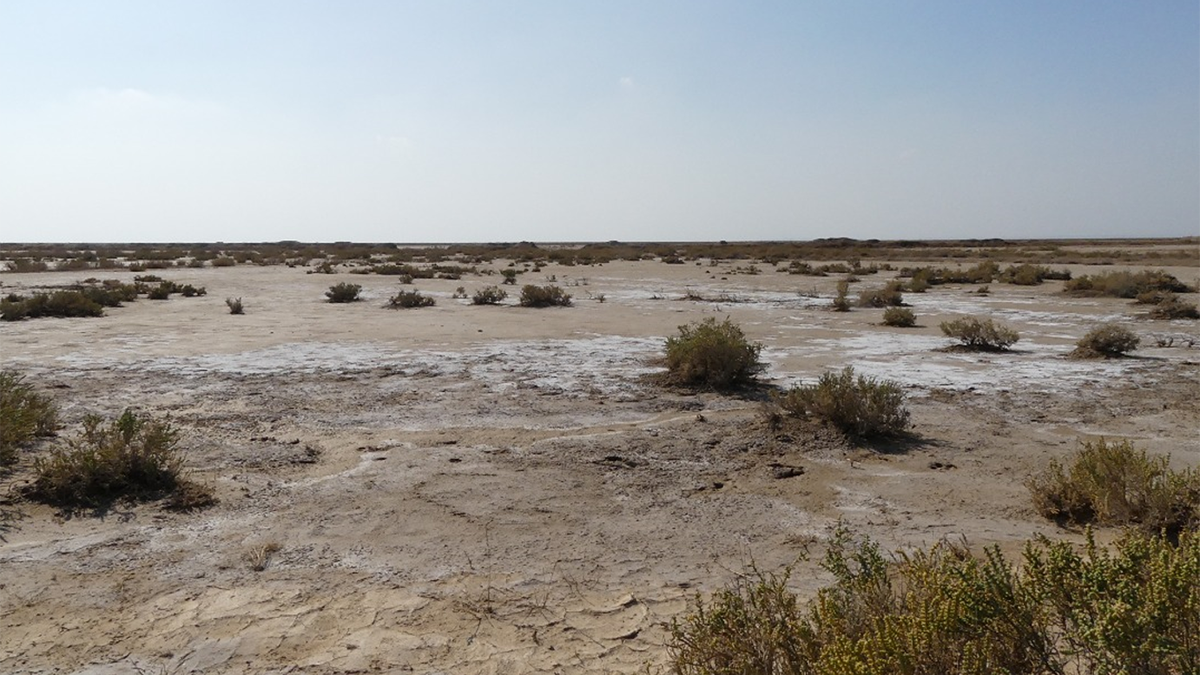
Soil Salinization: A Rising Threat to Ecosystems and Global Food Security
As soil salinization intensifies, it poses serious threats to ecosystems, soil health, global food security and socio-economic stability.
Lots of Dust Gets Sucked Up by Jet Engines
Changing flight times and holding altitudes could substantially reduce the amount of wear-inducing dust ingested by jet engines.
Fixing Pollution from Space Needs Global Coordination
Remote sensing is a tool of choice for monitoring regions for air pollution, but the scale of the problem requires extending geostationary soundings globally.
Many Forests in One: A Glimpse into the Amazon’s Diversity
In some areas of the Amazon rainforest, trees green up as a response to drought, while in others they die off. Scientists are trying to understand why.
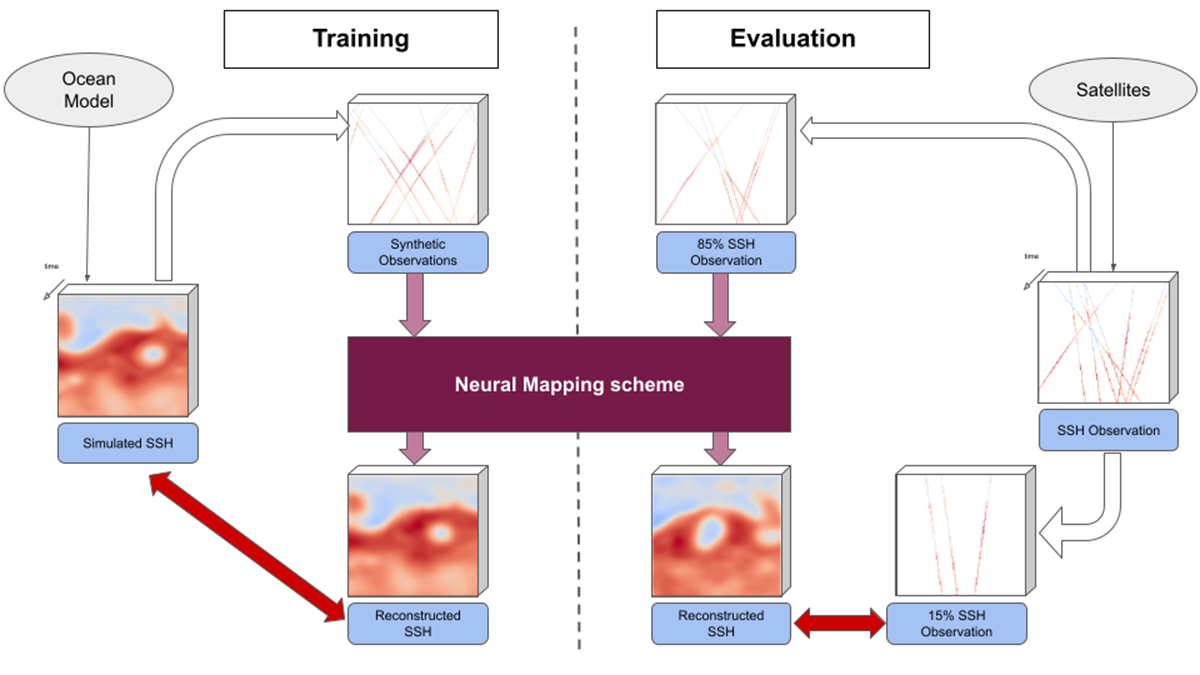
Physics + Machine Learning Provide a Better Map of Ocean Measurements
A new study offers a compelling example where the merger of dynamical modeling, machine learning, and ocean measurements enhances oceanographic understanding, monitoring, and mapping.
断裂成熟度和断裂走向,哪个对大地震更重要?
对青藏高原2021年玛多地震的详细研究表明,与先前的假设相反,断裂走向对地震破裂动力学特征的影响有时会超过断裂成熟度的影响。