Based on an extended stress database, scientists observe systematic changes in the tectonic stress state and a reduction in fault reactivation potential near salt walls in the Paradox Basin.
salts & sodium
Salty Soil May Release Methane on Mars
Through roving and drilling, Mars Curiosity Rover may be breaking up the ground’s salty, hardened soils that seal methane, possibly causing a temporal, local methane spike.
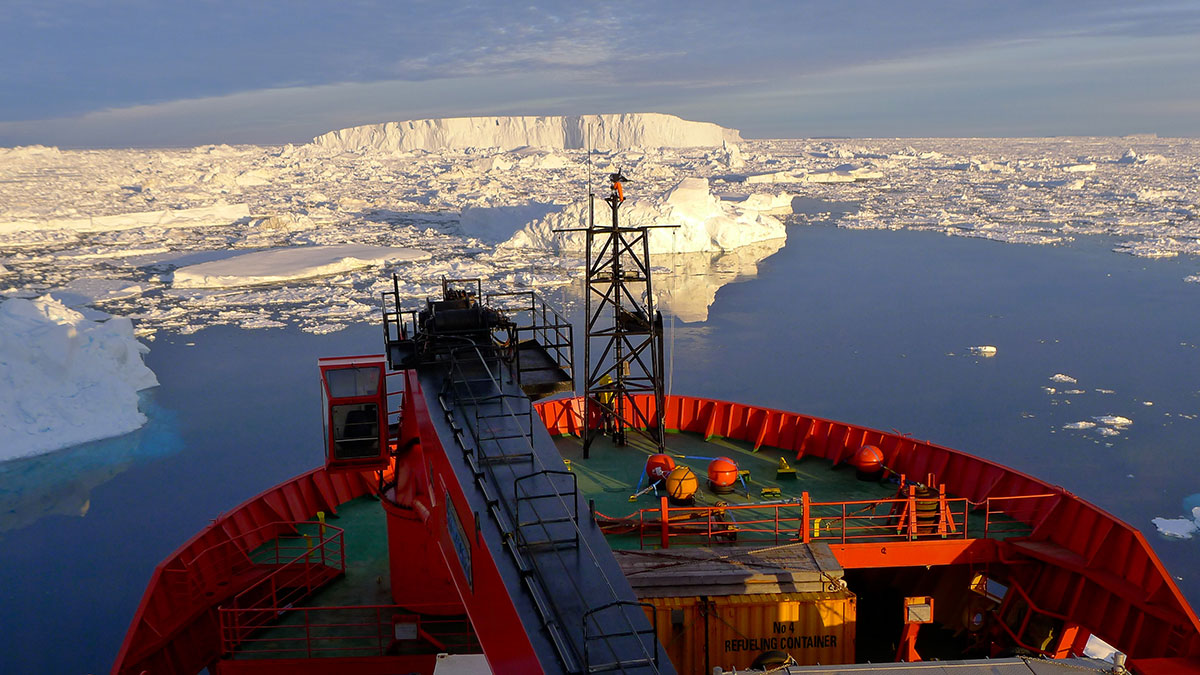
Meltwater from Antarctic Glaciers Is Slowing Deep-Ocean Currents
Antarctic ice drives crucial deep-ocean currents that help regulate Earth’s climate. But the system is slowing down.
Newly Discovered Salts May Exist on Icy Moons
For the first time in more than a century, scientists have identified new sodium chloride crystals. The discovery may reconcile puzzling spectroscopic images of Europa’s surface.
Salt Spray May Stifle Lightning over the Sea
New research suggests that sea-salt aerosols seed large raindrops that starve clouds of water needed to make lightning. But not all scientists are convinced it’s simply about salt spray.
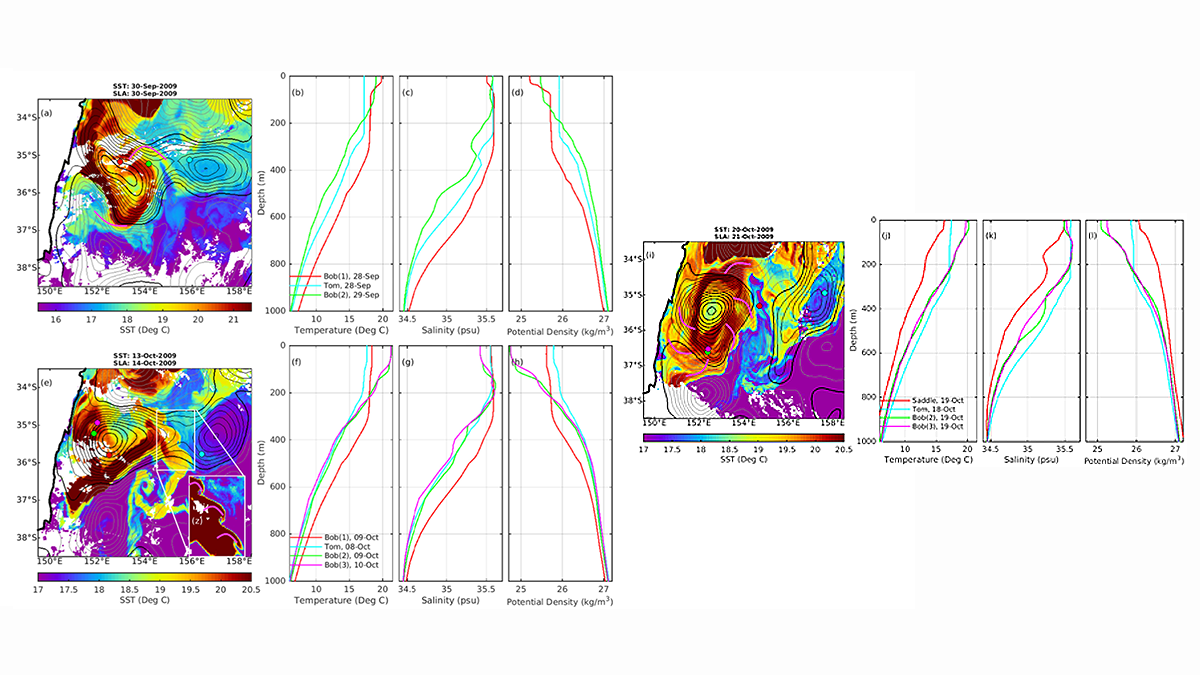
How do Bob and Tom Eddies Meet, Pair-Spin, and Twist?
Autonomous float data reveal that mergers of two eddies, known to have spiraling subducting water surrounding each other, happens more frequently than previously thought.
Abiotic Life and Energy on Water-Rich Rocky Celestial Bodies
The discovery of tiny crystals of the iron-rich hydroxychloride kuliginite in New Caledonia provides new insights into the hydrogen production from mantle rocks and saline water.
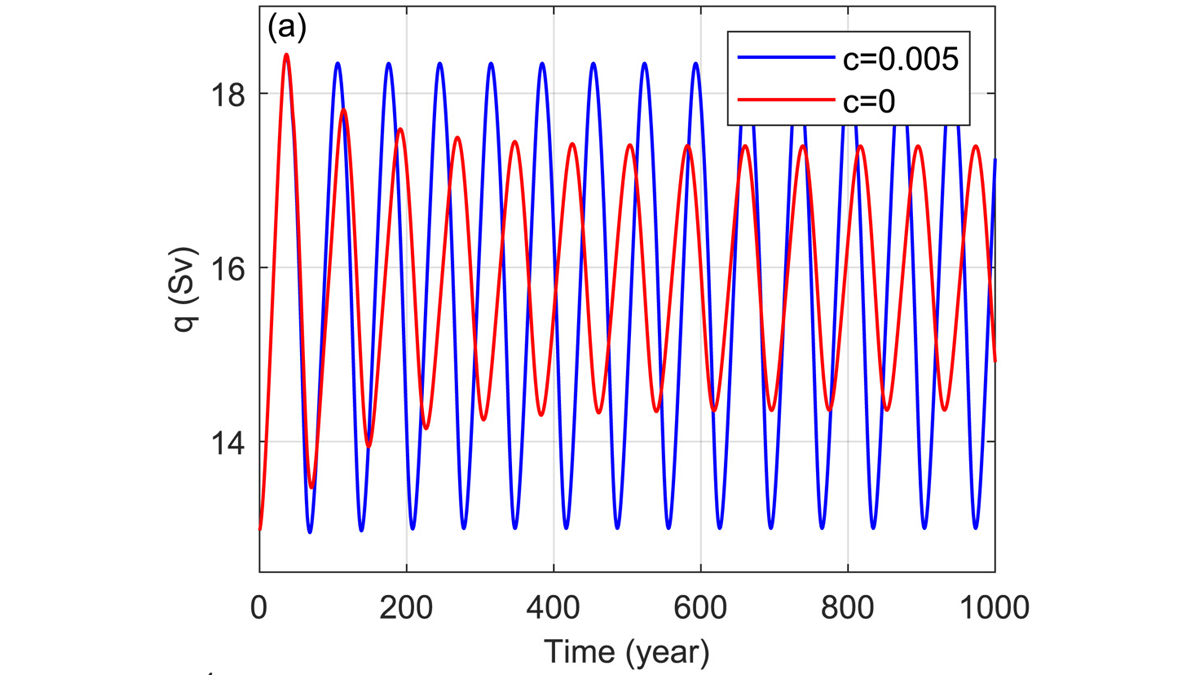
Arctic Salinity Pushes the AMOC Swing
A model of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), pioneered by Henry Stommel over 60 years ago, can exhibit realistic cyclic behavior if the role of Arctic salinity is included.
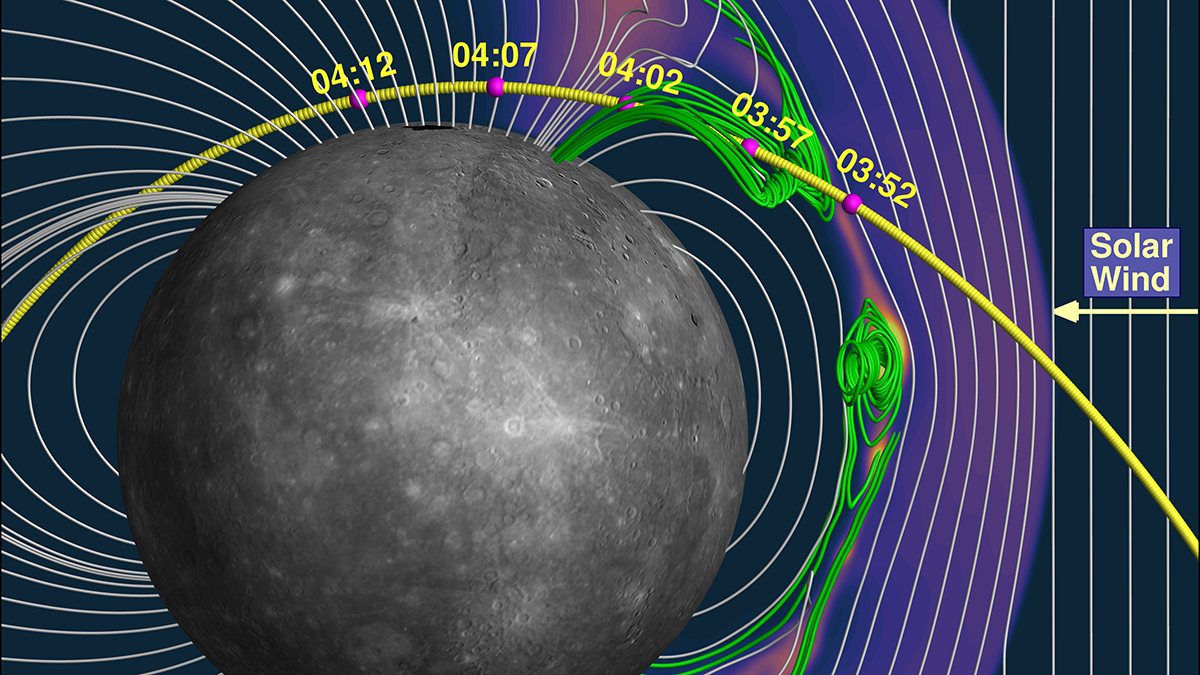
Solar Wind a Major Driver of Atmospheric Sodium at Mercury
MESSENGER observations show a 50% rise in atmospheric sodium-group ions during periods of high solar wind activity.
Lipids from Europa’s Ocean Could Be Detectable on the Surface
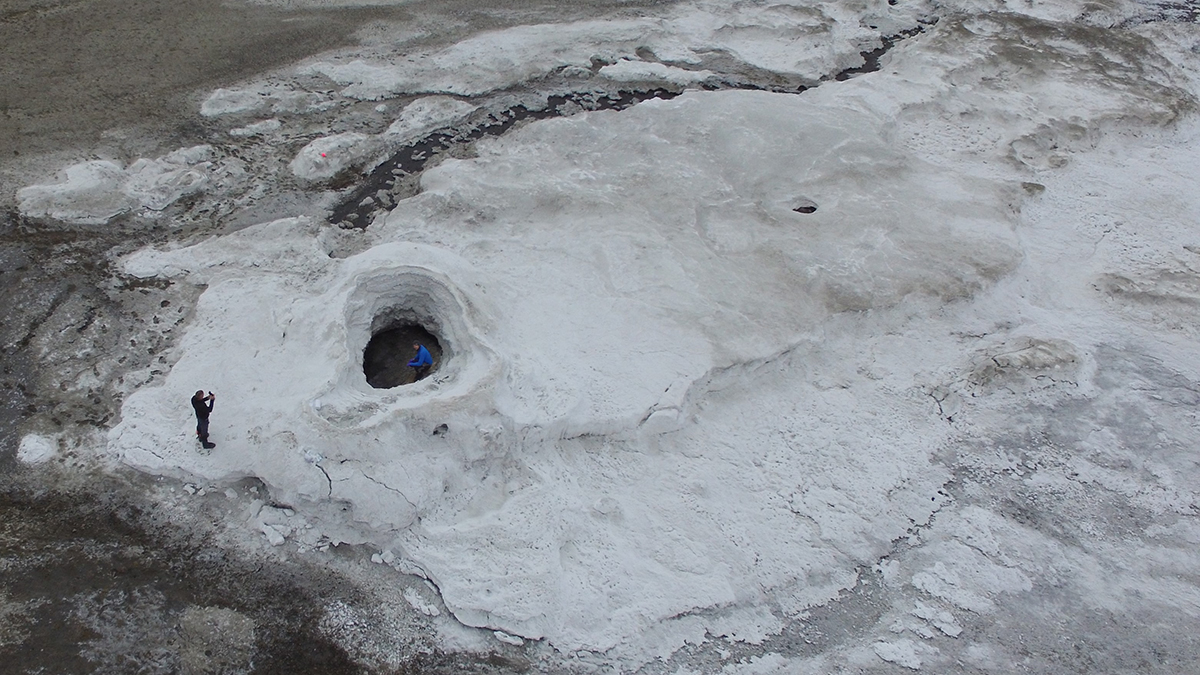
A super salty spring in the Canadian Arctic provides insights key to detecting life on a distant ocean world.