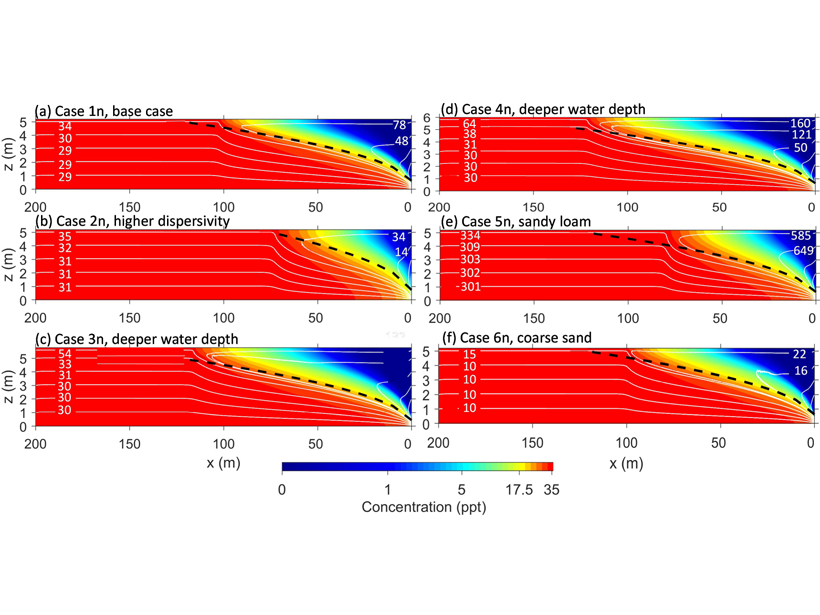
A numerical model of groundwater-surface water systems shows how floodplain evaporation can reverse stream-groundwater flow and produce strong buoyancy changes associated with salinity.
salts & sodium
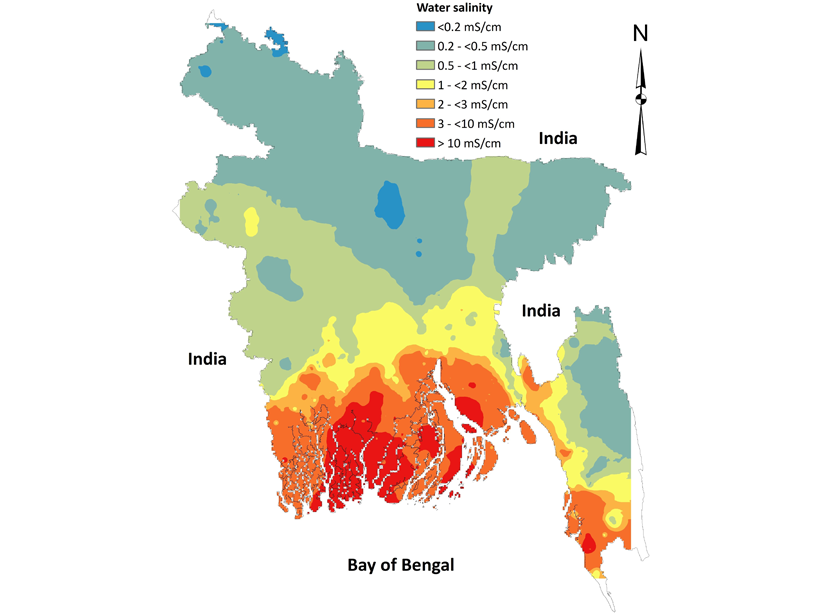
Does Drinking Water Salinity Affect Child Mortality?
An association between drinking water salinity and neonatal and infant mortality in Bangladesh indicates the critical role of water salinity on child health.
An Exoplanet with Evolving Clouds of Salts
Clouds form and dissipate on a gas giant orbiting a Sun-like star.
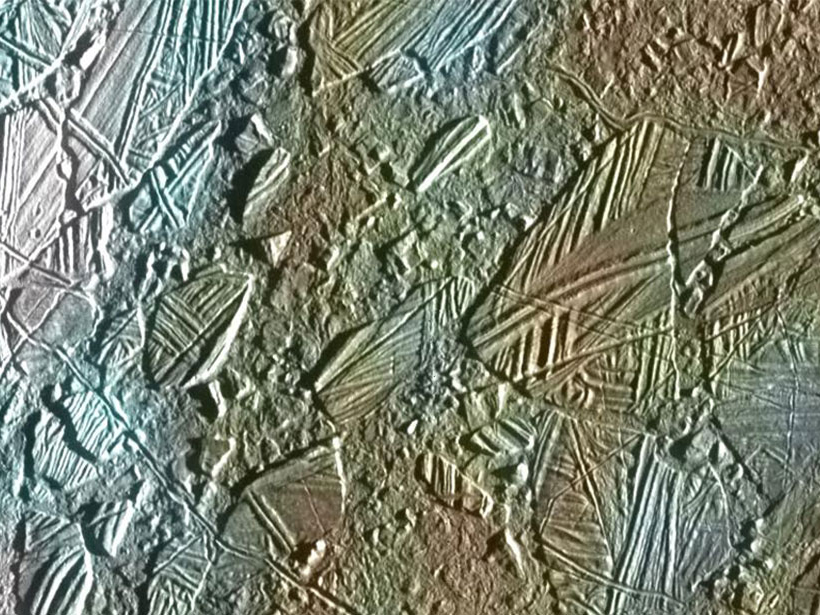
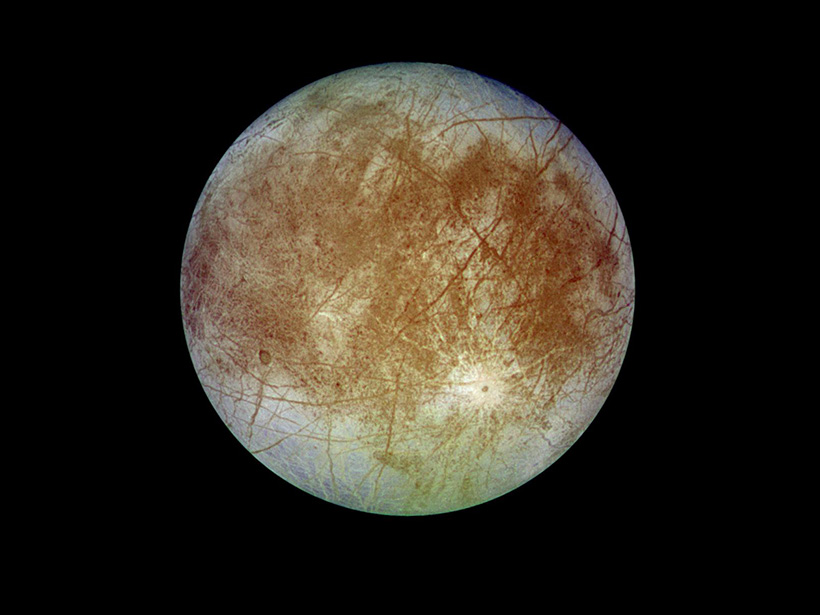
Mmm, Salt—Europa’s Hidden Ocean May Contain the Table Variety
Hubble Space Telescope observations suggest that sodium chloride exists in young, geologically active regions on Europa, likely fed by upwelling from the moon’s subsurface ocean.
Chemical Patterns May Predict Stars That Host Giant Planets
Stars with giant planets tend to have a few key elements in abundance. A new algorithm used these patterns to predict hundreds of stars that will likely have exoplanets if we go looking for them.
Take Weather Prediction with a Grain of Salt and It Gets Better
Sea surface salinity is starting to rival other methods for seasonal rain forecasting.
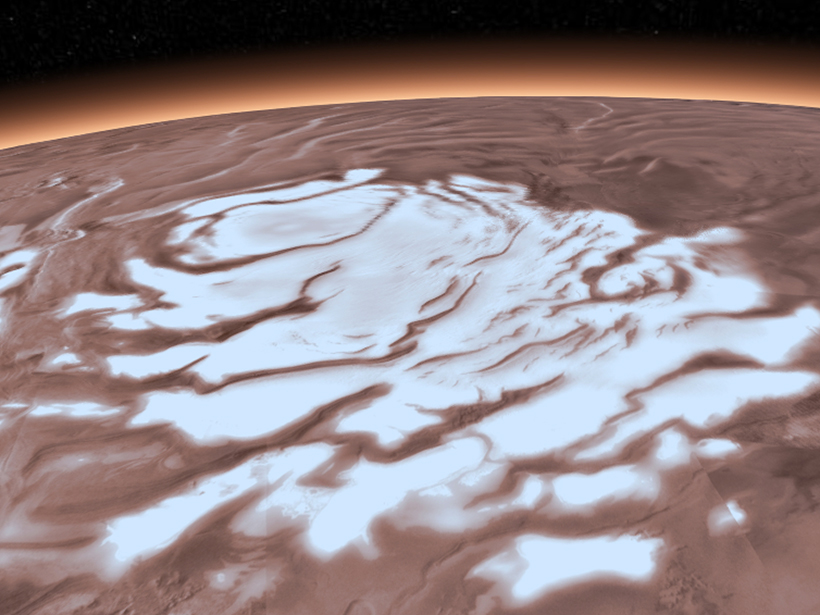
Local Heat Source Needed to Form Liquid Water Lake on Mars
Thermal modeling suggests that active magmatism in the past few hundred thousand years could account for the presence of a large lake previously hypothesized beneath the Red Planet’s southern ice cap.
Waves of Deadly Brine Can Slosh After Submarine Landslides
Brine pools—hypersaline, low-oxygen waters deadly to many forms of ocean life—can experience waves hundreds of meters high when hit by a landslide, potentially overspilling their deep-sea basins.
A Rock Guide to Fireworks
Before a firework was red, it was a strontium salt waiting for its moment.
Seeking Salt That Surfaces from Europa’s Hidden Ocean
Irradiation-induced color changes in sodium chloride could reveal whether it came from ocean water mixing with surface water, a key component of the moon’s potential to support life.