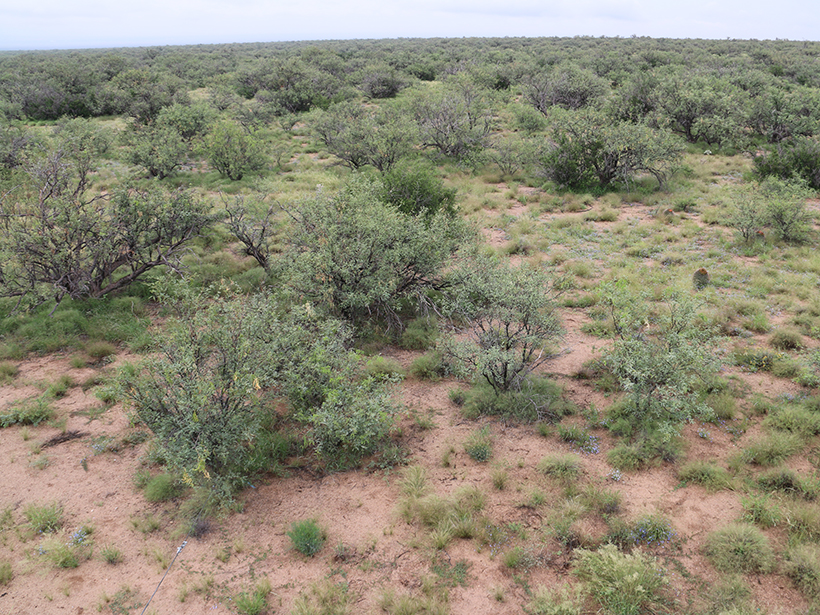
A new study shows that mesquites employ hydraulic redistribution to move water between soil layers in the savannas of Santa Rita.
soils
Studying Soil from a New Perspective
Cosmic ray neutrons probe soil moisture in the Great Plains.
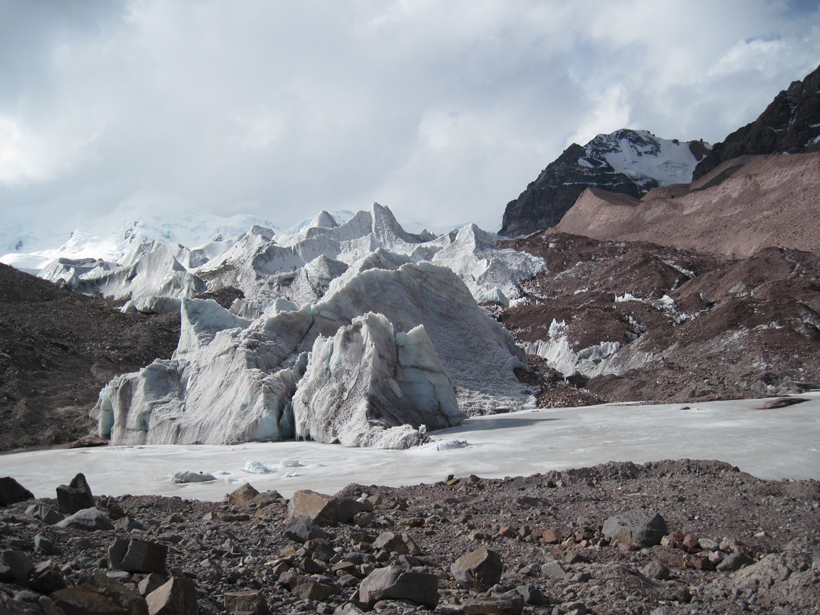
After a Glacier Retreats, Plants Thrive Thanks to Phosphorus
Grasses, small flowers, and mosses colonize glacial till in the Peruvian Andes when researchers apply a phosphorus fertilizer, an ecological surprise with implications for carbon sequestration.
Depth Matters in Peat Bog Nutrient Cycling
Peatlands store around a third of Earth’s soil carbon, and a new study begins to reveal how the ecosystems’ organic matter changes with depth.
Life in the Hyporheic Zone
Defining the chemical relationships between water, sediment, and organisms that thrive beneath riverbeds.
Major Uncertainty in Estimates of Carbon Trapped in Soil
A new study reveals discrepancies between global databases and field measurements.
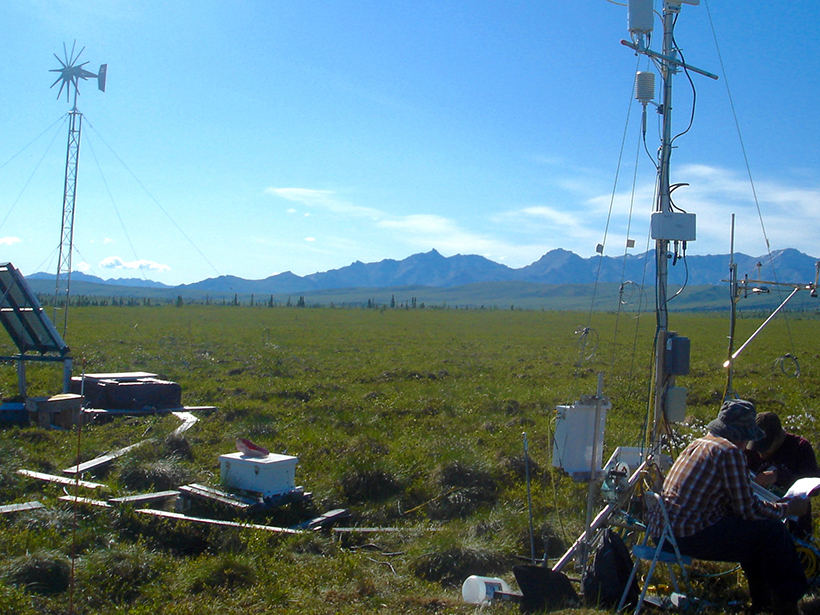
A Deeper Understanding of Carbon Decomposition in Arctic Soils
Physical parameters may help scientists extrapolate Arctic carbon soil losses from the local to the regional scale, according to the results of a yearlong incubation experiment.
Understanding High-Latitude Methane in a Warming Climate
Climate change could spur greenhouse gas release from the Arctic. A new project will synthesize existing data to improve uncertain predictions.
Pedotransfer Functions Bring New Life to Earth System Modeling
A recent paper in Reviews of Geophysics describes how currently available soil information furthers our understanding of soil processes and their integration in Earth system modeling.
Wet Soils Elevate Nighttime Temperatures
Soil moisture can elevate overnight temperatures, offsetting daytime cooling, especially over areas of strong land-atmosphere interactions.