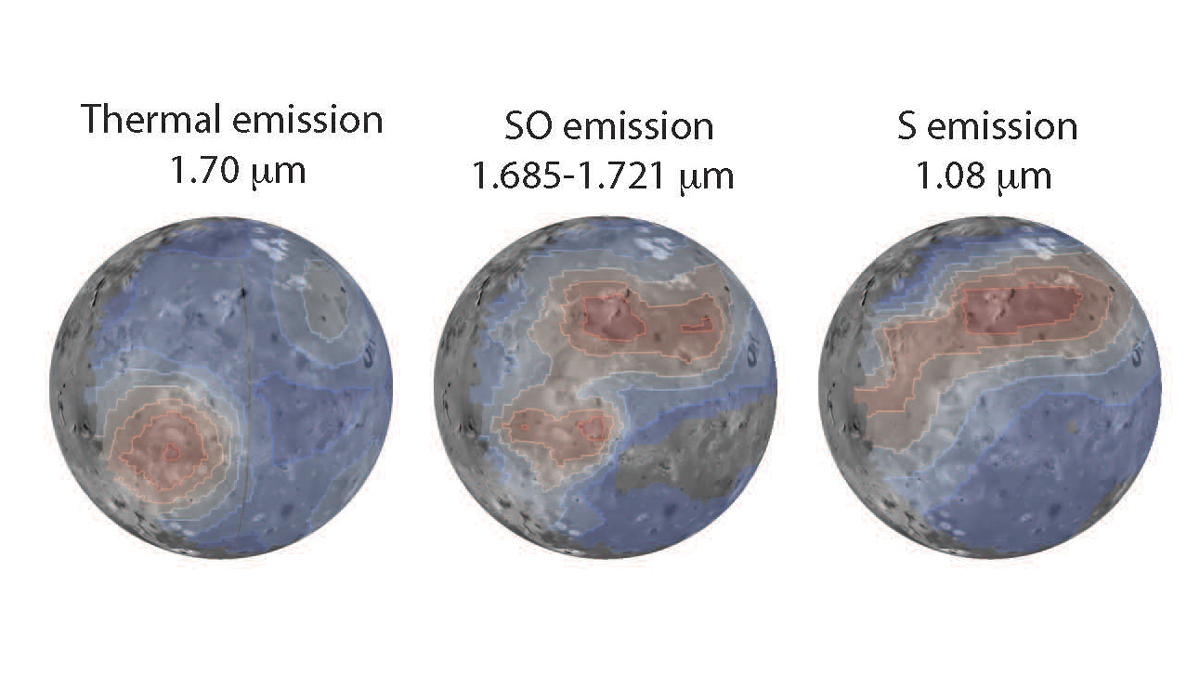
New James Webb Space Telescope images reveal cooling lava, volcanic sulfur monoxide gas, and sulfur gas emissions created by interactions between plasma and the moon’s atmosphere.
sulfur
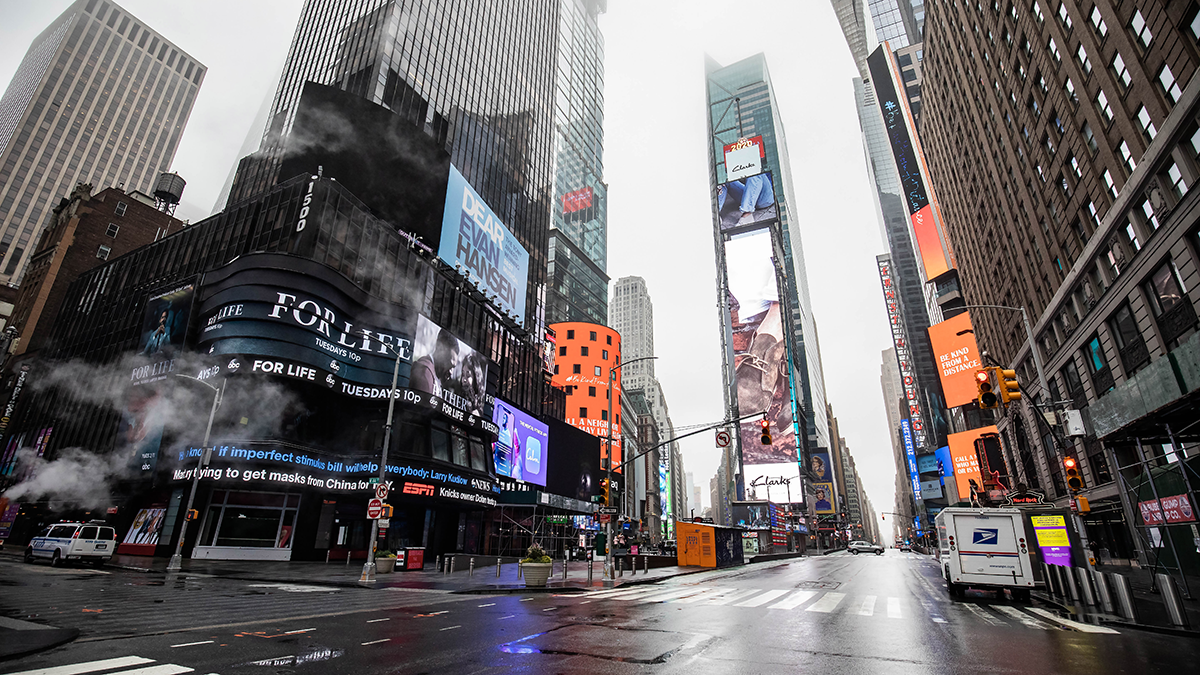
Particulate Pollution and its Climate Impacts During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The impacts of COVID-19 on short-lived pollutants highlight the predominant influence of the transportation sector and the resulting changes in regional climates and ecosystems.
Cave Deposit Links Greenland’s and Europe’s Climate Records with a German Volcano
Dating a late Pleistocene eruption has big implications for understanding the Younger Dryas—and current climate change.
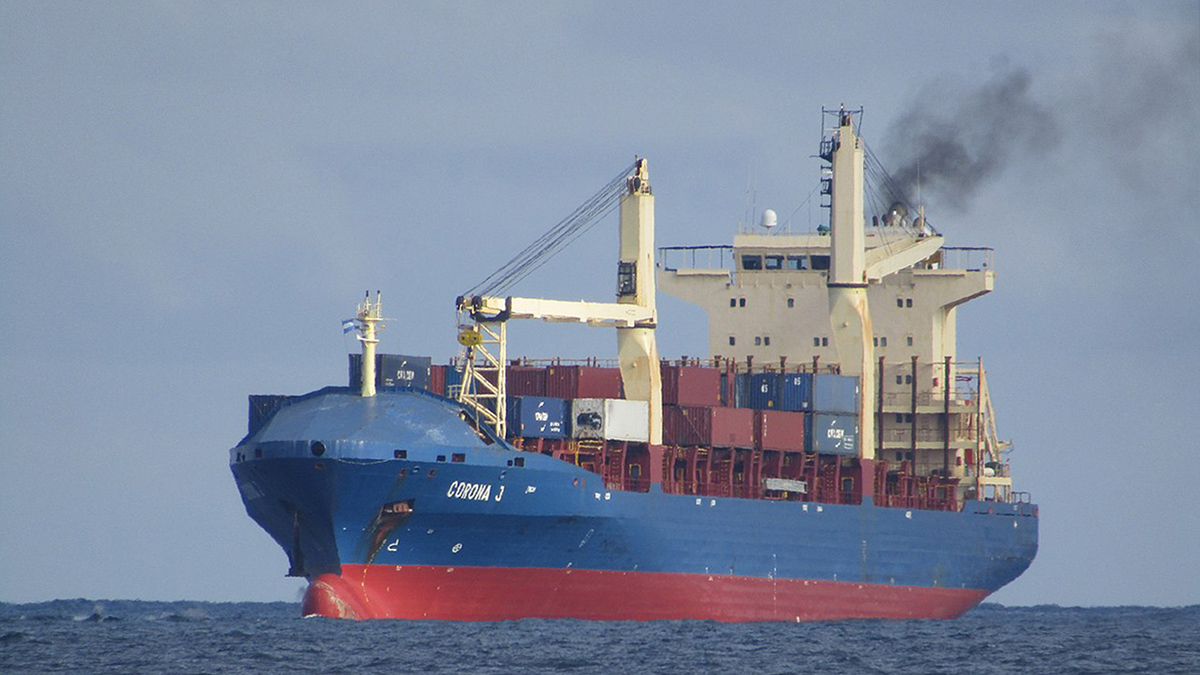
Lower Shipping Emissions May Lead to Higher Global Temperatures
Regulations designed to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions from the maritime shipping industry are linked to a change in cloud structure that raises atmospheric temperatures.
Toxic Metal on the Rise in the Baltic Sea
Postwar reconstruction is likely the cause of elevated thallium levels, but low-oxygen, high-sulfide conditions keep the material, which is extremely dangerous to mammalian health, from moving into the human food chain.
An Air Quality Model That Is Evolving with the Times
The pioneering Sulfur Transport and Deposition Model, initially designed to simulate atmospheric sulfur, continues to find new applications and value in environmental science and policymaking.
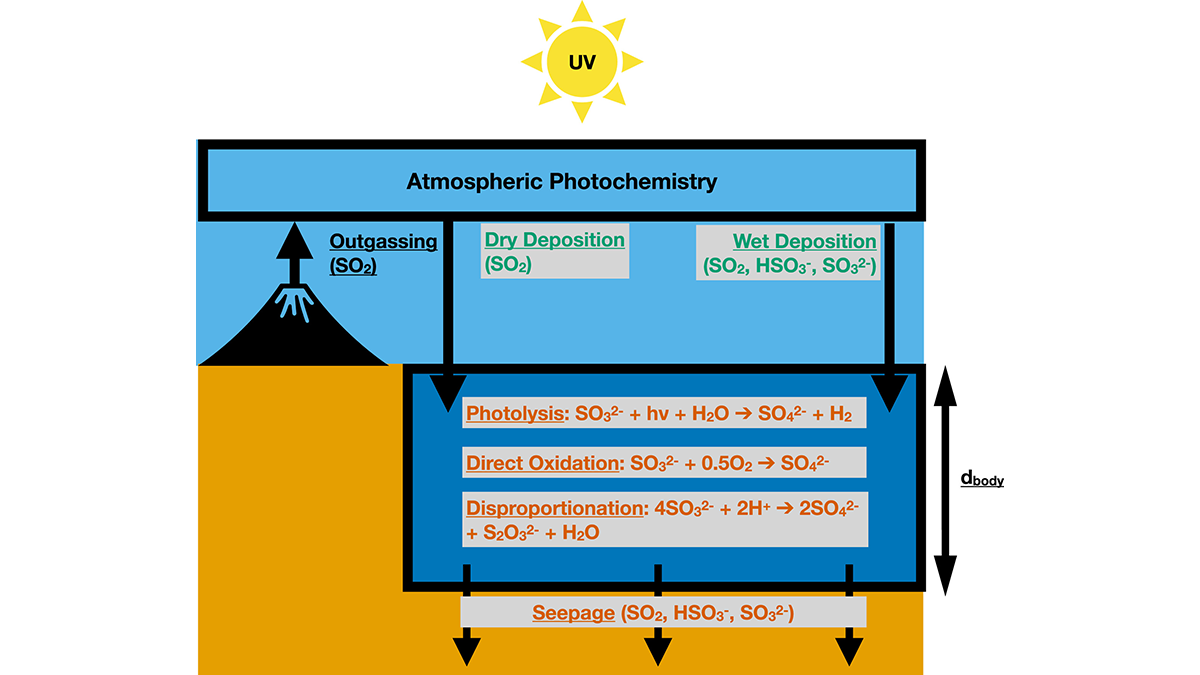
New Constraints on Sulfur Cycling in the Prebiotic Earth
Experiments constraining rates of aqueous reactions and photolysis coupled with a global model constrain the abundance and chemical speciation of sulfur in early Earth’s atmosphere and oceans.
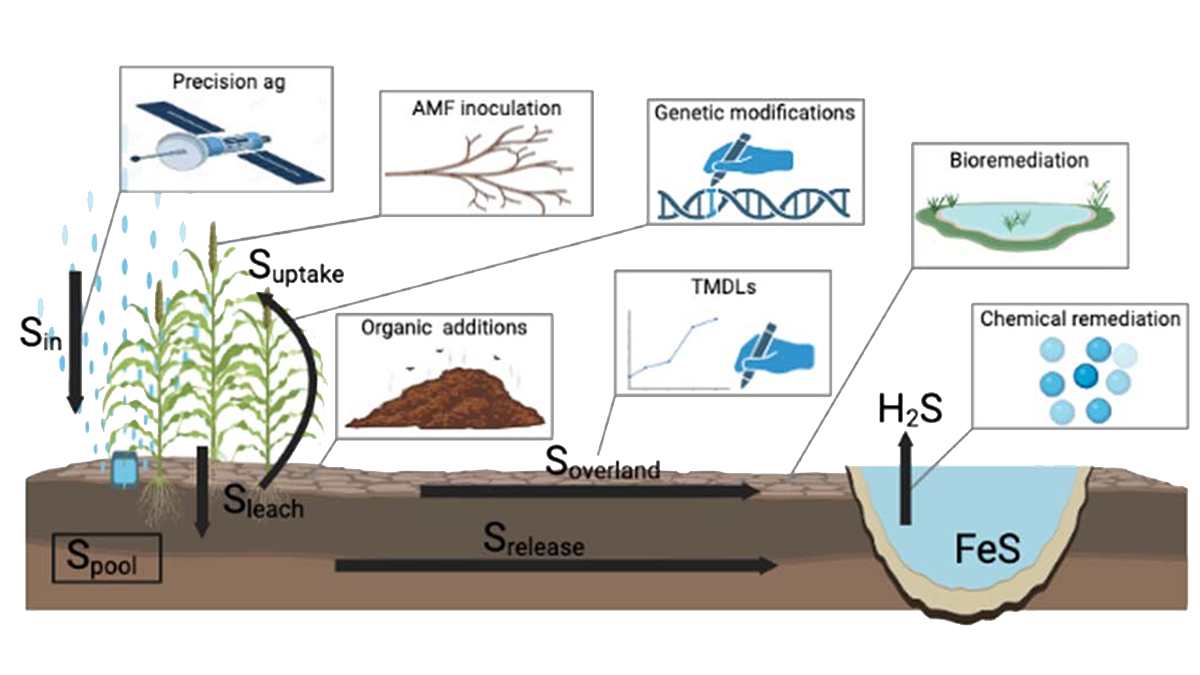
Sulfur is Demanding its Place in Crop Nutrient Budgeting
Scientists advocate for a more significant consideration of sulfur from a multidisciplinary perspective as a necessary step towards sustainable crop management.
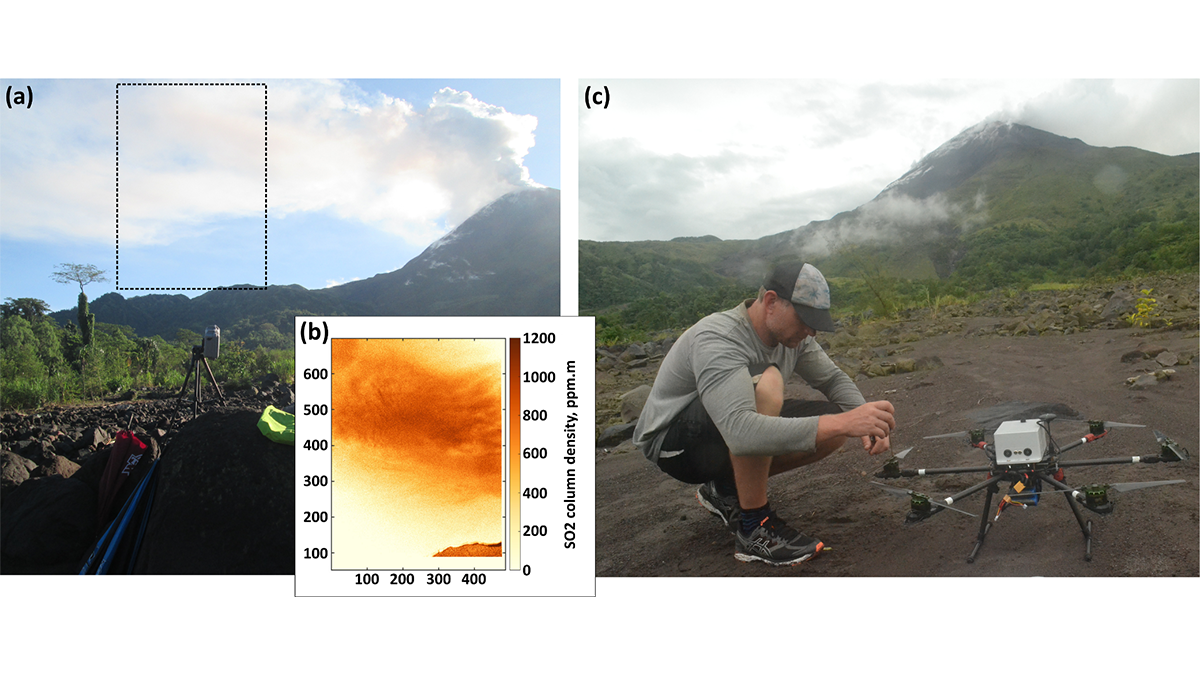
Send in the Drones: Safely Monitoring Volcanic Gas Emissions
New drone technology was combined with satellite and ground-based data to improve volcanic gas flux monitoring at the remote Bagana Volcano in Papua New Guinea.
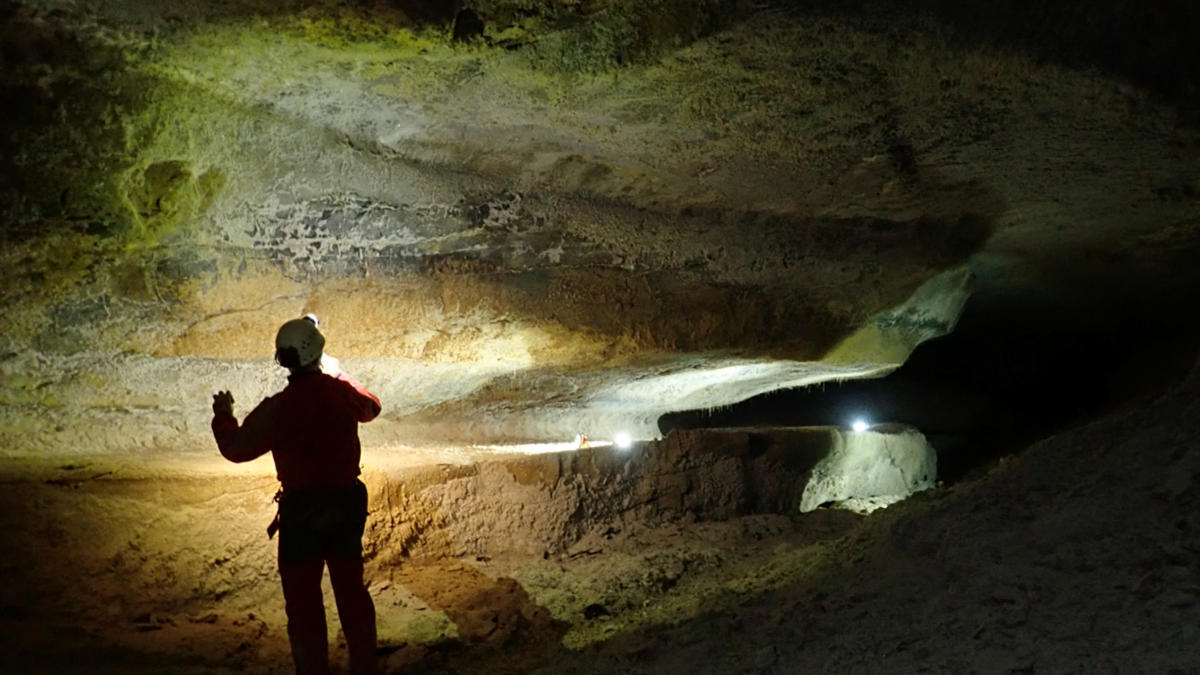
Searching for the Sculptor of France’s Caves
Spelunking scientists searched for the original source of the French Pyrenees’ magnificent caves.