The dwarf planet’s ring makes astronomers question whether a long-held theory about ring and moon formation needs tweaking.
unsolved mysteries
Mercury Isn’t Alone in Orbit, and Scientists Don’t Know Why
A cloud of dust traces the innermost planet’s orbital path. By all accounts, it shouldn’t be there.
“Hot Jupiter” Is in a Possible Death Spiral
Kepler’s first exoplanet is migrating toward its star, an evolved subgiant that is much bigger than first thought.
The Crust Travels to the Earth’s Core and Back in Record Time
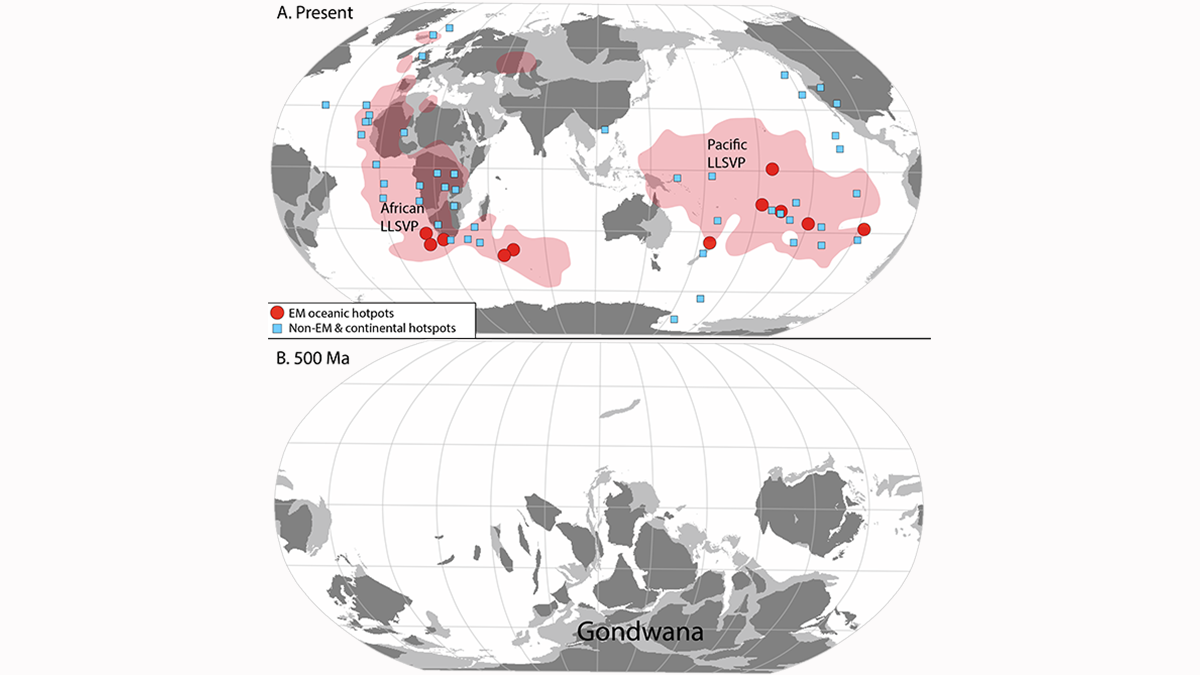
Subduction of continental crust around the Gondwana supercontinent may explain the mantle Dupal anomaly of the southern hemisphere.
New Crowdsourced Science Project Will Study Sprites
The NASA-funded project is asking sky gazers, storm chasers, and scientists to capture photos of sprites and other optical phenomena that flash above thunderclouds after a lightning strike.
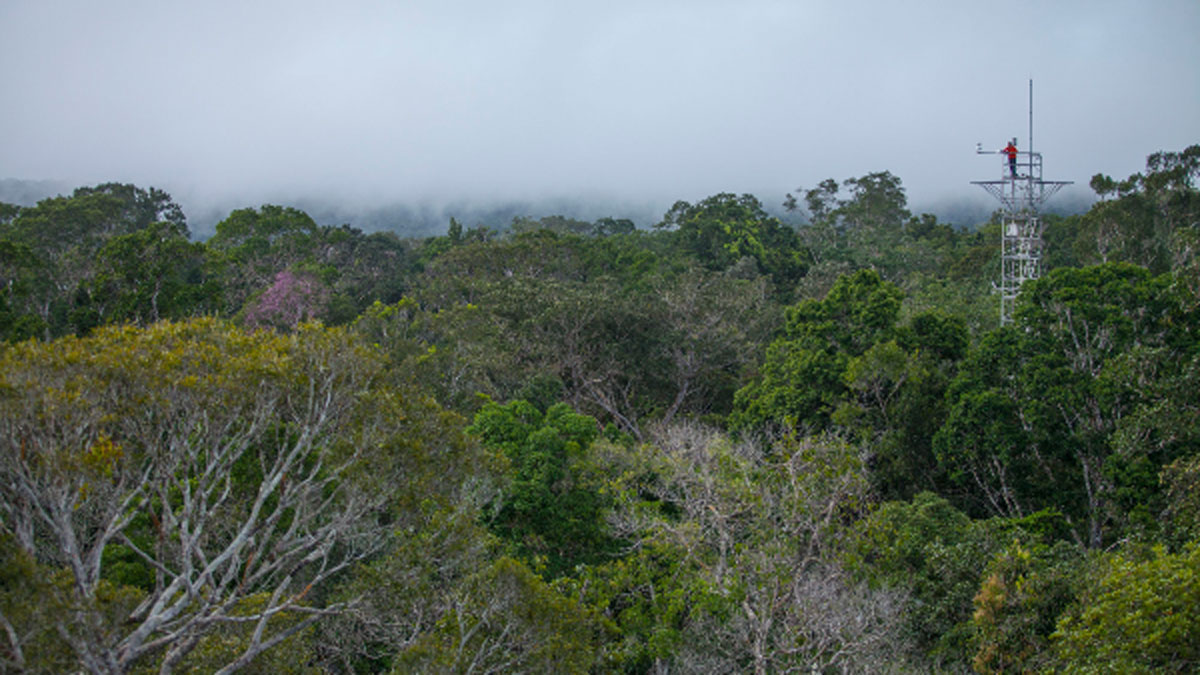
Testing the Resilience of the Amazon
A mega-experiment in Brazil will evaluate how tropical rain forests absorb carbon as emissions increase.
A Day in the Life Used to Be 17 Hours
The Moon was a lot closer to Earth 2.46 billion years ago, and the shorter distance contributed to shorter days.
Could Jupiter’s Heat Waves Help Solve a Planetary Energy Crisis?
Infrared observations reveal that Jupiter’s upper atmosphere is much warmer than models predict. The discovery may be a clue to finding missing heat sources in other giant planets.
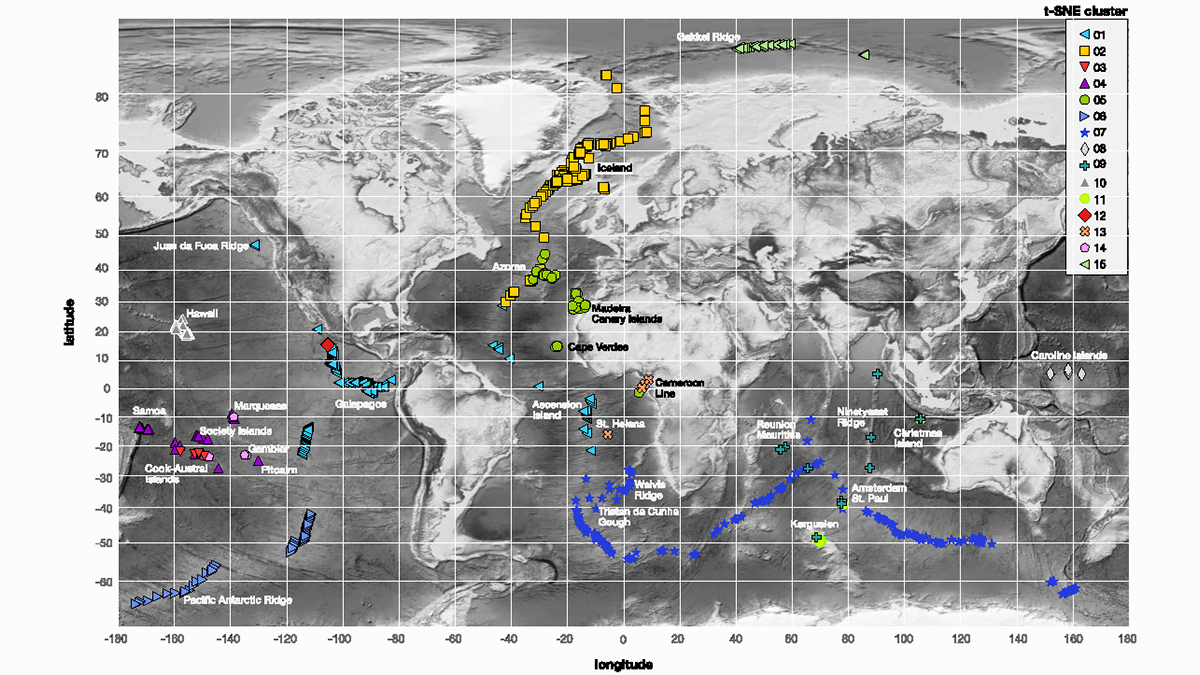
Machine Learning Looks Anew at Isotope Ratios in Oceanic Basalts
While past attempts to define isotopic endmembers and assign them a geodynamic significance ended in controversy, a machine-learning clustering algorithm offers a solution to this classical problem.
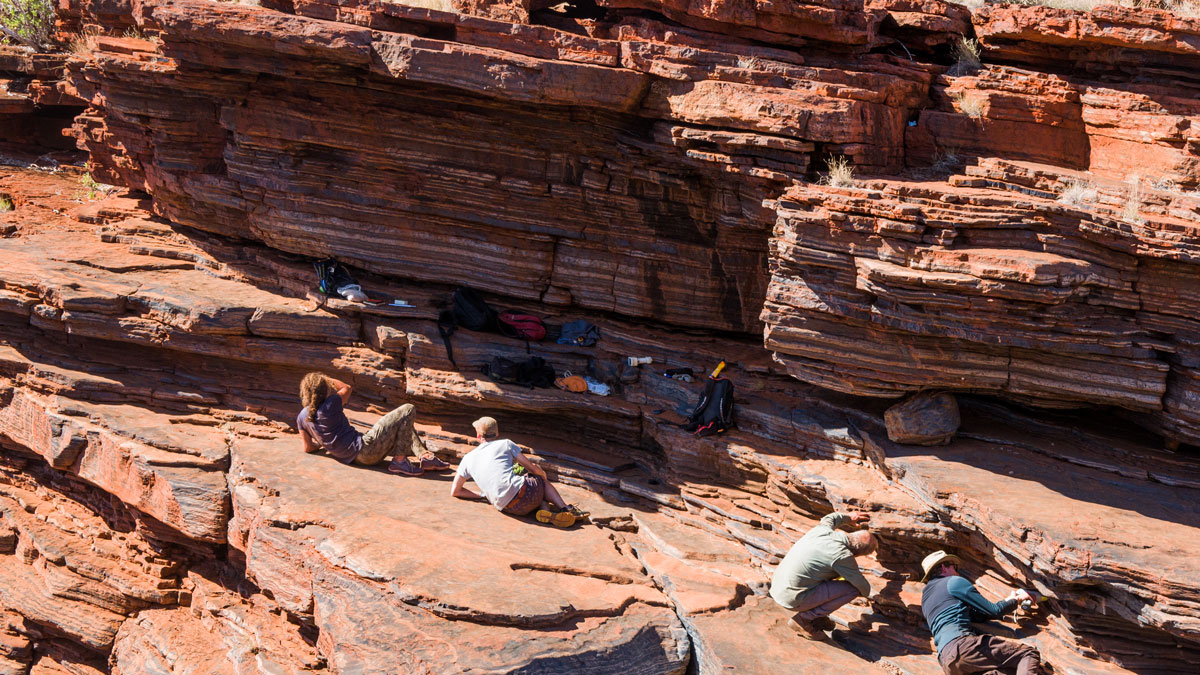
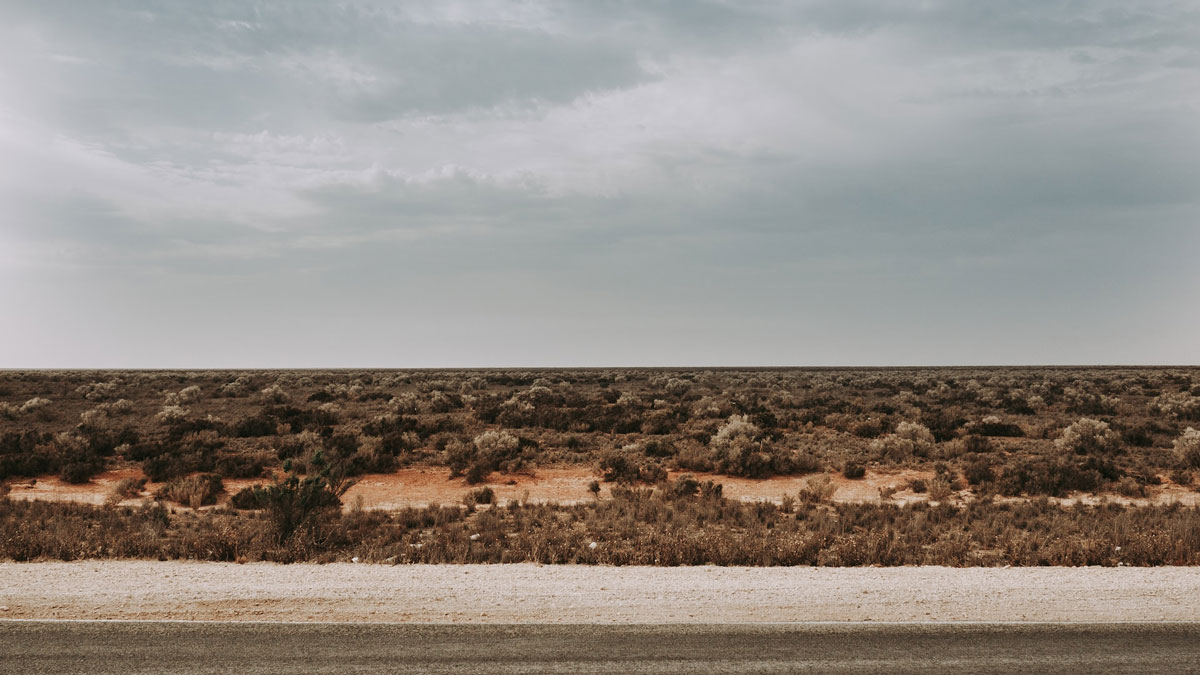
A Mysterious Dome Reveals Clues to Australia’s Miocene History
The Nullarbor Plain has been relatively untouched by geological forces, leaving traces of the continent’s deep past.