Fiberoptic strain meters capable of measuring micron-scale subsidence reveal a Holocene sediment package on the Mississippi Delta that is mostly stable.
wetlands
Tropical Wetlands Emit More Methane Than Previously Thought
Climate models could be vastly underestimating methane emissions from the world’s tropical wetlands, according to observational surveys of wetlands in Zambia.
Bank Retreat Controls River and Estuary Morphodynamics
Understanding and predicting the geomorphological response of fluvial and tidal channels to bank retreat underpins the robust management of water courses and the protection of wetlands.
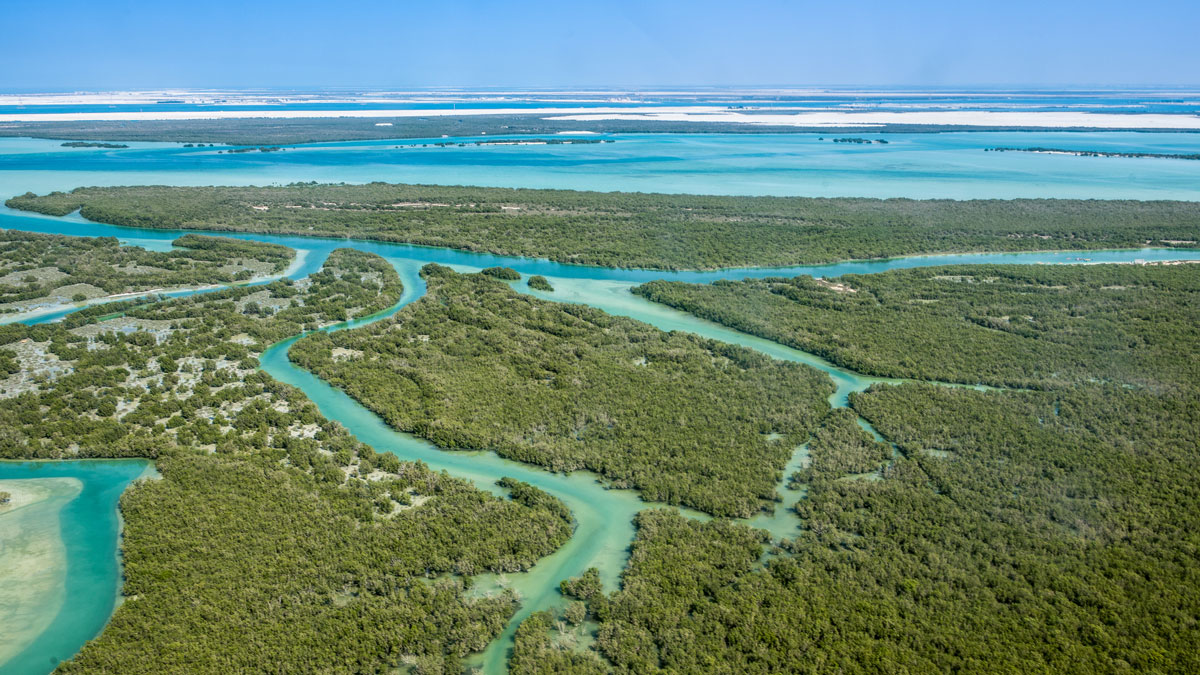
Estimating Land Loss in River Deltas
Some deltas are susceptible to land loss during sea level rise, whereas others gain land because of changes in the courses of rivers.
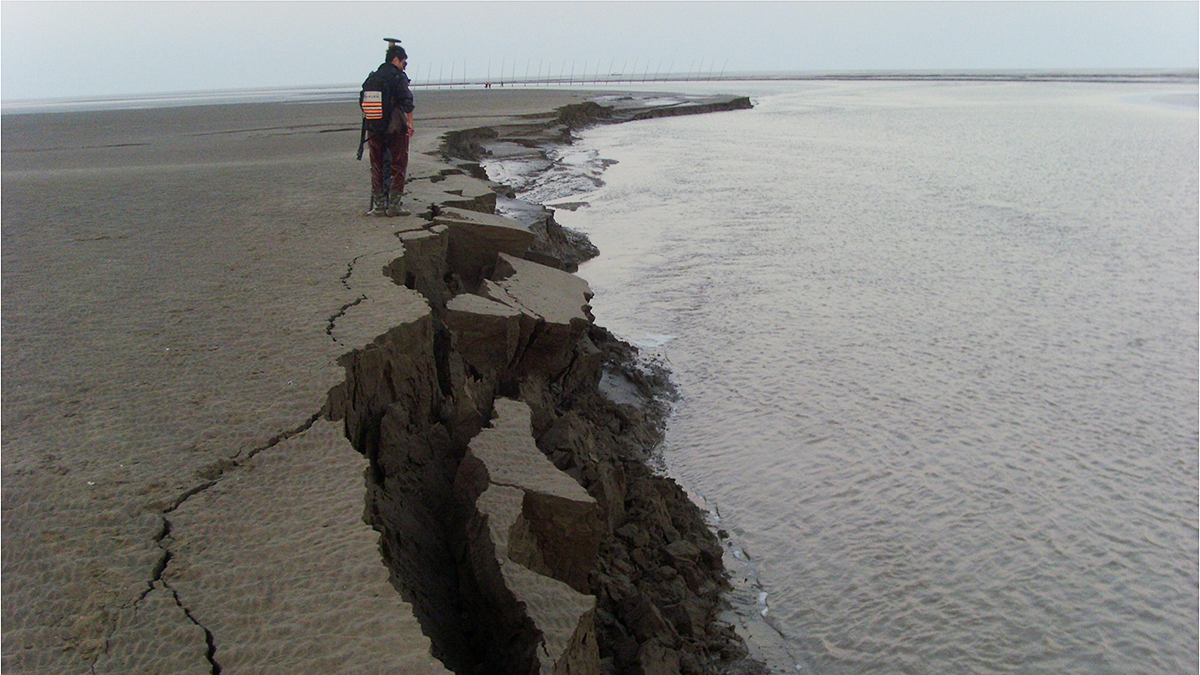
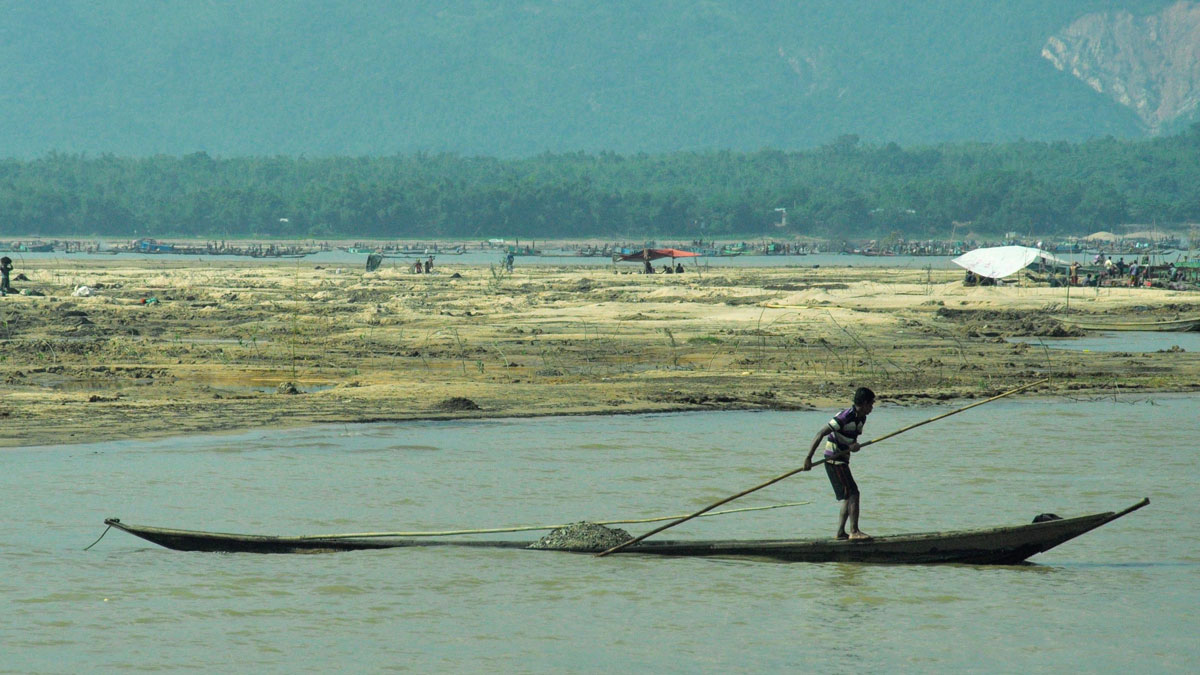
Bangladeshis Feel Increased Consequences of Sedimentation
In northern Bangladesh, residents are losing their livelihoods, homes, and personal safety when water carries sand and gravel into their communities.
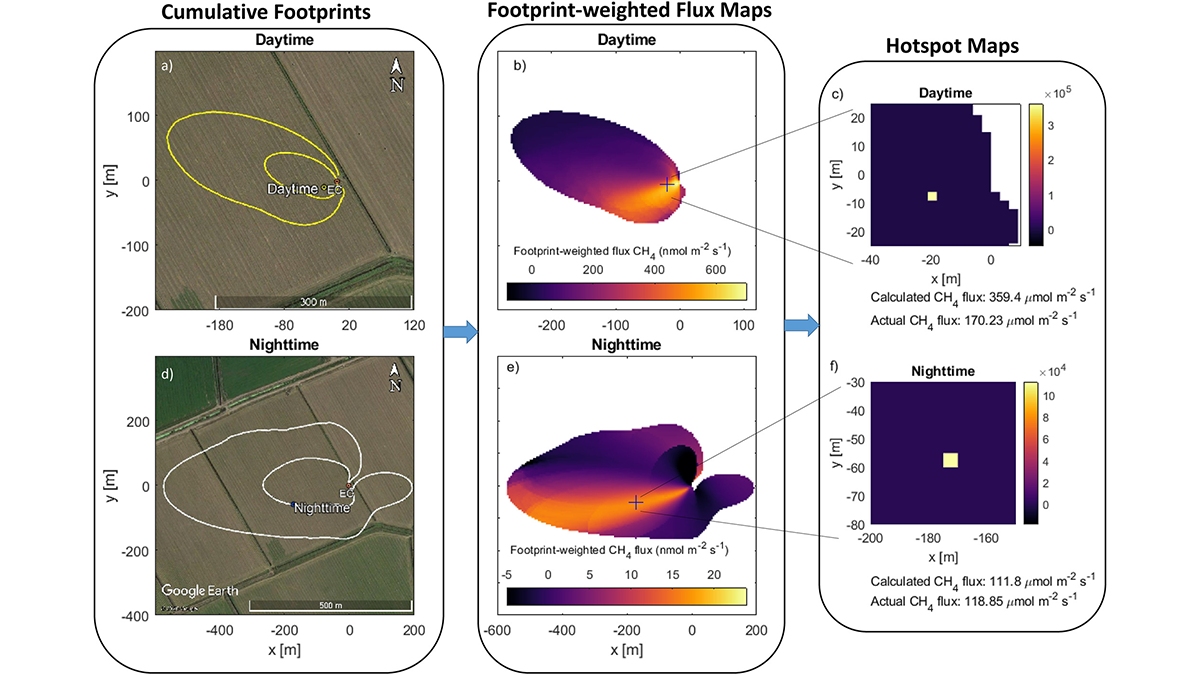
Sleuthing for Culprits of Greenhouse Gas Emissions
A new approach to detect hot spots of methane emissions with eddy covariance flux towers proves to be a worthy contender.
Atmospheric Rivers Help Coastal Wetlands Build Up Sediment
Accounting for these storms and flooding can help experts predict and respond to rising sea levels.
Planting Wetlands Could Help Stave Off Climate Catastrophe
A shift in priority and approach to wetland restoration could reduce atmospheric carbon.
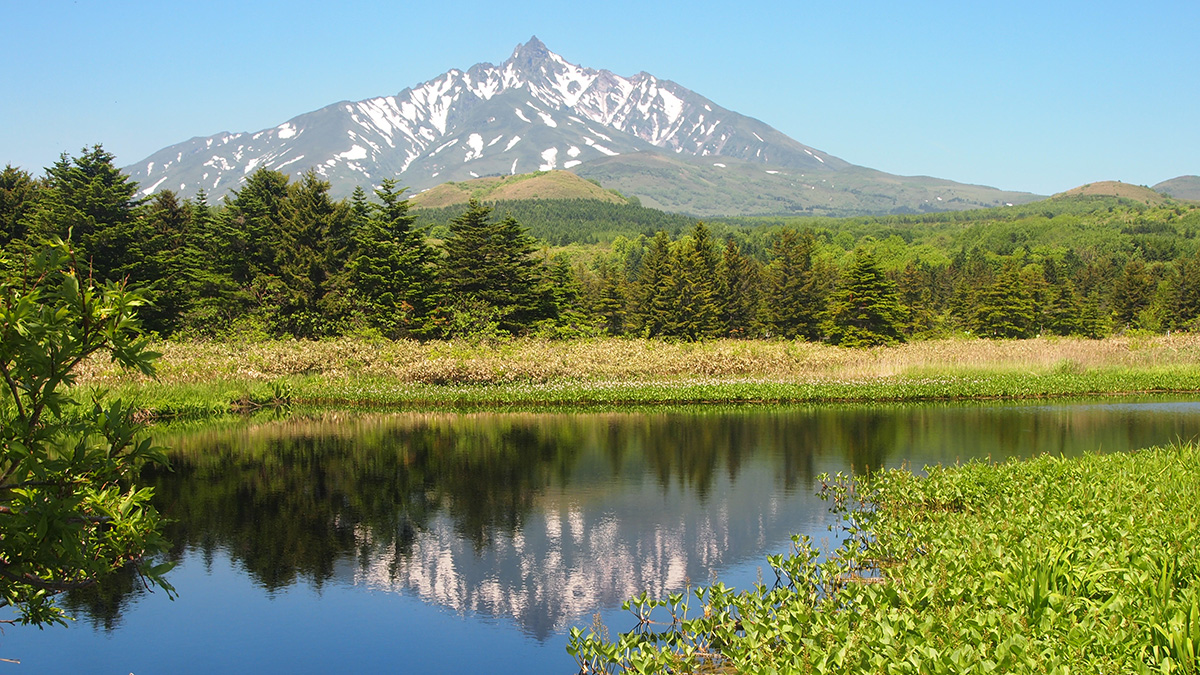
Climate and Currents Shaped Japan’s Hunter-Gatherer Cultures
New climate records from a peat bog show how two neighboring cultures responded differently to shifts in climate and ocean currents.
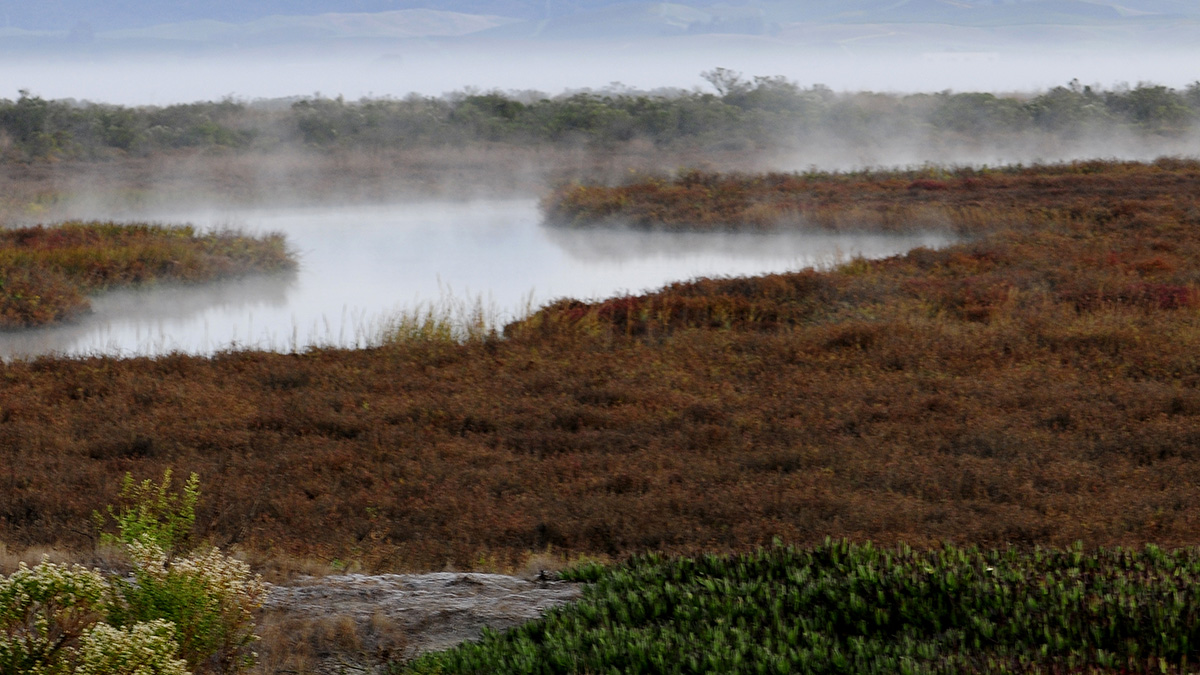
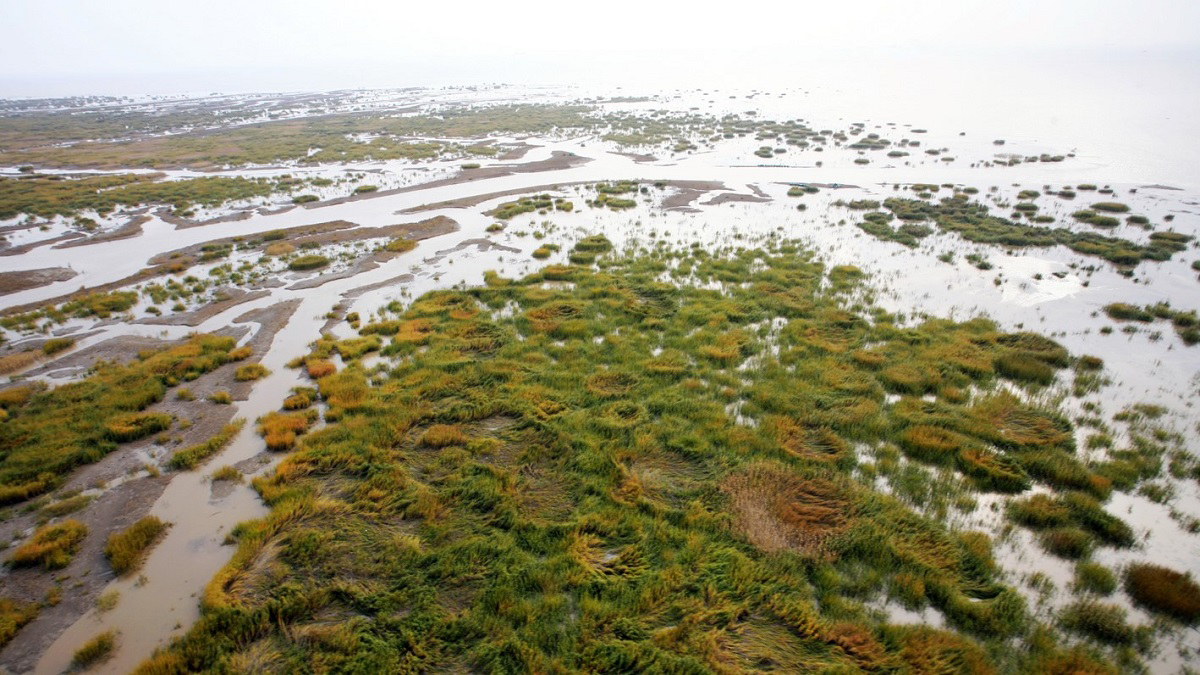
Understanding the Importance of Salt Marshes
Hydrological processes affect plant ecology and the biogeochemical exchange between salt marshes and the sea.