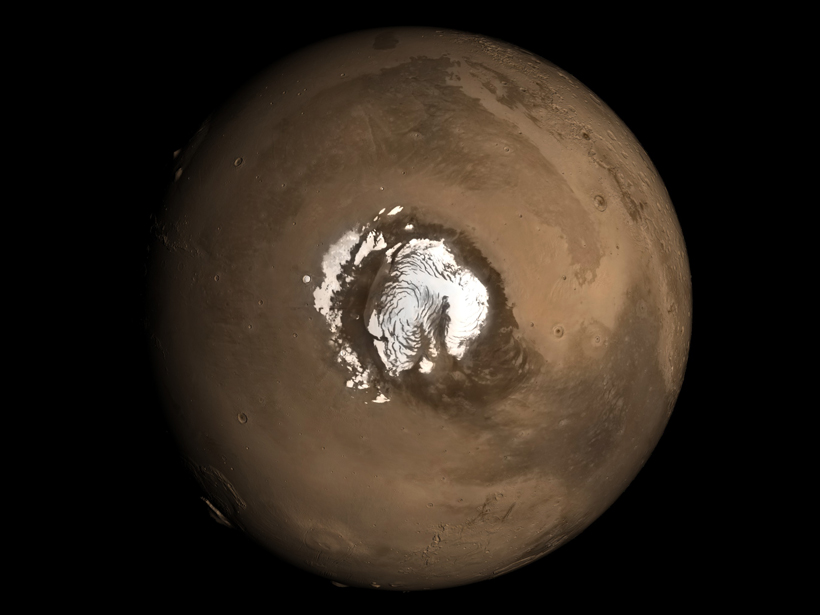
Orbital wobbling shaped the dome of ice and dust at the planet's north pole.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
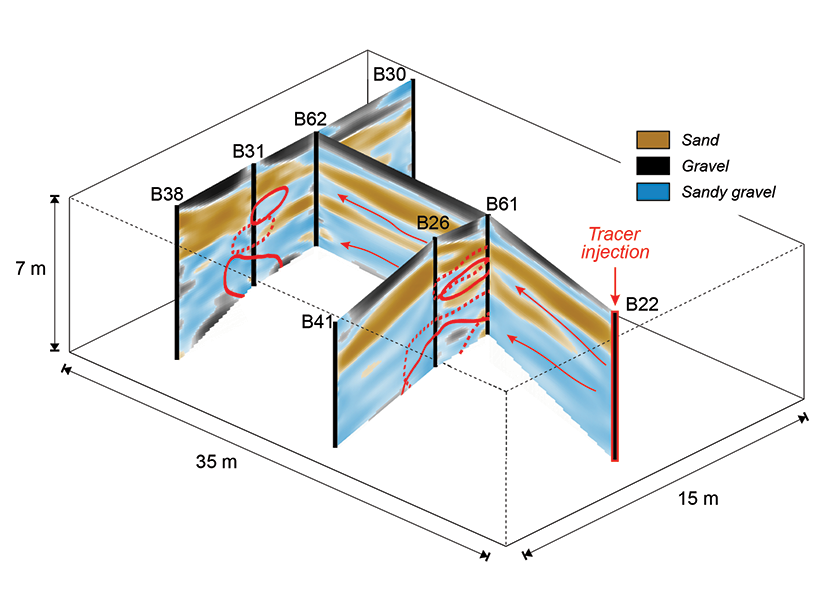
New Ground-Penetrating Radar Method Shows Promise in Aquifer
Recent advances in ground-penetrating radar data analysis could help reveal aquifer structure in unprecedented detail.
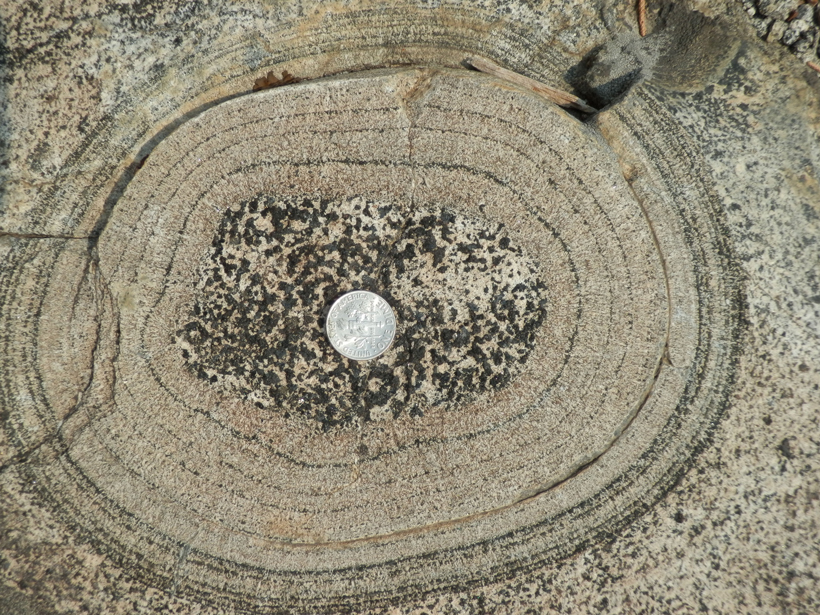
Pulses of Rising Magma in Sierra Nevada's Past
A detailed study of layered igneous material at California's Fisher Lake offers a novel approach to identifying the pathways and timescales of individual magma pulses in volcanic arcs.
Deep Drilling Reveals Puzzling History of Campi Flegrei Caldera
Results show that caldera collapse attributed to a super eruption almost 40,000 years ago was smaller than what scientists expected. So what might have really happened?
Tiny Creatures Form Massive, Bright Ring Around Antarctica
Dense algae populations in the Great Calcite Belt could cause carbon dioxide release from the ocean into the atmosphere.
Clouds Don't Reflect as Much Sunlight as Previously Thought
Icy clouds may actually increase, not decrease, the amount of solar energy that reaches Earth.
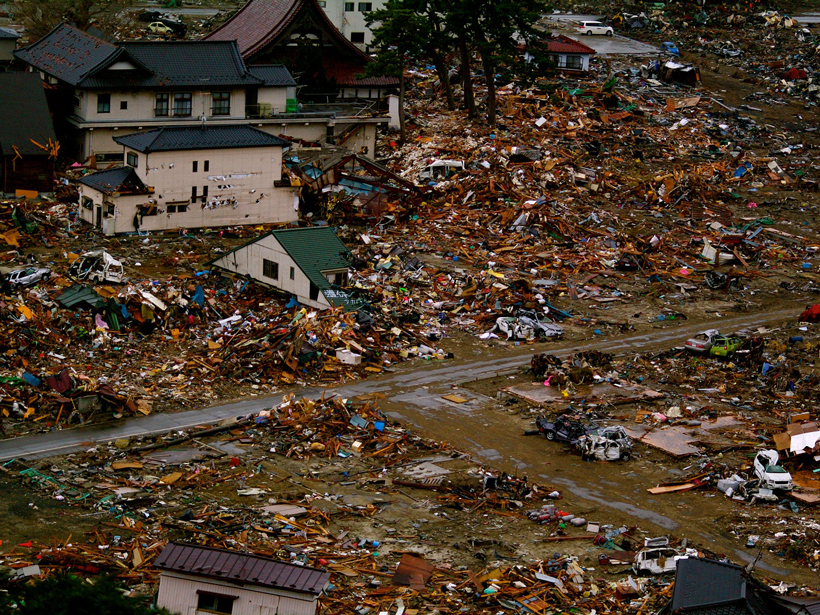
An Up Close Look at the Megaquakes That Cause Tsunamis
Researchers recreate changes in the seafloor during Japan's devastating 2011 tsunami.
A Comparison of Surface Thinning in West Antarctic Glaciers
An uninterrupted 24-year altimetry record of Amundsen Sea Embayment glaciers indicates the initiation and pace of thinning have been inconsistent across the region.
Martian Mantle Models Pave the Way for NASA's InSight Lander
The most detailed simulations to date of how heat flows through Mars's interior are good news for the upcoming lander and will help scientists interpret its data.
River's Rise Linked to Oklahoma's Largest Earthquake
As human-induced earthquakes increase in frequency and magnitude, researchers race to uncover their effects on surface water and groundwater.