Primordial solar storm conditions are believed to have significantly enhanced the loss of water and other atmospheric volatiles in Mars’ history.
CC BY-NC-ND 2017
A Superb Summer of Science Journalism
At National Geographic, Ph.D. paleontologist and Mass Media Fellow Shaena Montanari savored the challenge of covering everything from vintage Apollo photos to bone-eating giraffes.
A New Model Yields a Better Picture of Methane Fluxes
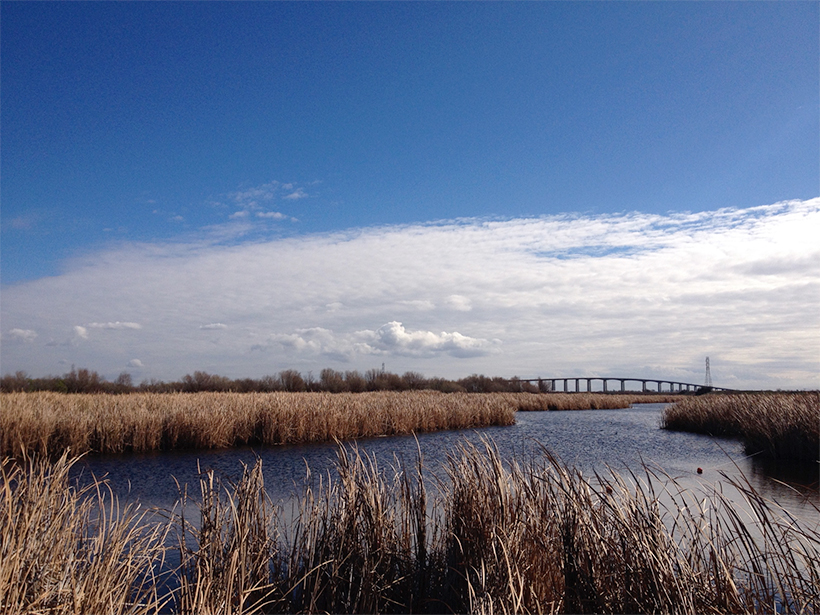
Scientists update an old model with recent findings, allowing for a more accurate understanding of methane dynamics in wetlands.
Exact Moonlight Measurements Could Aid Earth-Observing Missions
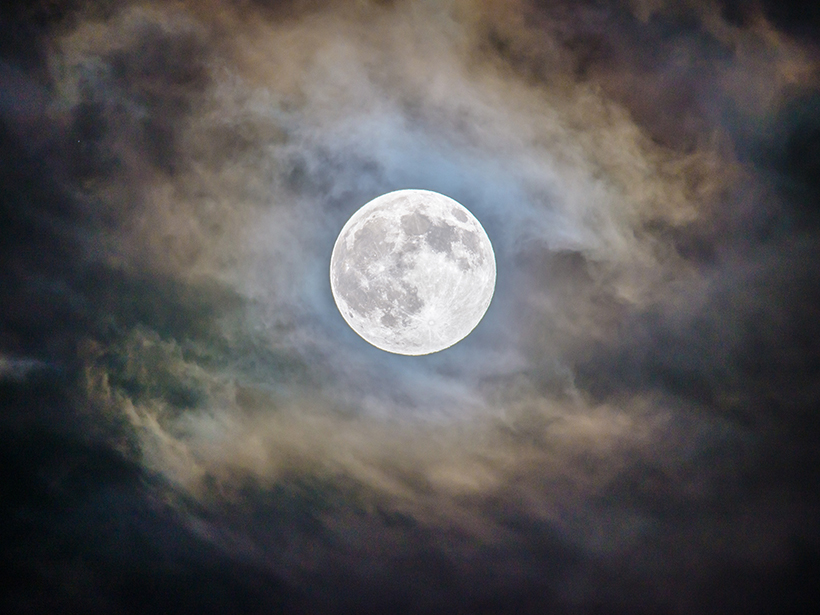
A new telescope’s unprecedented study of subtle variations in lunar light could finally give Earth-facing satellites a common reference point for their observations.
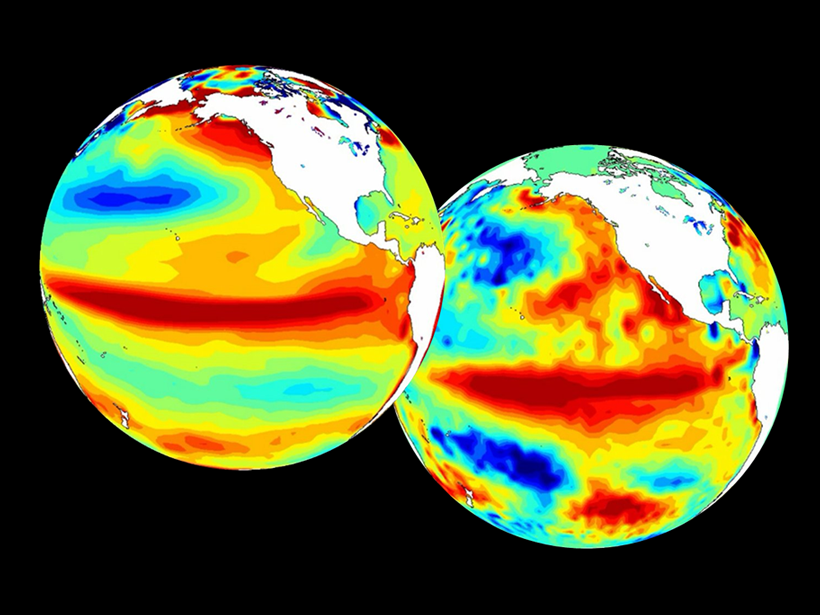
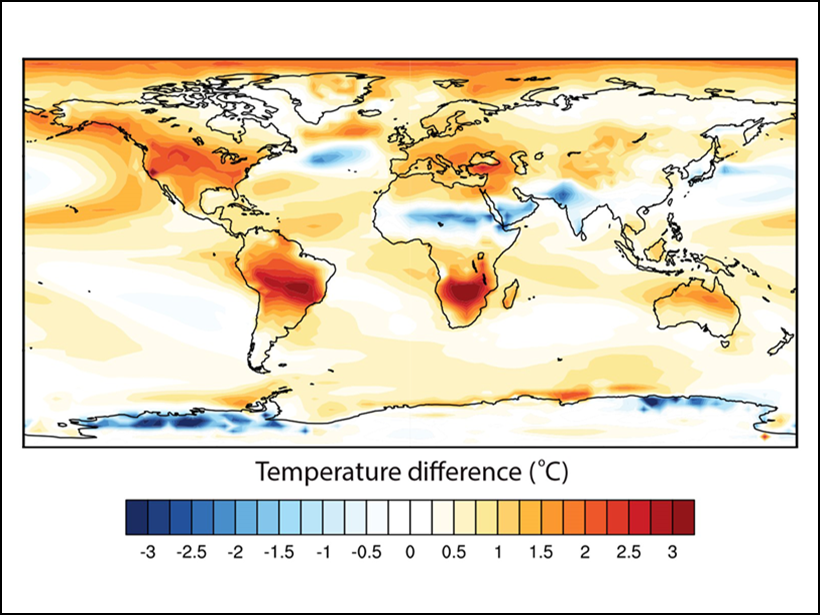
Advancing Climate Forecasting
Better forecasts, new products: The World Climate Research Programme coordinates research aimed at improving and extending global climate forecasting capabilities.
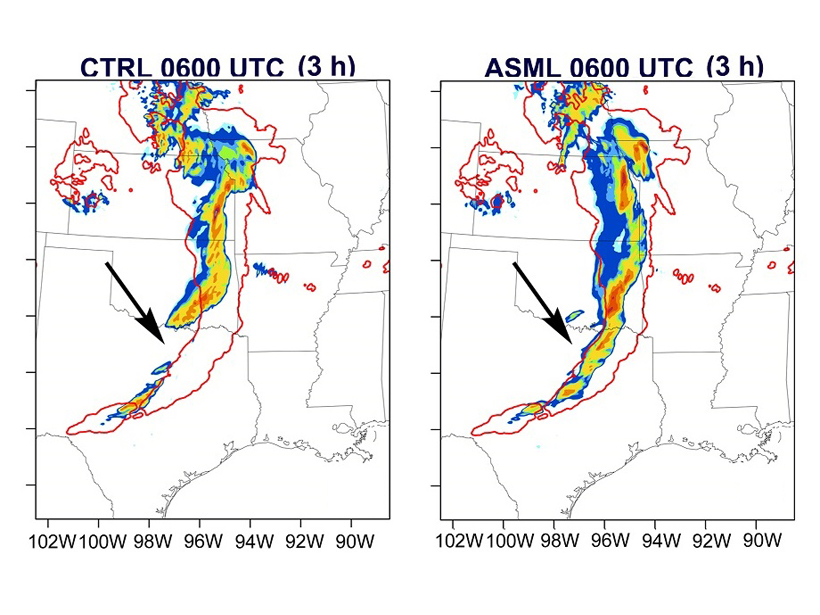
Lightning Data Improves Precipitation Forecasts
Short-term forecasts of precipitation and convection can be improved when lightning data are assimilated in the Weather Research and Forecasting system.
Deep-Seabed Mining May Come Soon, Says Head of Governing Group
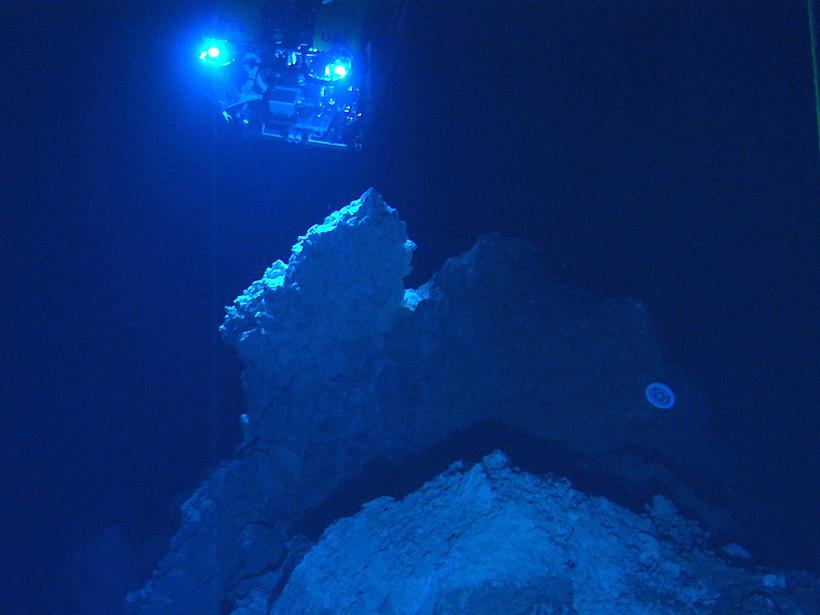
New regulations could open the door for sustainable mining, says the head of the International Seabed Authority. However, he and others pointed to environmental, financial, and technical challenges.
How Earth’s Orbit Affected Ice Sheets Millions of Years Ago
A new study of the late Pliocene era could help scientists predict future sea level rise.
AGU’s Developer Contest Unlocks Scientific Research
Announcing its Open API Challenge winners, the American Geophysical Union explores what open data mean for science.
Plumbing the Depths of the Marine Carbon Cycle
Scientists measure dissolved black carbon in South China Sea water samples to better understand the carbon cycle in the oceans, which absorb roughly half of all carbon emitted into the atmosphere.