Editors’ Highlights are summaries of recent papers by AGU’s journal editors.
Source: Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans
Ripples are bedforms on sandy sea beds in coastal regions that form and react to waves and currents. The sediment dynamics of these features are complex but important for understanding how coastal morphology can change at this scale.
DeVoe et al. [2025] investigate how sand and water behave inside and above these ripples. They use advanced computer models that combine fluid (using a Large Eddy Simulation) and sediment behavior (using a Discrete Particle Model) to find out how forces and shear stresses vary over and within a moving bed using a new mathematical method. The numerical method does not need assumptions of the near-bed boundary layer as required by other models and is an important new contribution toward understanding coastal sediment transport.
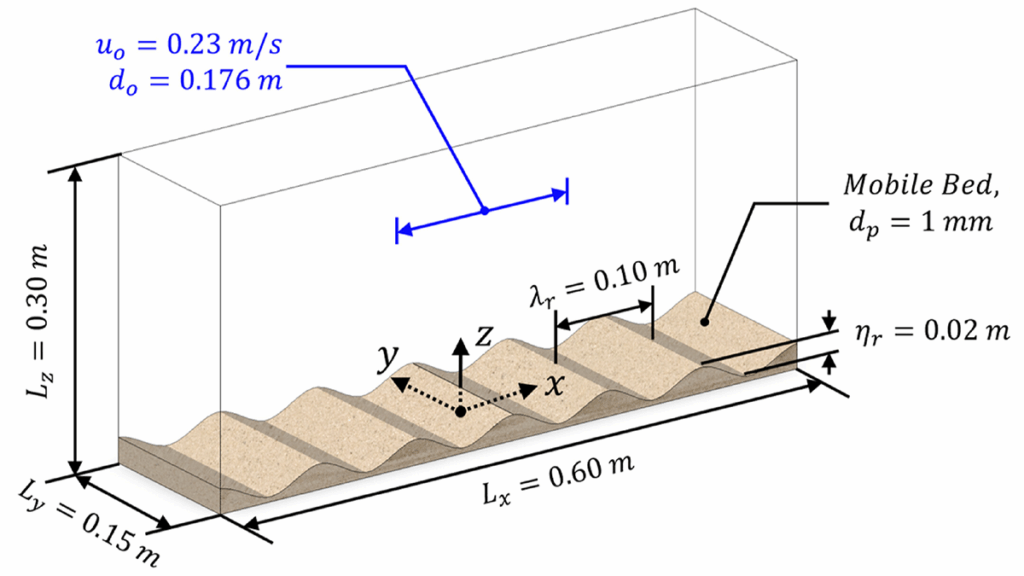
Citation: DeVoe, S. R., Wengrove, M. E., Foster, D. L., & Hagan, D. S. (2025). Characterization of the spatiotemporal distribution of shear stress and bedload flux within a mobile, rippled bed. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 130, e2025JC022369. https://doi.org/10.1029/2025JC022369
—Ryan P. Mulligan, Editor, JGR: Oceans

