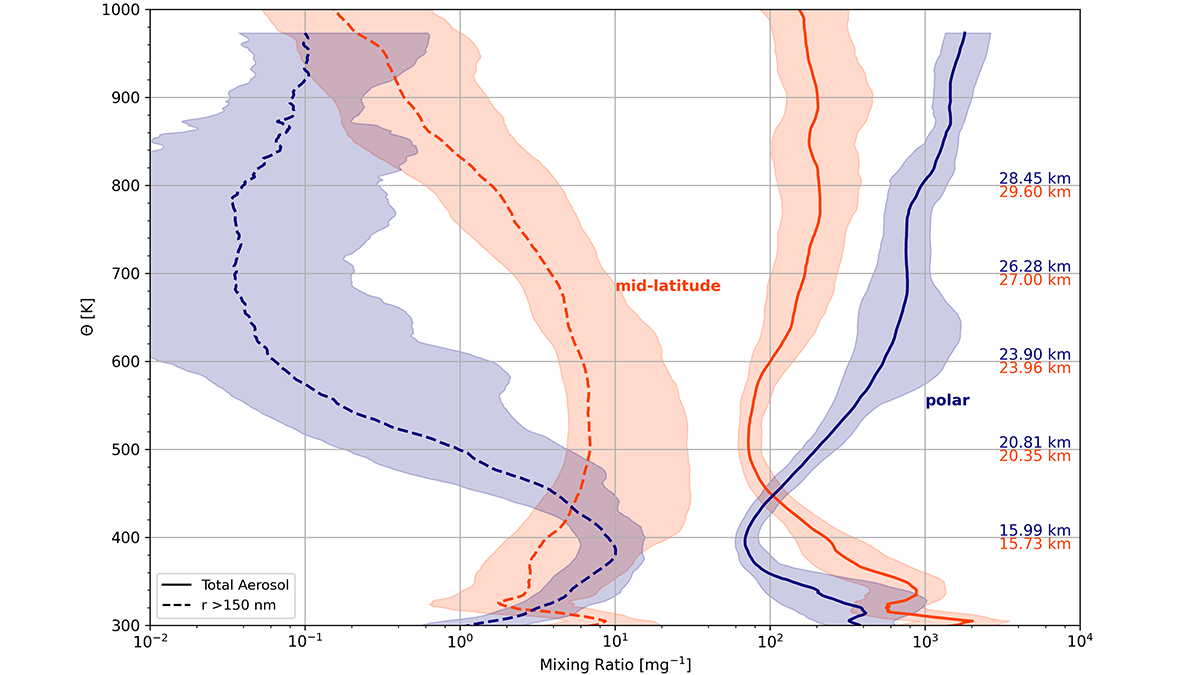
Long-term global measurements of stratospheric aerosols reveal climatological structures and processes controlling new particle formation.
Editors’ Highlights
Counting from One to Nine to Detect Debris Flows
A groundbreaking method using Benford’s law allows the detection of debris flows from seismic signals.
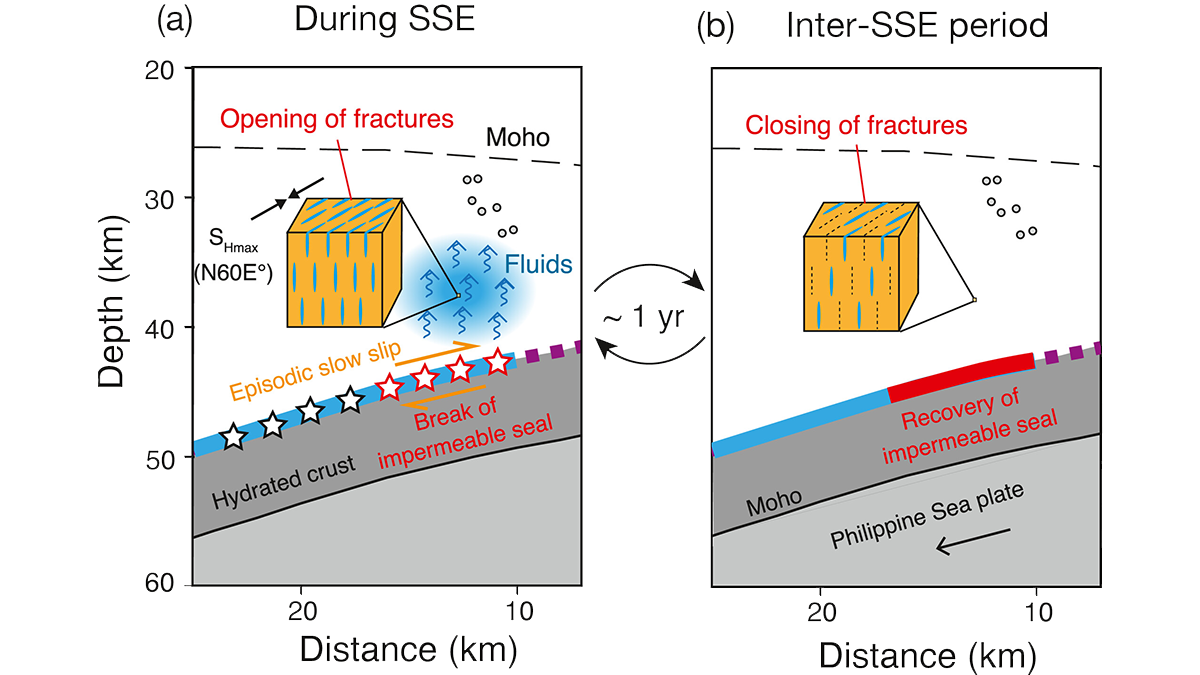
Cyclic Opening of Deep Fractures Regulates Plate Boundary Slip
Seismic anisotropy changes through time suggest that cyclical opening of fluid-filled fractures is synchronized with subduction zone slow slip events.
New Insights into a Blind Spot in Aquatic Carbon Dioxide Exchange
Multi-annual measurements across Lake Superior indicate remarkable similarities between large lakes and ocean CO2 exchange during the ice-free season.
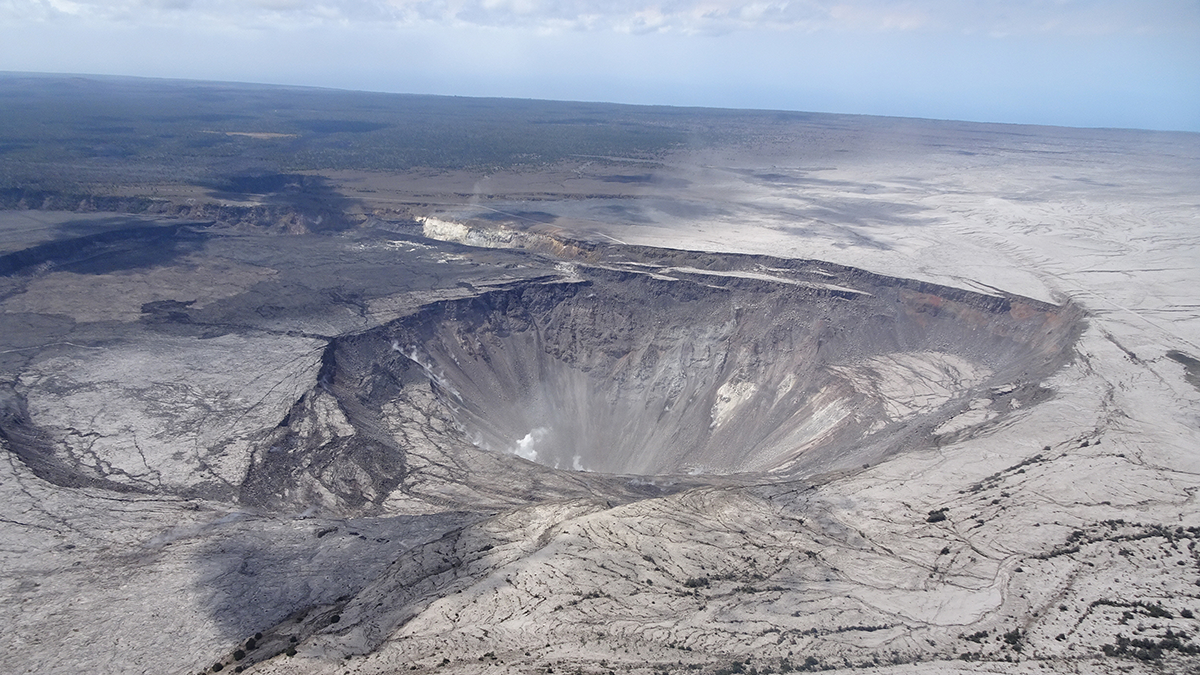
Forecasting Caldera Collapse Using Deep Learning
A deep learning model trained with geophysical data recorded during the well-documented 2018 Kilauea volcano eruption, Hawaii, predicts recurrent caldera collapse events.
Air-Ice-Ocean Coupling Observed in an Arctic Cyclone Event
New observations show detailed features of the ice-ocean response to a strong Arctic cyclone in the winter of 2019-2020.
Sediment Dampens the Impact of Glaciation on Cenozoic Denudation
Rates of continental-scale sediment flux and denudation are similar between glacial and interglacial periods when the aggradation of glacier-eroded sediment inhibits fluvial erosion downstream.
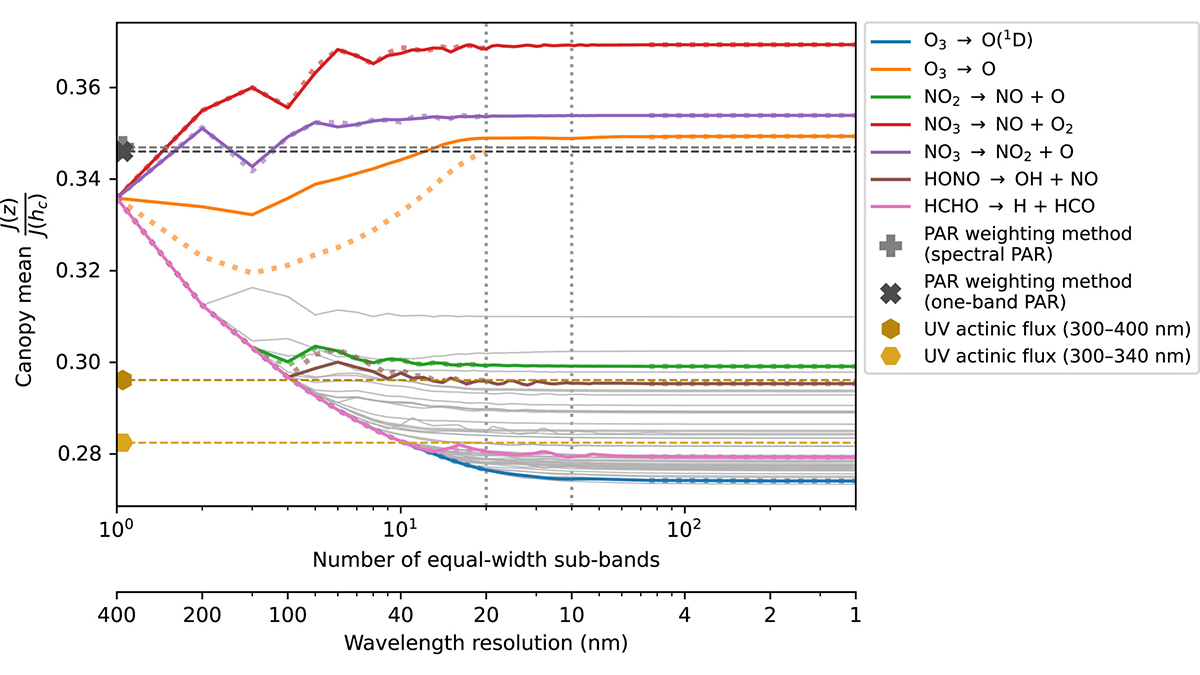
Spectral Solar Radiative Transfer in Plant Canopies
Spectrally resolved radiative transfer is needed to compute reliable estimates of sunlight transmission and photolysis of molecules within plant canopies.
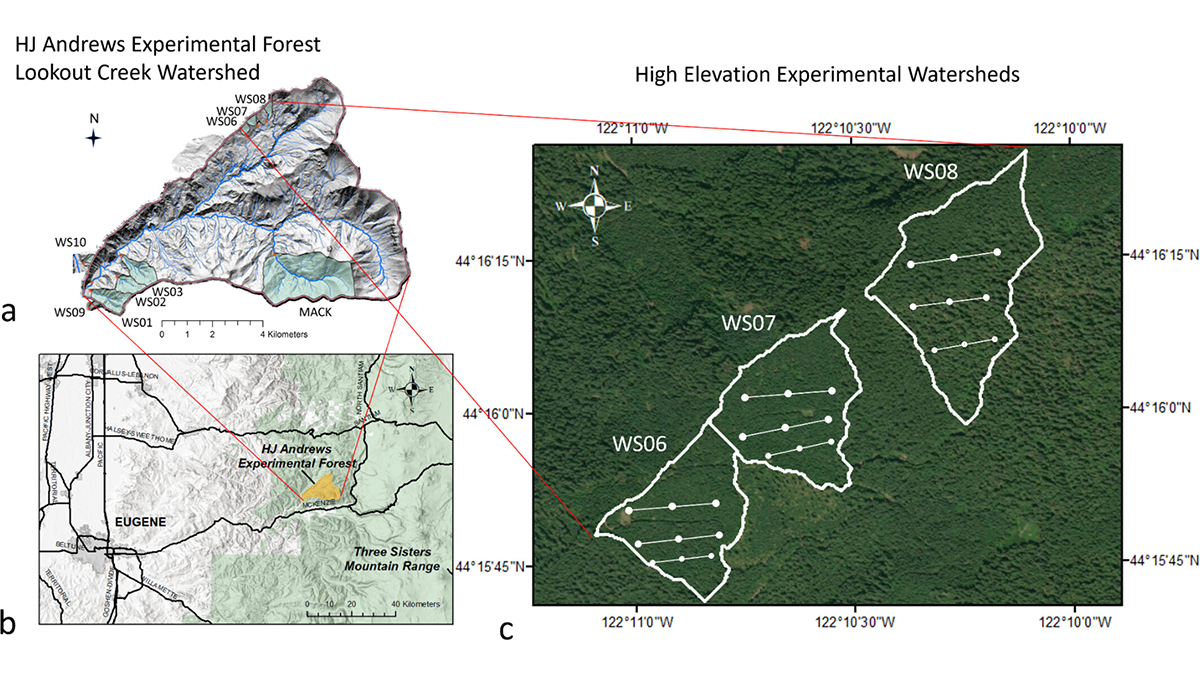
Understanding Carbon-Water Tradeoffs in Pacific Northwest Forests
A new study documents how spruce forests differing in management and age structure influence individual tree growth, carbon stocks, and landscape-water balance in the Pacific Northwest.