Source: Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
Even though volcanic emissions are well known for their role in causing multi-month cooling effects at the top of the atmosphere and the surface, in some cases there is substantial warming from sulfur dioxide that can offset the cooling from sulfate particles.
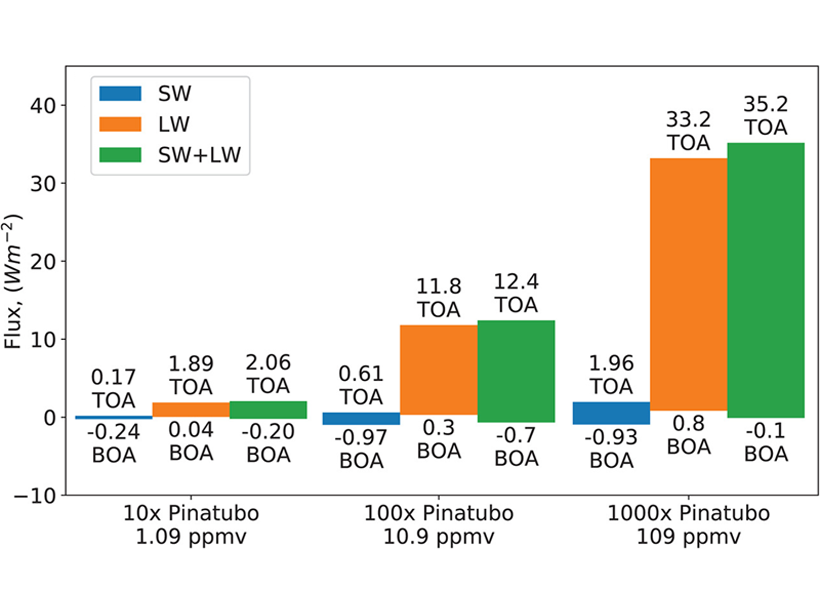
Osipov et al. [2020] show the significant role of volcanic sulfur dioxide effects on chemistry, dynamics, and aerosol radiative forcing, using the Toba eruption simulation as an example. Such effects usually are not included in assessing the volcanic climate effects from large volcanic eruptions, and this study has made a compelling case for considering it in the future assessments. Specifically, the authors demonstrate the “soothing” greenhouse effect of sulfur dioxide on the cooling of sulfate aerosol. These offsets to sulfate cooling are particularly important to consider for simulating the impacts of future volcanic eruptions on climate.
Citation: Osipov, S., Stenchikov, G., Tsigaridis, K., LeGrande, A. N., & Bauer, S. E. [2020]. The role of the SO2 radiative effect in sustaining the volcanic winter and soothing the Toba impact on climate. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125, e2019JD031726. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031726
—Lynn Russell, Editor, JGR: Atmospheres
Text © 2020. The authors. CC BY-NC-ND 3.0
Except where otherwise noted, images are subject to copyright. Any reuse without express permission from the copyright owner is prohibited.