The seasonality of fine-scale, near-surface ocean dynamics raises important considerations for an upcoming satellite mission to measure global sea surface height.
Research Spotlights
Research spotlights are plain-language summaries of recent articles published in AGU’s suite of 24 journals.
Understanding Tectonic Processes Following Great Earthquakes
Scientists parse out the processes underlying tectonic signals detected by GPS networks.
Earth's Carbon-Climate Feedbacks Varied in Past Warming Episodes
Records from drill holes in the eastern equatorial Pacific indicate that Earth's orbital eccentricity played an important role in controlling climate as the planet warmed.
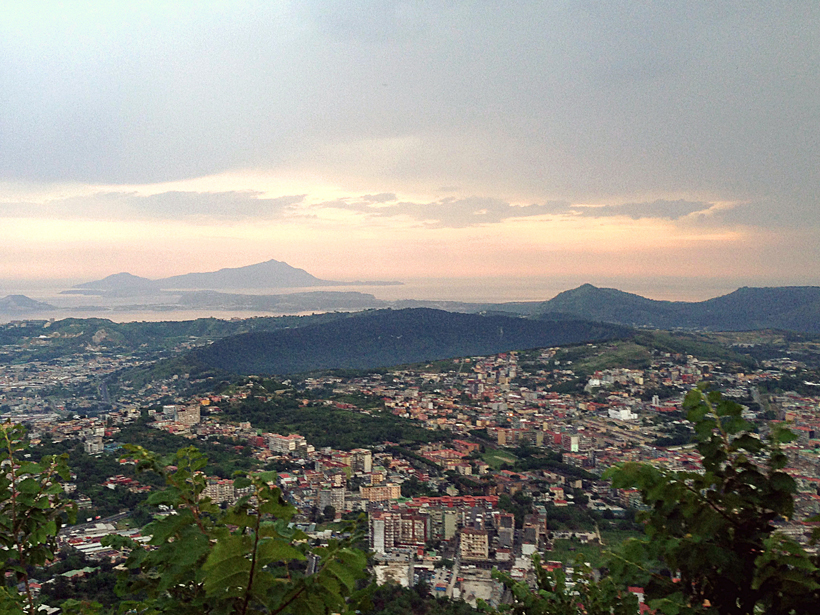
When Might the Campi Flegrei Caldera Erupt Again?
The clock may be ticking for Italy's Campi Flegrei caldera, a region with a pattern of numerous and sometimes large explosive eruptions. The next explosion could be less than 100 years away.
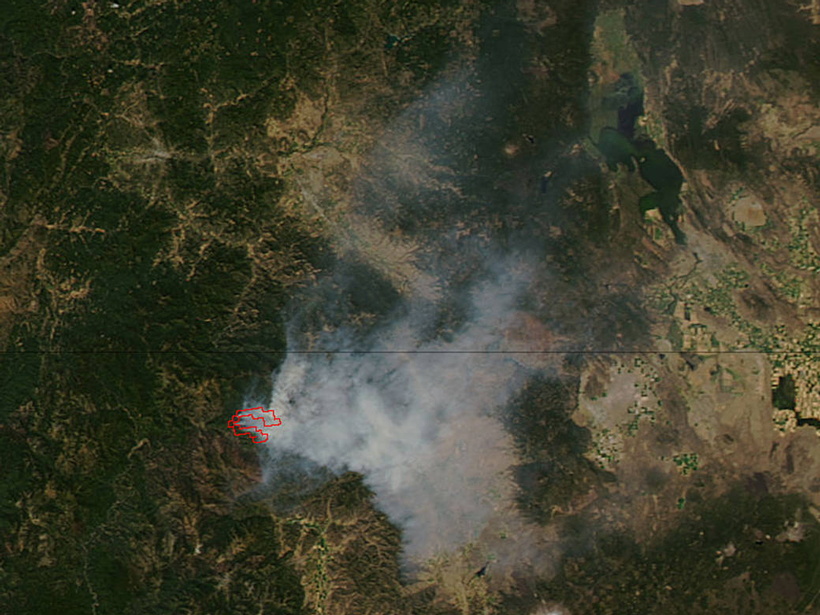
Fighting Fire with Satellite Data
As climate change worsens wildfire impact, scientists use satellites to study climate-fire interactions.
A Significantly Hotter Mantle Beneath Iceland
Estimates of crystallization temperatures from four eruptions in northern Iceland offer improved constraints on the mantle's temperature beneath this anomalous divergent plate boundary.
A Wetter Climate Increases Methane Production in Peat
As northern Minnesota's climate got wetter, precipitation drove mobile forms of young carbon deeper into peatlands, doubling the size of methane-producing strata.
Tracing the North Atlantic's Bottom Waters
Chemicals released by two European nuclear fuel reprocessing plants, along with certain chlorofluorocarbons, are helping to constrain the speed and behavior of North Atlantic deep-ocean circulation.
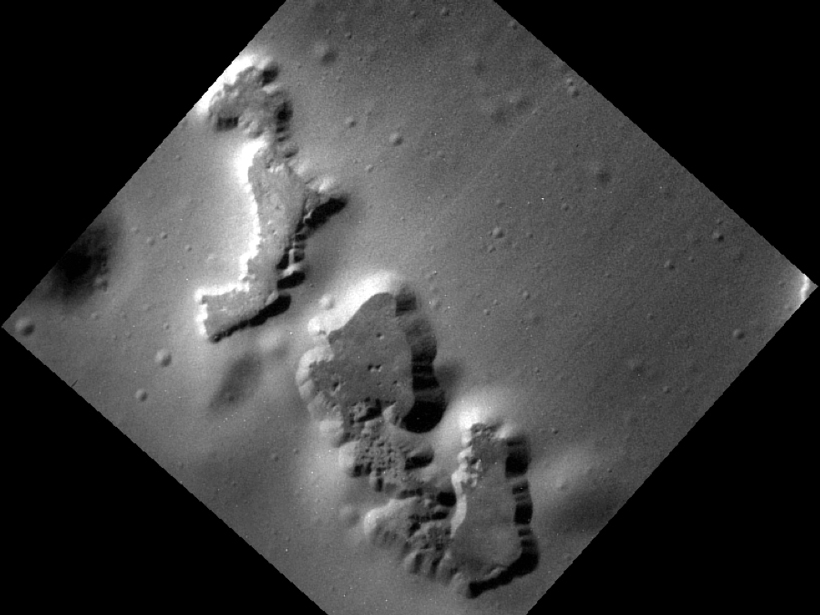
Unprecedented Views of Mercury Constrain Hollow Formation
The consistently shallow depths of the depressions scattered across Mercury's surface suggest their morphology is not determined by the thickness of a volatile-rich outer layer.
Isotopes Track Carbon Cycle in Northern Wisconsin Wilderness
Researchers collected carbon from 3 years' worth of air samples and traced it back to its source.