At AGU’s Annual Meeting 2024, activist Sharon Lavigne spoke about living in Louisiana, in what is commonly known as “Cancer Alley.” The 85-mile stretch along the Mississippi River is home to more than 200 industrial facilities, including the Denka Performance Elastomer plant, which uses chloroprene to manufacture synthetic rubber for products such as automotive parts, adhesives, and construction materials.
air pollution
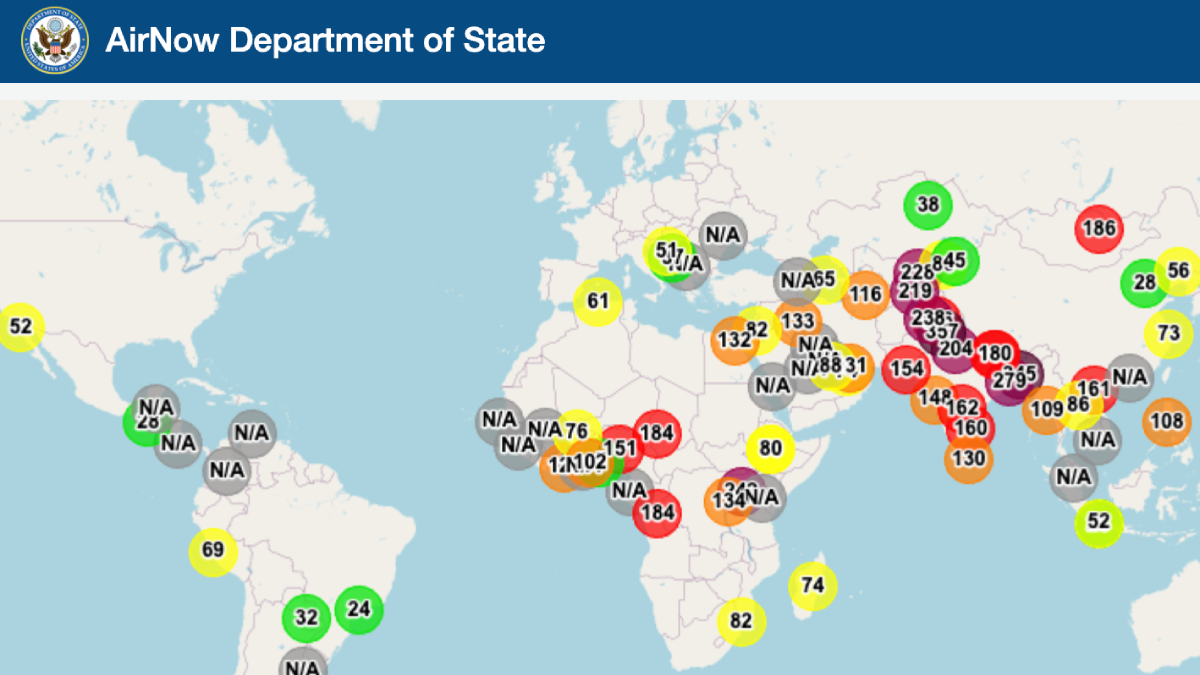
404: Air Quality Data from U.S. Embassies Removed
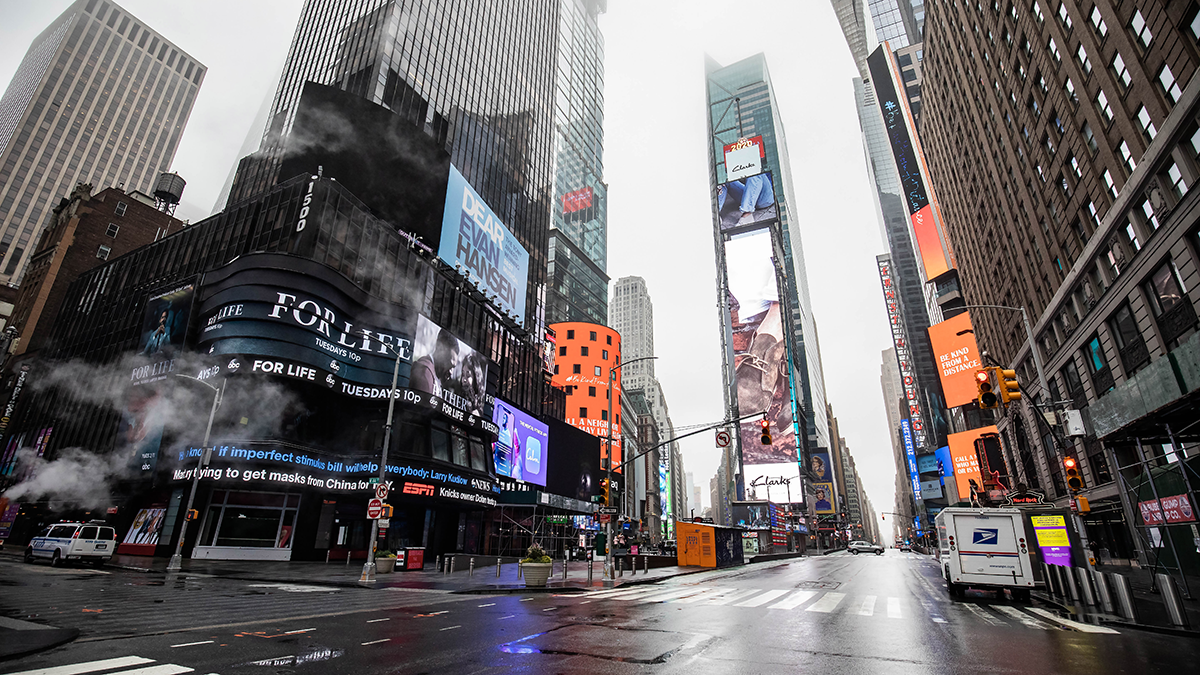
On 4 March, AirNow, the home of the U.S. Air Quality Index, shut down its webpage that reported data from air quality monitors at U.S. embassies and consulates around the world. Eos learned of the removal of these data from Dan Westervelt, a climate change and pollution scientist at Columbia University’s Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory in Palisades, New York.
Particulate Pollution and its Climate Impacts During the COVID-19 Pandemic
The impacts of COVID-19 on short-lived pollutants highlight the predominant influence of the transportation sector and the resulting changes in regional climates and ecosystems.
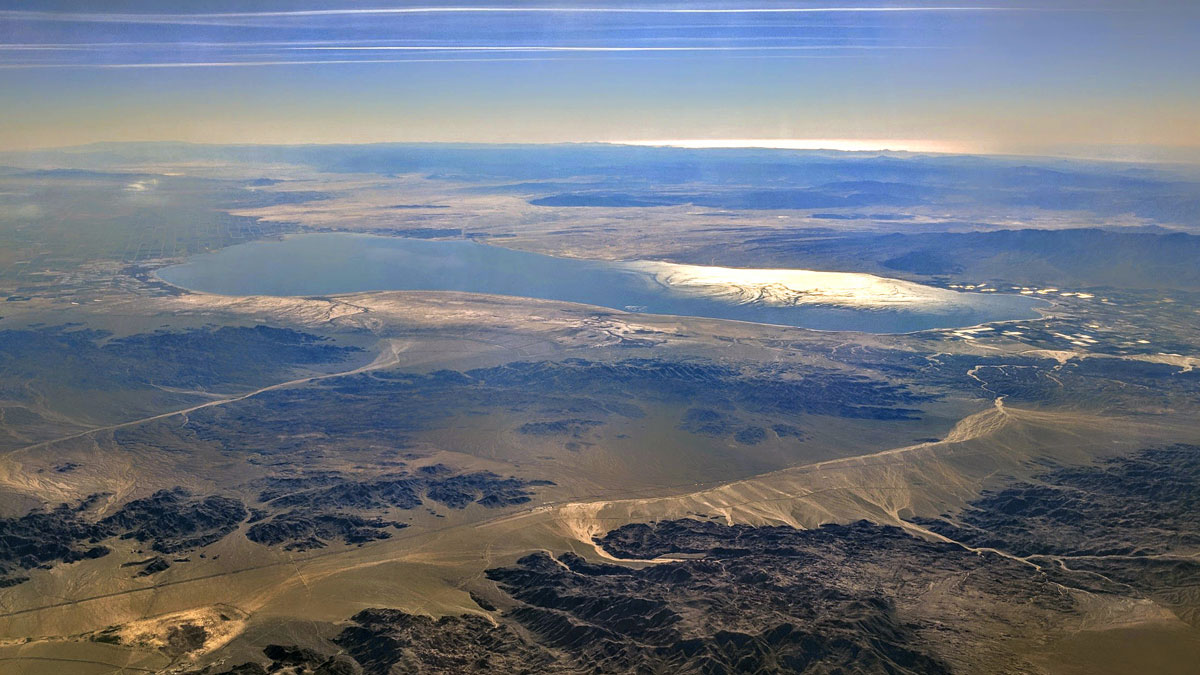
The Deleterious Dust of the Salton Sea
Coarse particulate matter deriving from California’s largest lake is linked to an increased risk of respiratory-related hospitalizations.
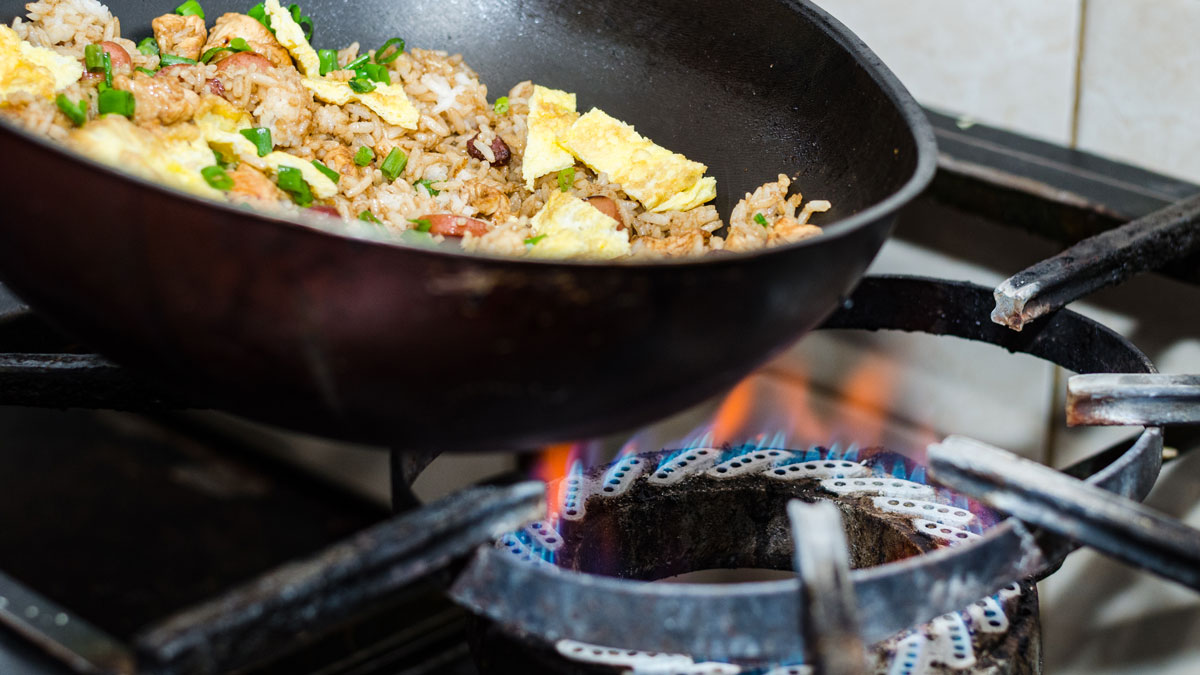
Cooking with Gas Creates Unhealthy Work Environments
Even with ventilation, commercial kitchens can have air pollution levels that exceed health-related limits.
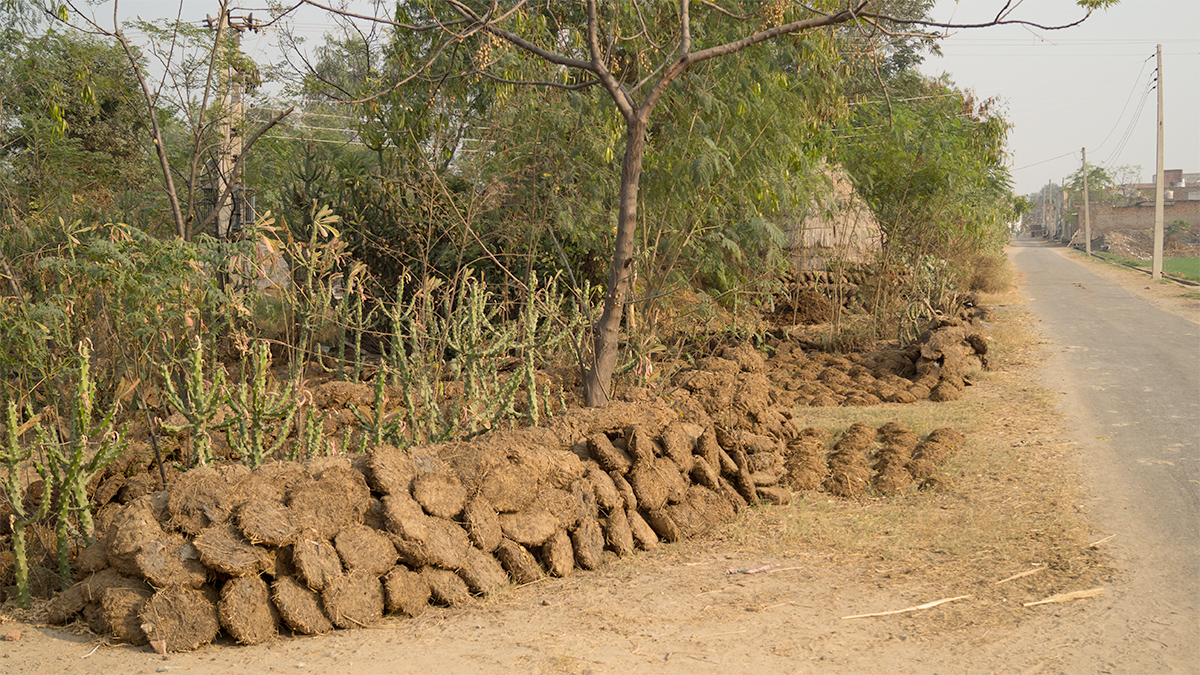
Burning Cow Dung Emits an Inordinate Amount of Air Pollution in India
Dried cow dung, a main source of household cooking fuel for many in rural India, releases more particulate matter across the country than wood and other biofuels.
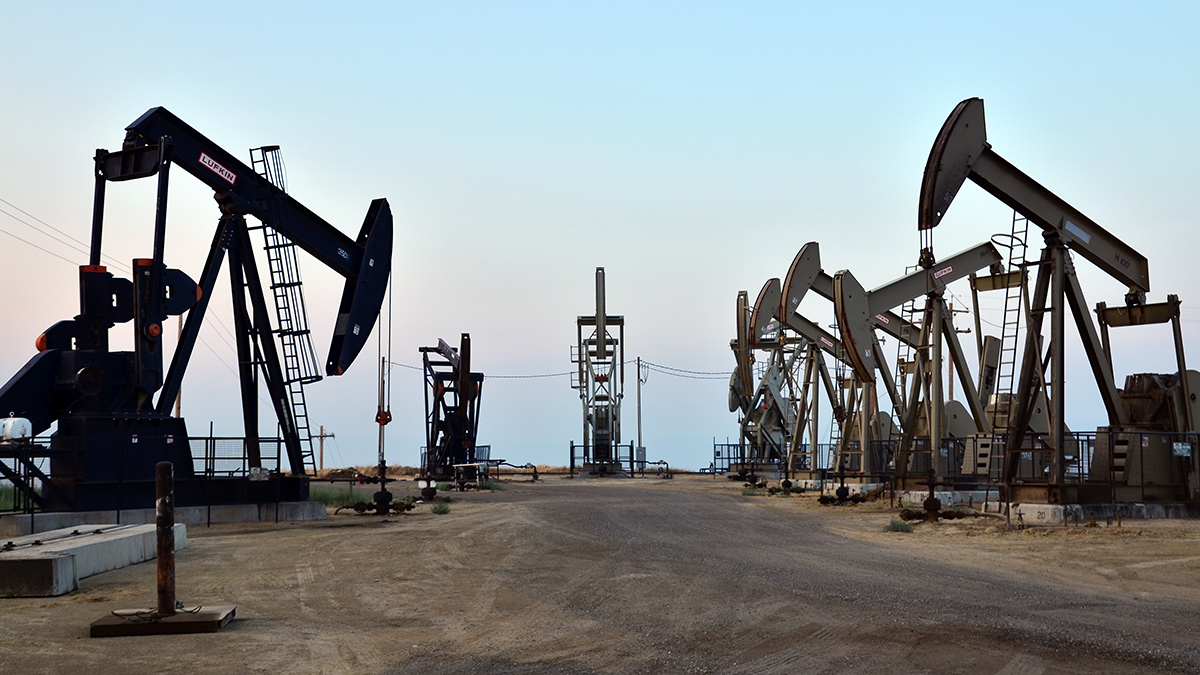
Oil, Gas, and COVID-19
Early in the pandemic, people living near oil and gas wells experienced higher rates of COVID-19 and related mortality compared with those with no exposure to well pollution.
EPA Air Monitoring Network Misses 2.8 Million Americans in Pollution Hot Spots
Current EPA air monitoring may not capture the extent of particulate air pollution.
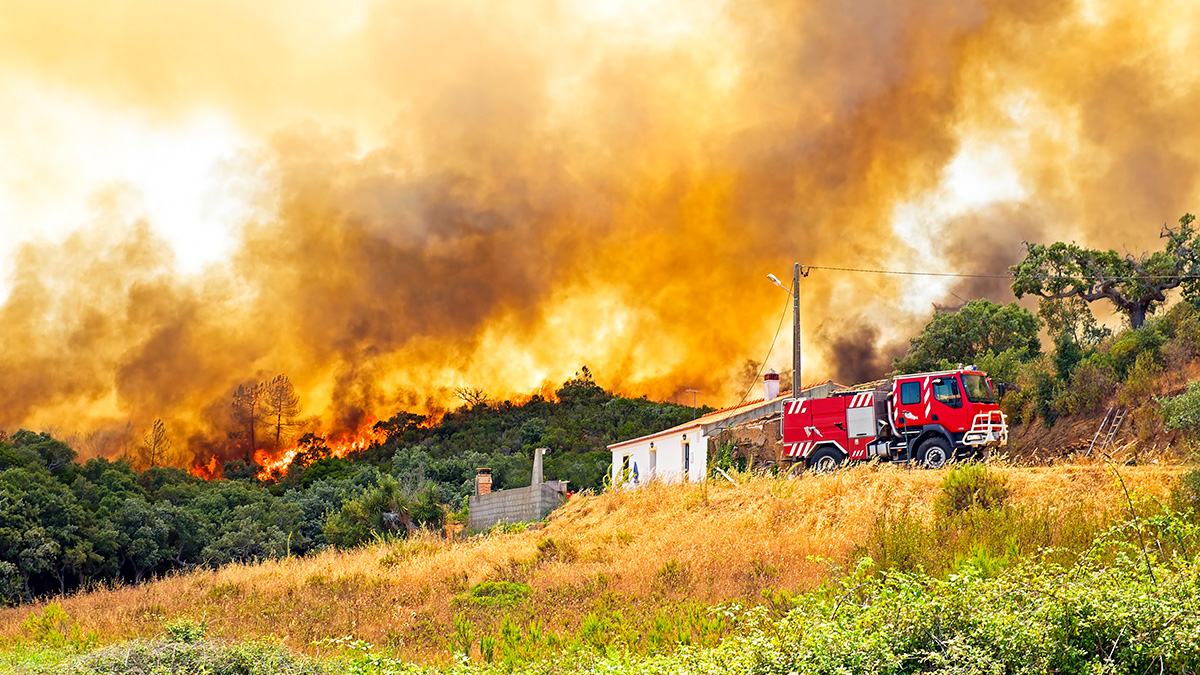
Como os Incêndios e o Clima Afetam a Saúde Pública de Portugal
Os investigadores analisaram os dados para examinar os efeitos dos incêndios florestais, dos poluentes e dos fatores meteorológicos na mortalidade e na saúde cardiovascular no país ibérico.
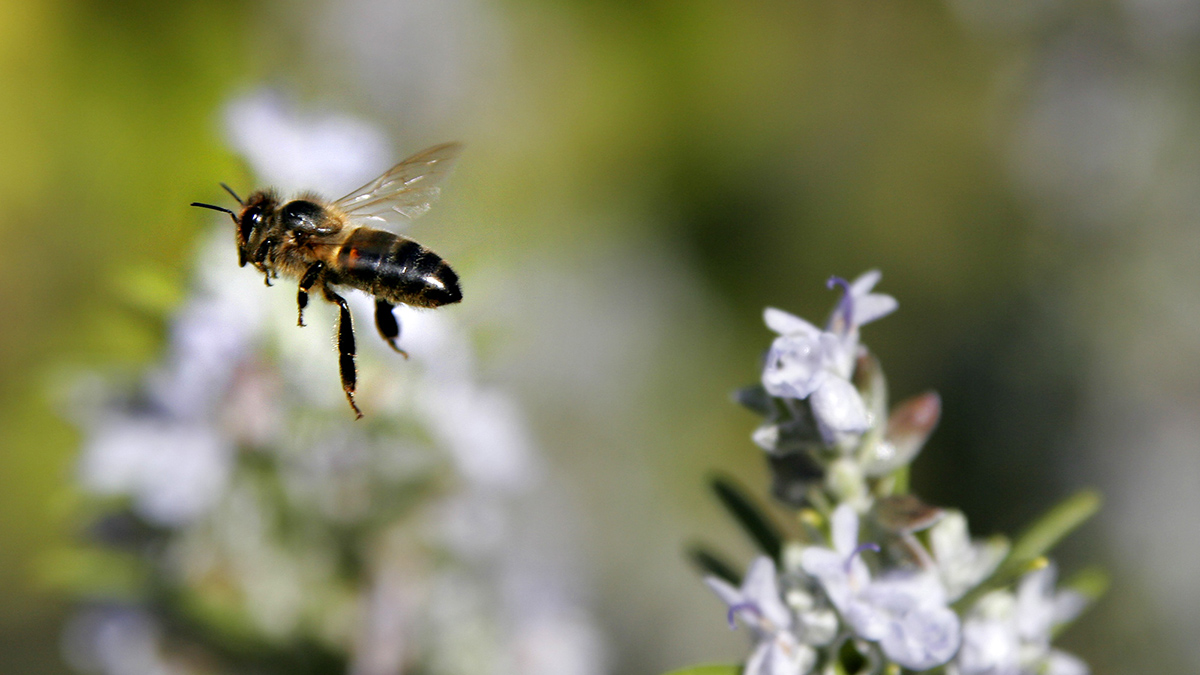
Air Pollution Could Make It Harder for Bees to Navigate
Fine particulate matter in the atmosphere reduces the degree of polarization of sunlight, which insects use to guide themselves home.