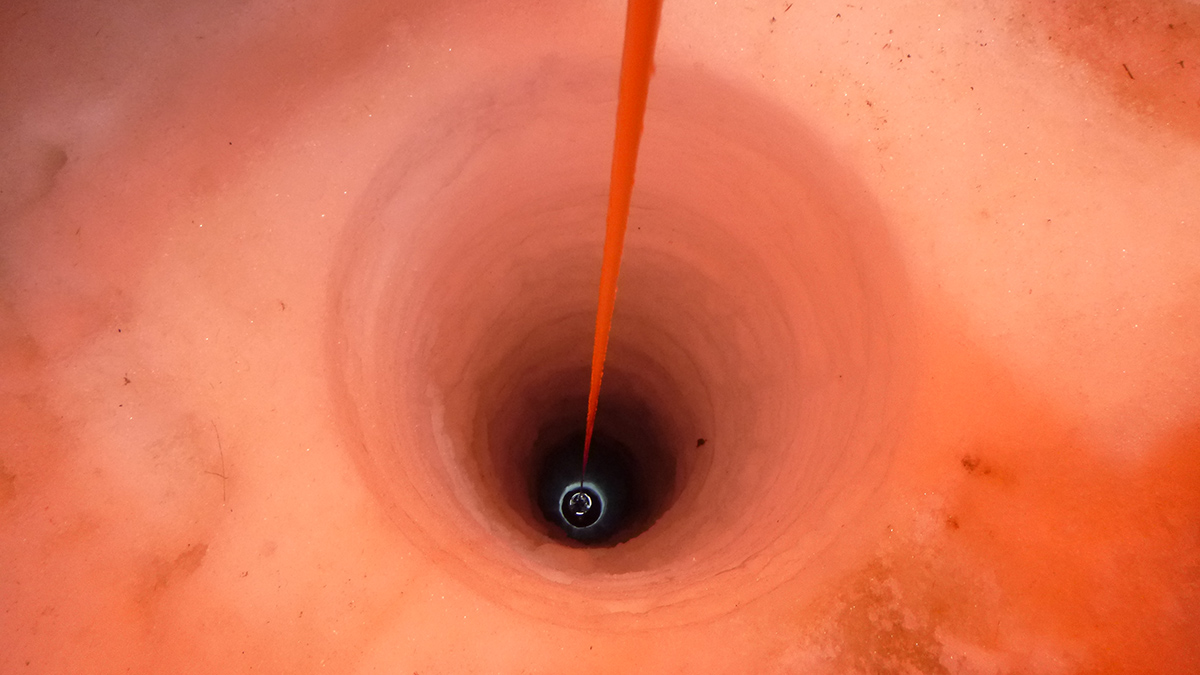
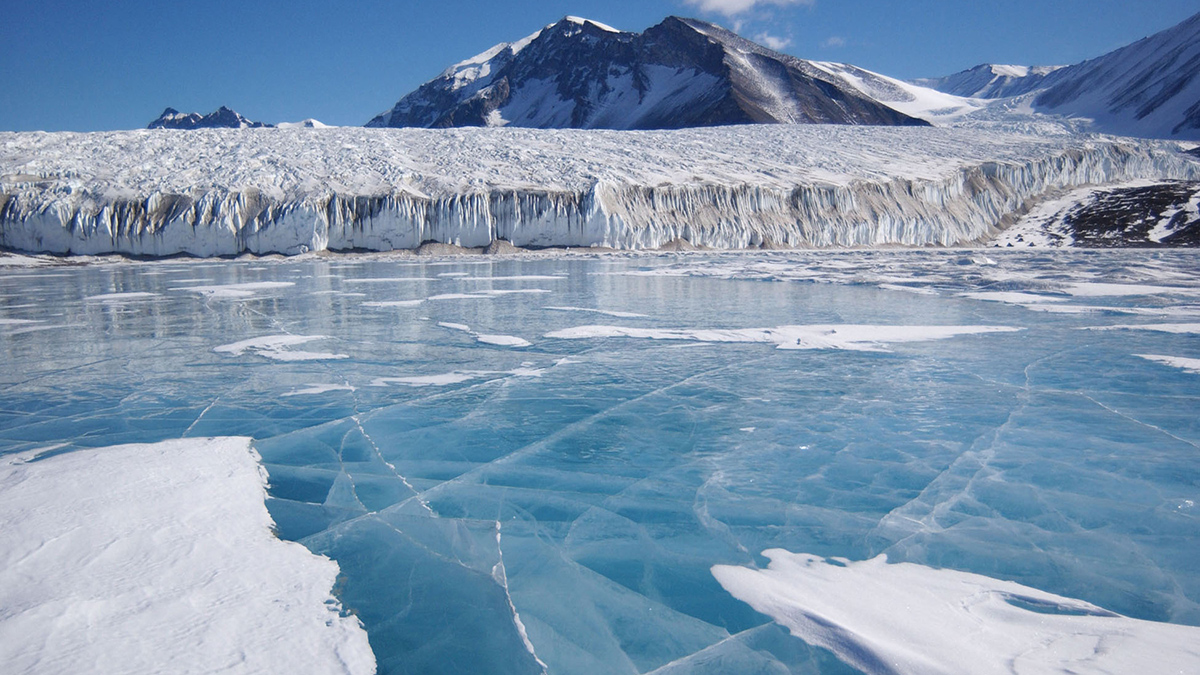
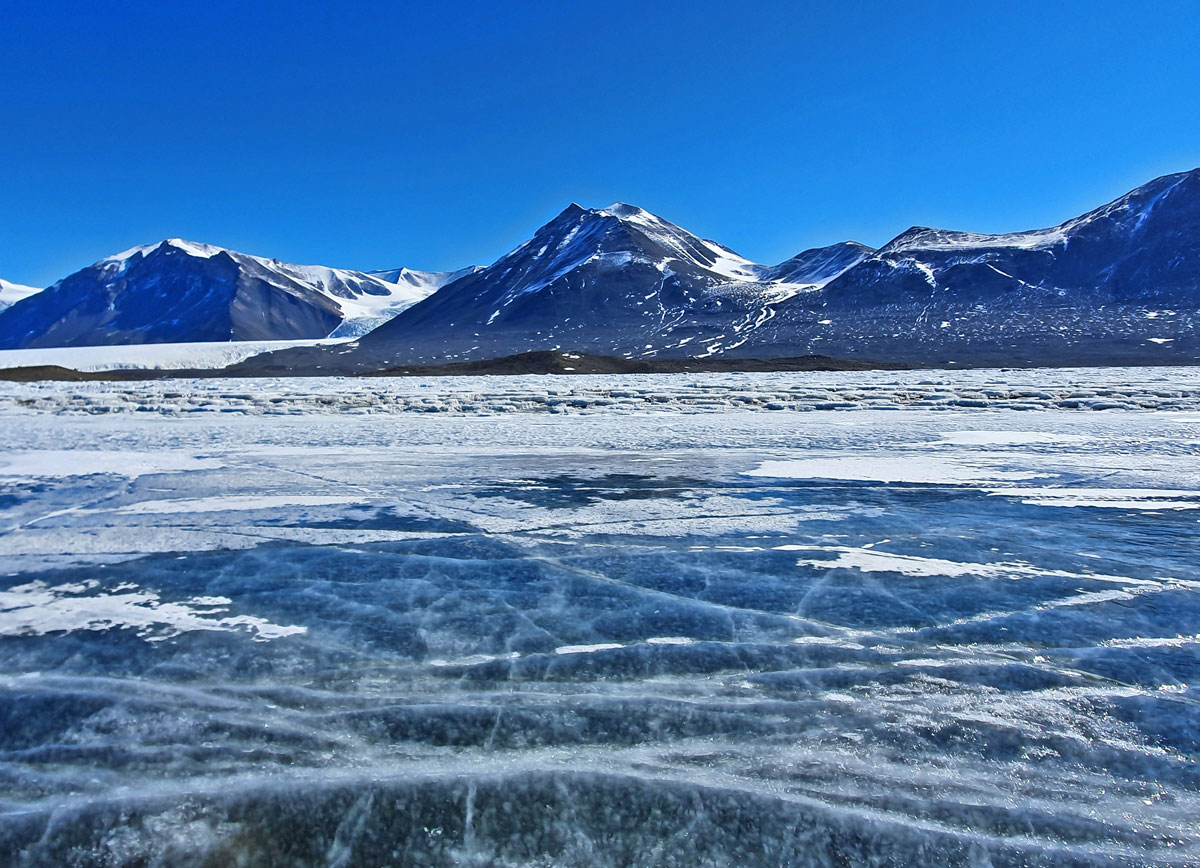
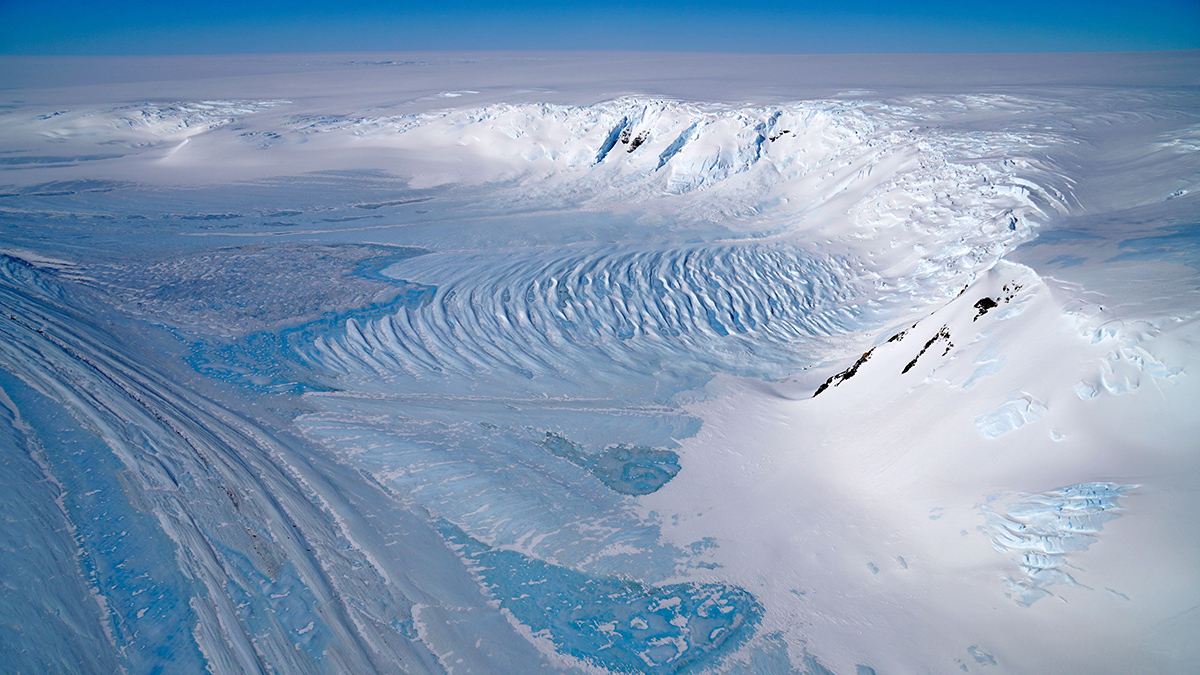
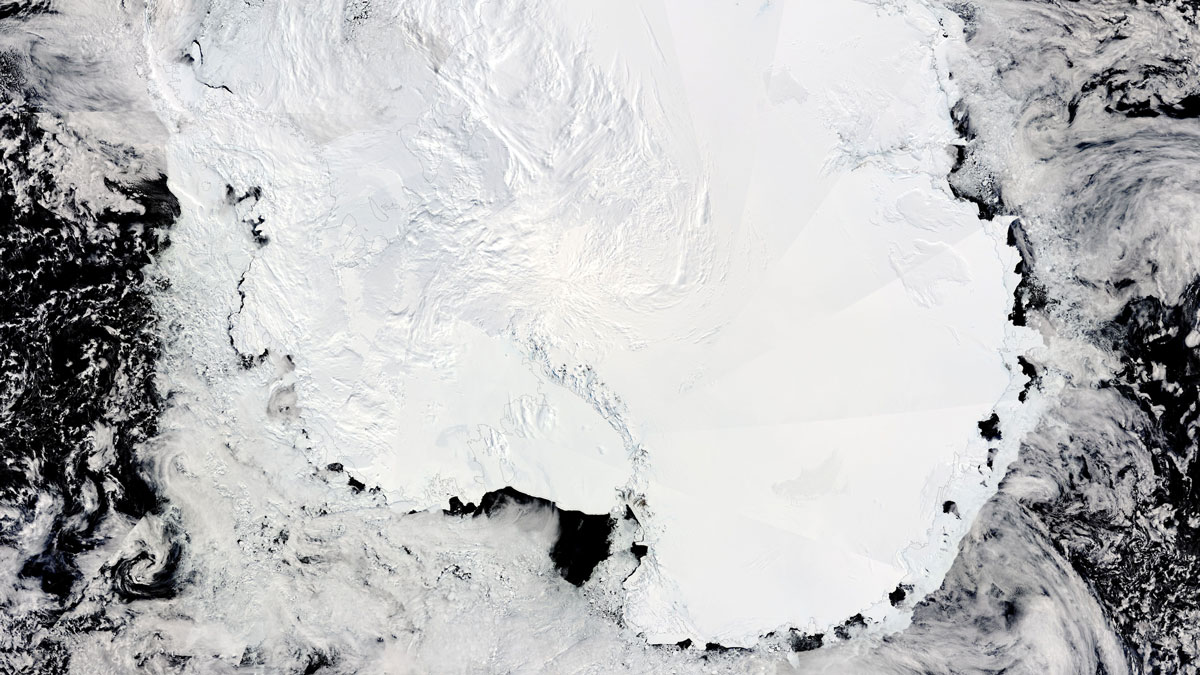
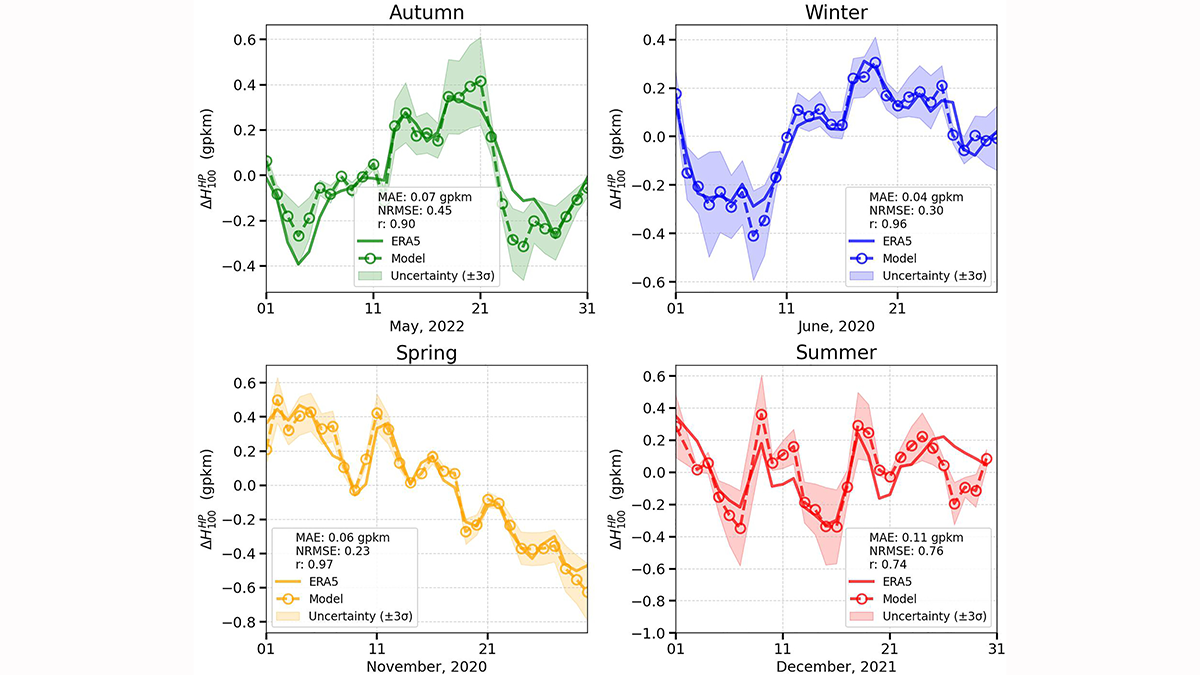
More than 4 years of data from a borehole in the Ross Ice Shelf reveal supercooled water and more.
Antarctica
Antarctic Ice Sheet Has Lost a Connecticut-Sized Amount of Ice Over the Past 30 Years
A new study of Antarctica has found that since 1996, its ice sheet has lost 12,820 square kilometers (nearly 5,000 square miles) of ice—nearly enough to cover the state of Connecticut, or 10 cities the size of Greater Los Angeles.
These South Pole Seismometers Will Detect Vibrations 1.5 Miles Under the Ice
The instruments will freeze into Antarctica’s ice sheet, where they will collect detailed, global-scale seismic data.
Sediments Offer an Extended History of Fast Ice
Scientists used sediments to create a millennia-long archive of Antarctic fast ice. Along the way, they discovered that the freezing and thawing of this enigmatic ice appear to be linked to solar cycles.
Linking Space Weather and Atmospheric Changes With Cosmic Rays
Water-Cherenkov cosmic-ray detectors can be used as a tool for monitoring and studying changes in the lower stratosphere over Antarctica.
Snowball Earth’s Liquid Seas Dipped Way Below Freezing
Iron isotopes show that salty seawater pockets beneath the ice were as cold as −15°C.
The Land Beneath Antarctica’s Ice Might Be Full of Water
Seismic surveys hint at the extent of a potential groundwater system in the White Continent.
New Lessons from Old Ice: How We Understand Past (and Future) Heating
Fragments of blue ice up to 6 million years old—the oldest ever found—offer key insights into Earth’s warming cycles. Researchers are using these ancient data to refine models of our future climate.
Satellite Data Reveal Changing Lakes Under Antarctic Ice
Radar altimetry observations have pinpointed 85 active subglacial lakes, shedding light on how water moves beneath the Antarctic Ice Sheet.