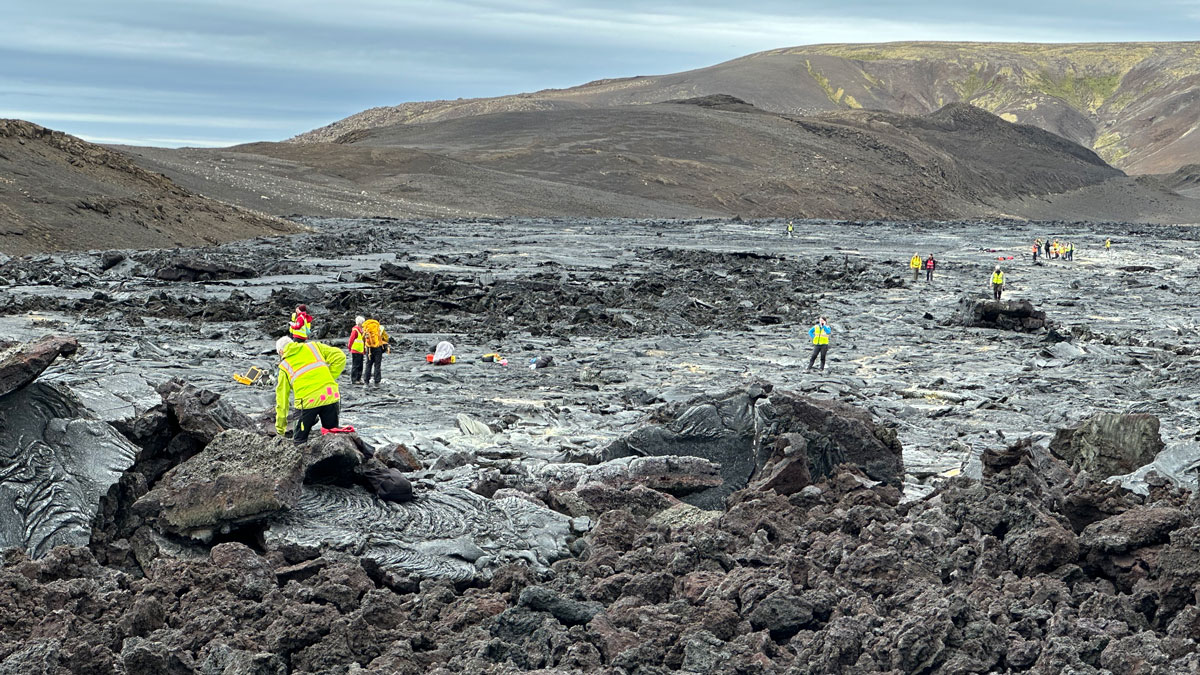
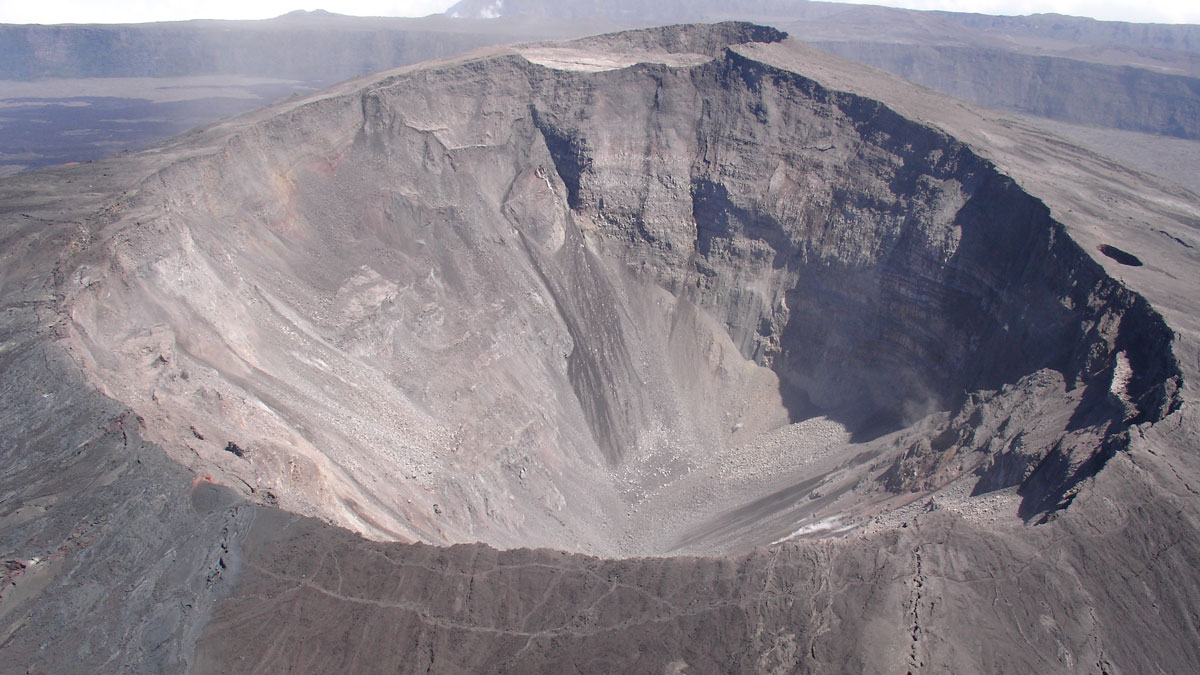
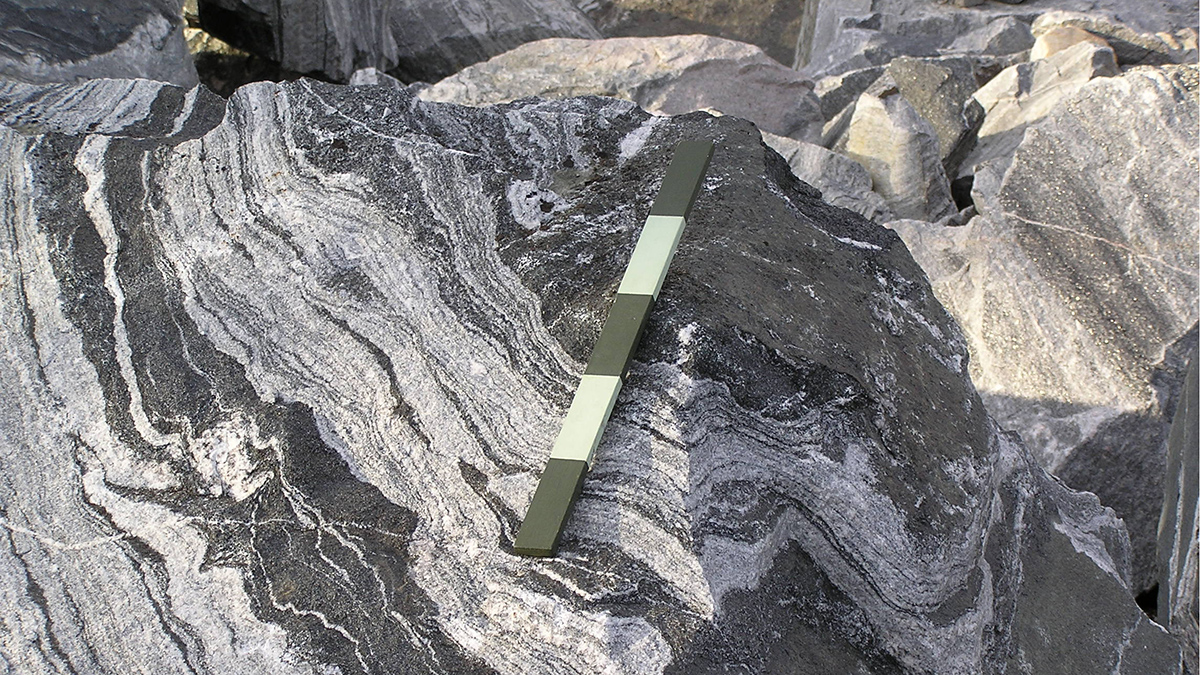
Scientists trekked across Icelandic lava flows that served as stand-ins for Venus’s volcanic landscapes, testing tools and methods the upcoming VERITAS mission will use when it reaches the planet.
basalts
Lessons and Lingering Questions from Collapsing Basaltic Calderas
Research into the hazardous collapses of basaltic volcanoes has revealed common physical processes, but addressing remaining questions requires learning more from historical events.
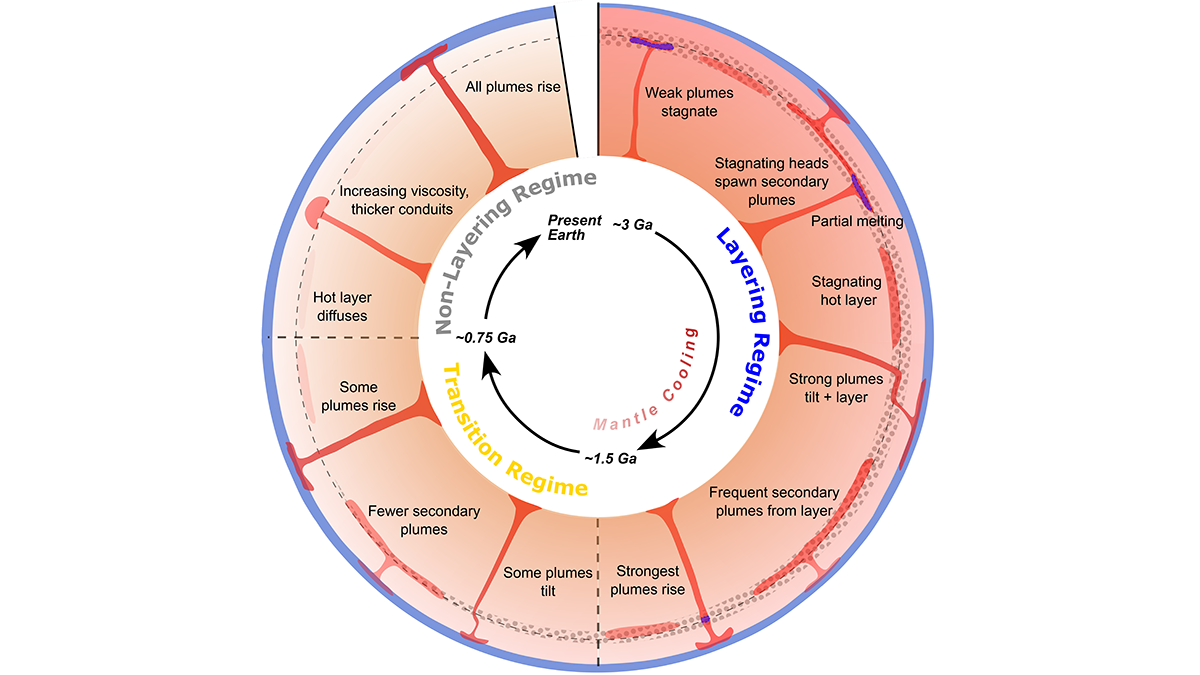
Modeling Mantle Dynamics as the Earth Slowly Cools
An update of the convection code ASPECT enables full coupling of plume dynamics with buoyancy effects of transition zone phase relations, showing how early layering gave way to whole-mantle plumes.
Turning Carbon into Stone: Unlocking Mineralization in Fractured Rock
Carbon mineralization is a promising solution for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions, but we must learn to optimize the complex interplay between reactions and mechanics in fractures to develop a scalable solution.
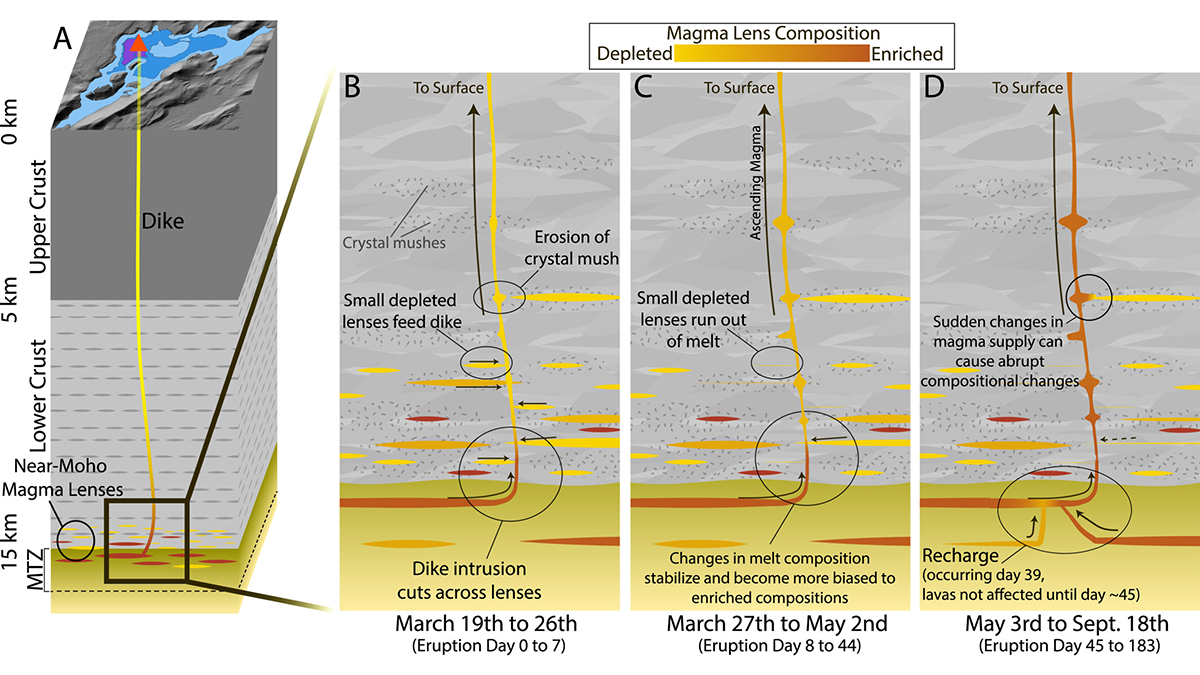
Magma Diversity in Iceland
Iceland’s recent basalt eruptions originated at the crust-mantle boundary and show chemical variability over remarkably short timescales of weeks, suggesting exchanges between diverse magma sources.
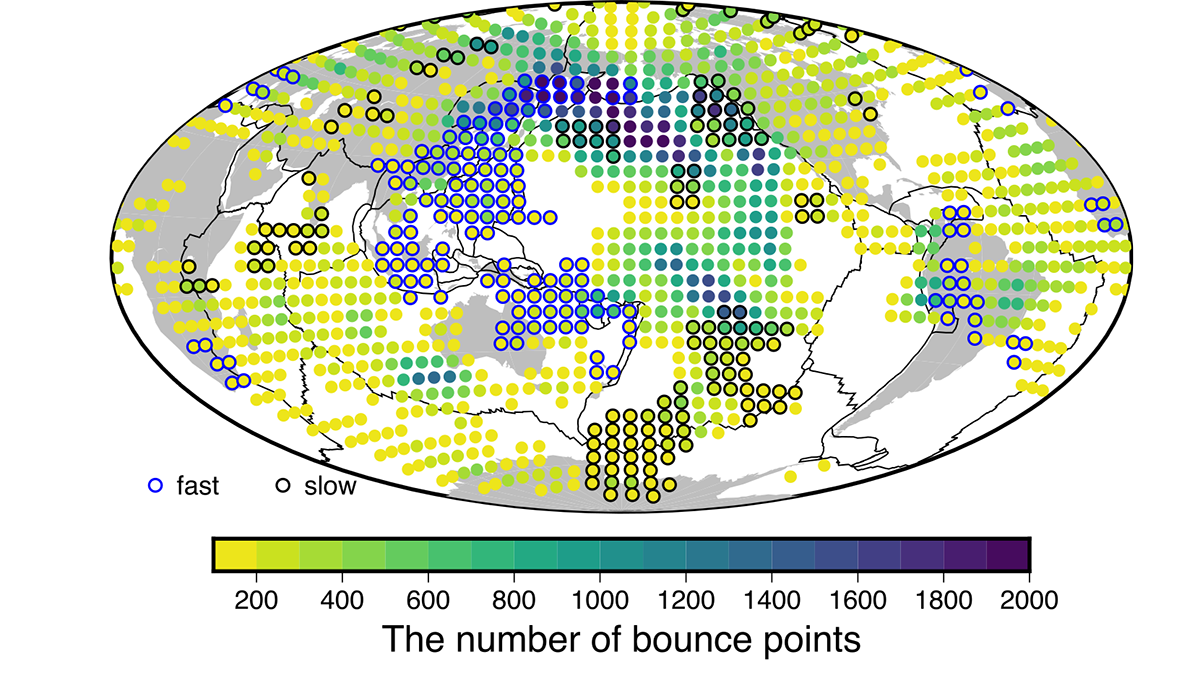
Compositional Anomalies Complicate Our Model of Mantle Convection
A new study expands on recent research which suggests that oceanic crust accumulates in the mid-mantle. The new seismological constraints advance our understanding of thermo-chemical planetary evolution.
Hot Spot Lavas Around the World May Have Something in Common
A global study of lavas from volcanic hot spots suggests that contrary to accepted wisdom, Earth’s deep mantle may have the same composition throughout. Not everyone is convinced, however.
From First Continents to Fancy Countertops
A new study suggests melting gabbros may have helped form Earth’s first continents, riling a long-standing debate.
The Depleted Mantle Merry-Go-Round
Abyssal peridotites show through their isotopic composition a complex history. From differences we can infer the existence of ultra depleted mantle and an uneven contribution to ridge magmatism.
Baked Contacts Focus a Lens on Ancient Lava Flows
Two studies, conducted 40 years apart, show how combining field observations and thermal modeling can reconstruct the history of massive lava flows and how they altered the surrounding landscape.