By analyzing hydrographic information gathered by seals and an undersea glider, researchers found new meltwater currents, as well as a new seafloor trough.
currents
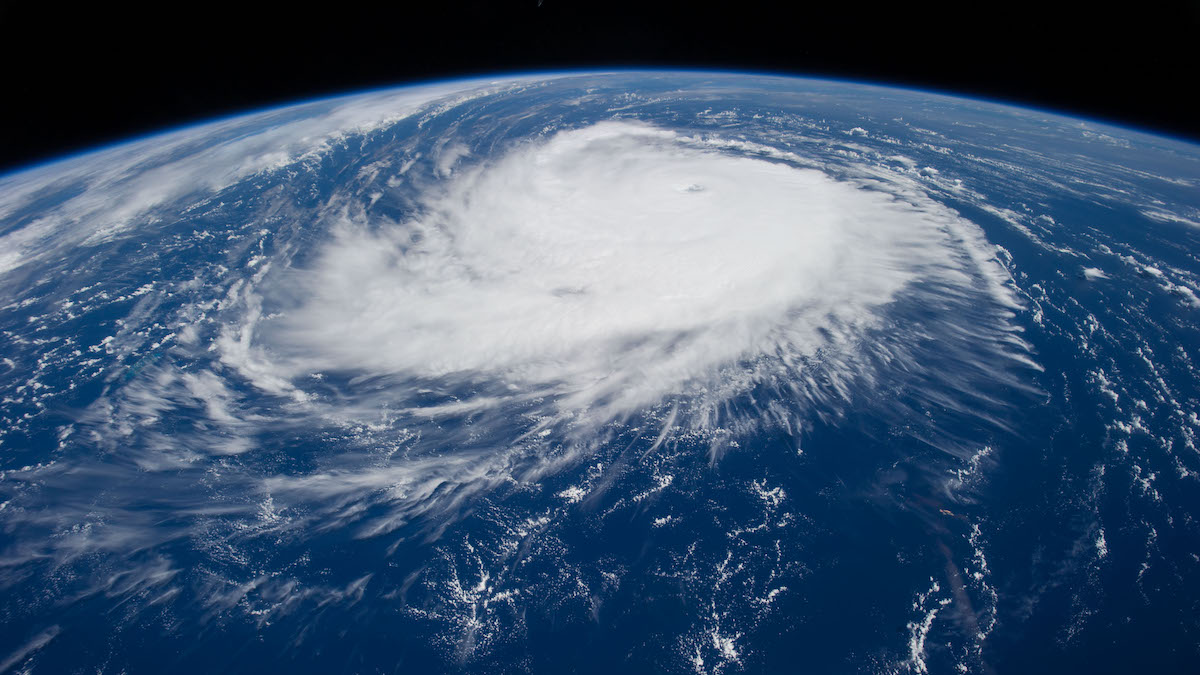
2024 Could Be Among Most Active Hurricane Seasons Ever
A new NOAA report predicts an extraordinarily active Atlantic hurricane season spurred by record ocean temperatures and a shift to La Niña conditions.
Coral Larvae Journey Far and Wide in the Western Indian Ocean
Researchers mapped coral reef connectivity across the Seychelles archipelago to inform conservation efforts in the face of climate change.
Verifying the Mathematics Behind Ocean Modeling
A series of test cases designed to confirm the accuracy of ocean models could help improve our understanding of large-scale climate processes.
Melting Ice in the Polar North Drives Weather in Europe
Influxes of meltwater into the North Atlantic eventually lead to warmer and drier conditions over Europe.
Mars as a Driver of Deep-Sea Erosion
An analysis of breaks in deep-sea sediment links the geological record to a 2.4-million-year cycle that heats Earth and ventilates our oceans.
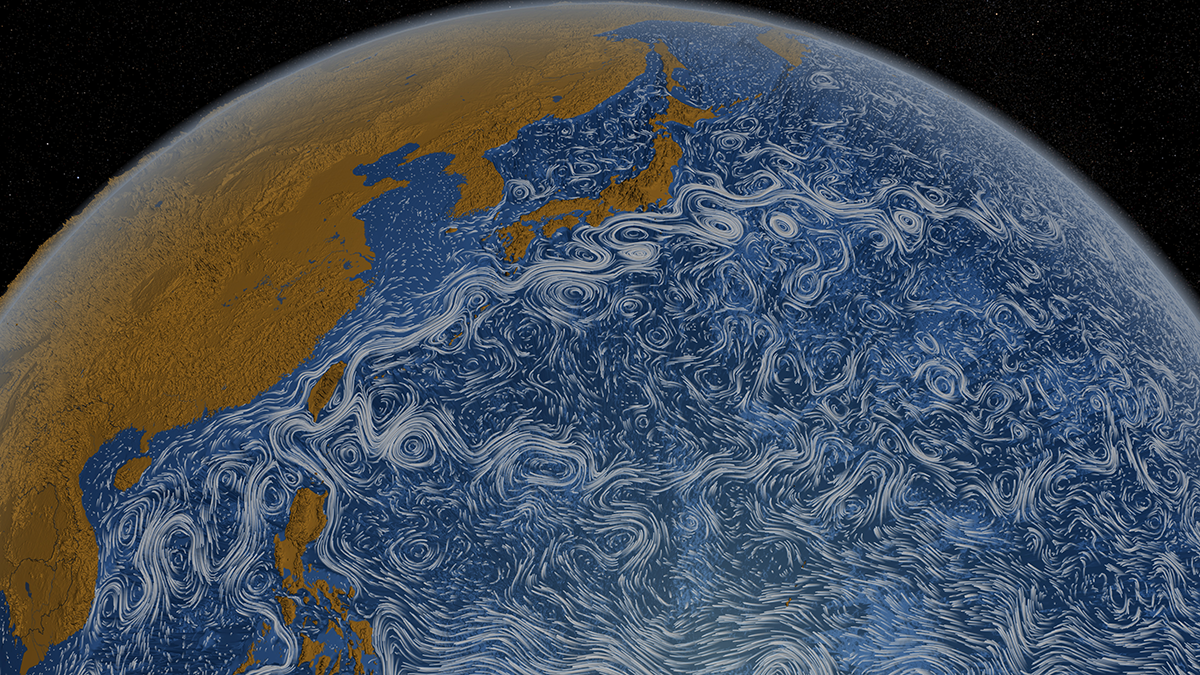
Mapping the Ocean’s Motion Energy
The ocean is a central component of Earth’s climate system. But it is in perpetual motion, and understanding the transfer of kinetic energy is key to better ocean models.
Step Aside, Internal Tides: Supercomputer Modeling Improves Satellite Altimetry Precision
New supercomputer models can provide valuable information about the ocean’s layers and movements, particularly slow moving features such as eddies and currents.
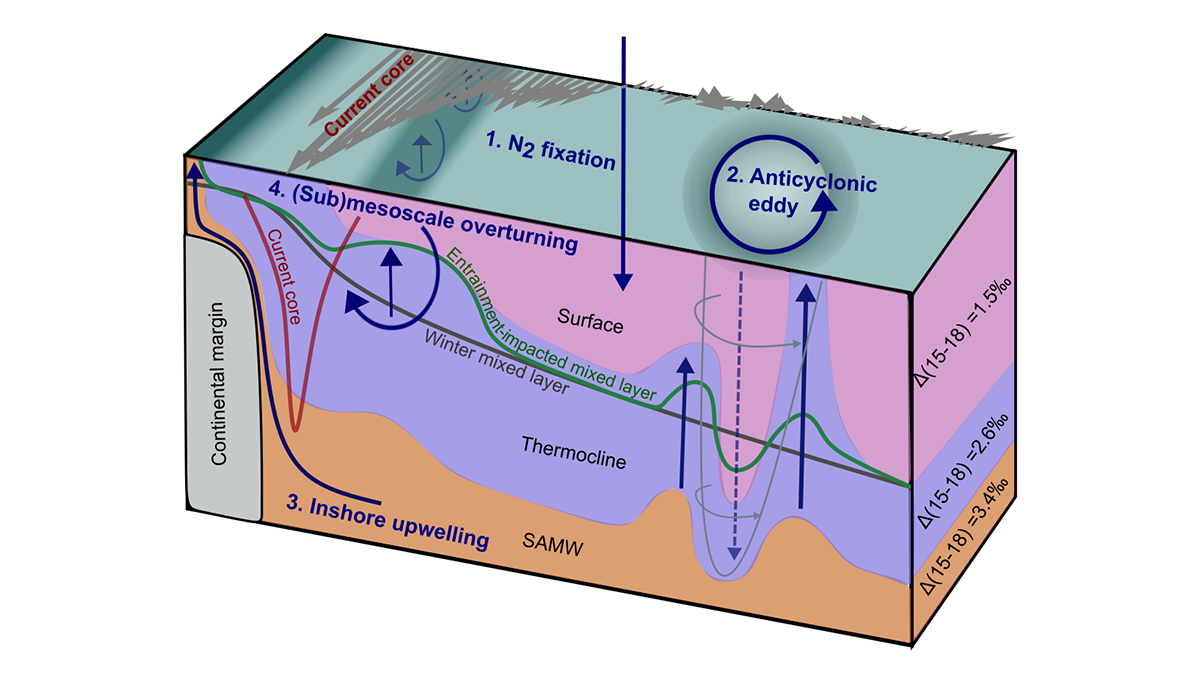
How Nutrients Get Back Up to the Surface Ocean
A new dual isotope tracer technique is used to assess the role of a number of poorly understood nutrient supply mechanisms fueling biological productivity in the ocean.
Nutrients at Depth Can Be Uplifted by the Kuroshio Large Meander
Aperiodic, southward deflection of the Kuroshio, a.k.a. the Kuroshio large meander, uplifts the nutrients in deep layers to induce offshore phytoplankton bloom.