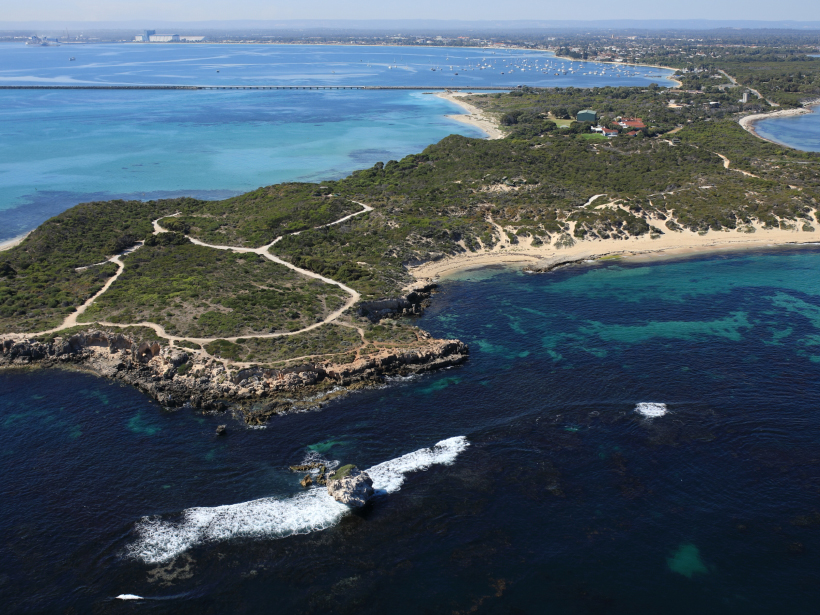
A field survey in Australia links rugged seafloor terrain to erosion-causing waves.
erosion & weathering
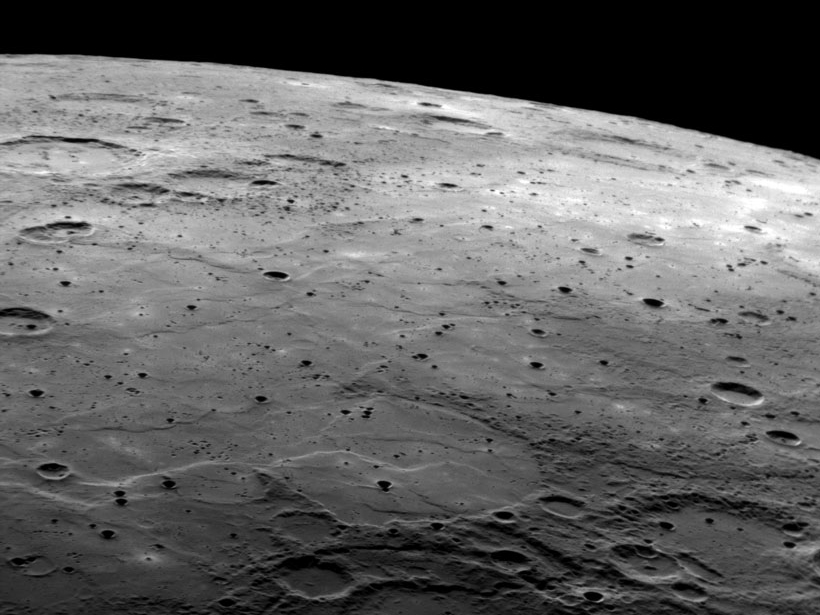
How Quickly Is Mercury’s Surface Evolving?
New measurements of impact craters on Mercury’s smooth plains suggest that the topography of the solar system’s innermost planet is changing at twice the rate of landforms on the Moon.
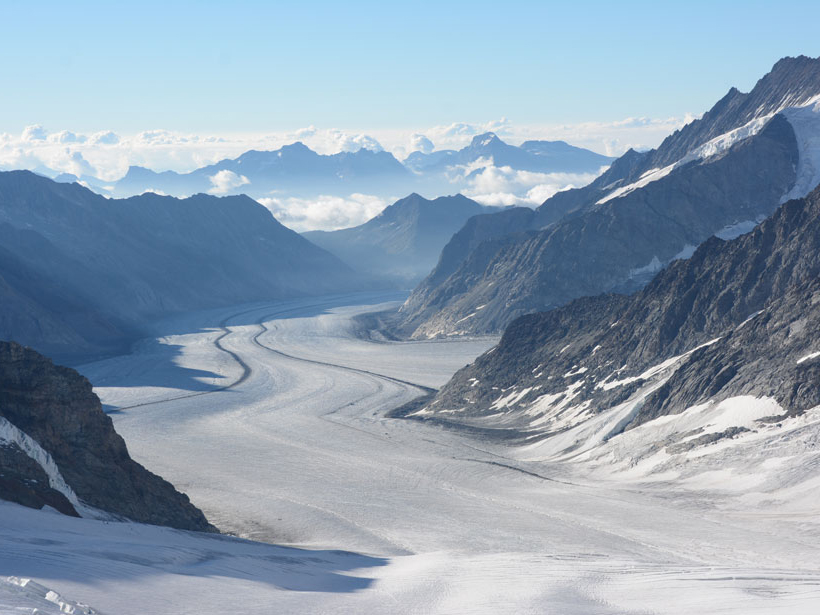
Cosmic Muons Reveal the Land Hidden Under Ice
Scientists accurately map the shape of the bedrock beneath a glacier using a new technique.
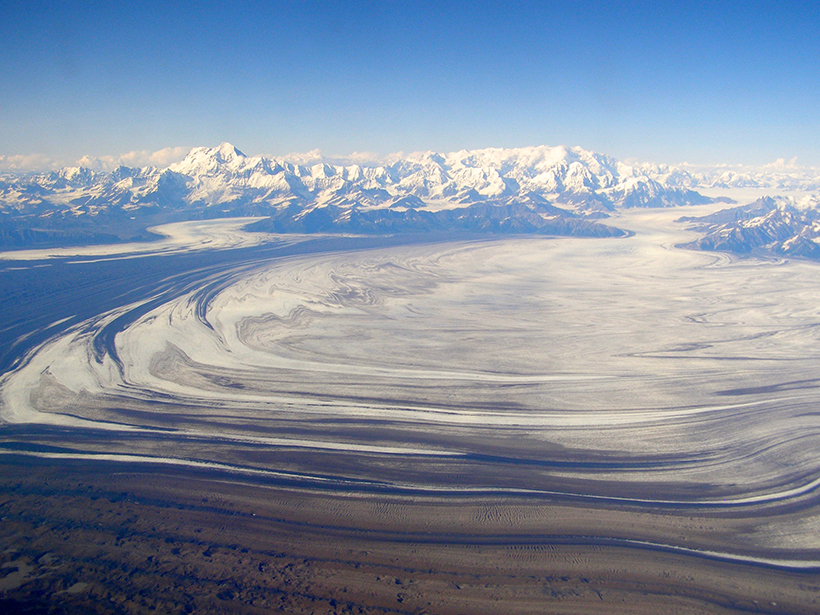
A Mountain Range's History Preserved in Ocean Sediments
Fission track dating core samples from the Gulf of Alaska demonstrates that offshore sediments can be used to reconstruct a mountain range's changing exhumation patterns.
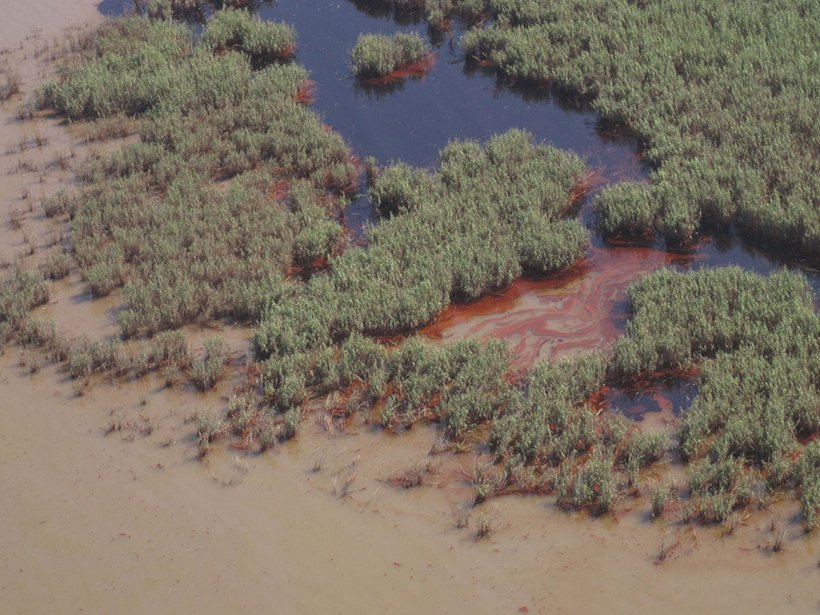
Oil Residues Accelerate Coastal Wetland Losses
Coastal wetland loss after an oil spill can be more extensive than after a hurricane.
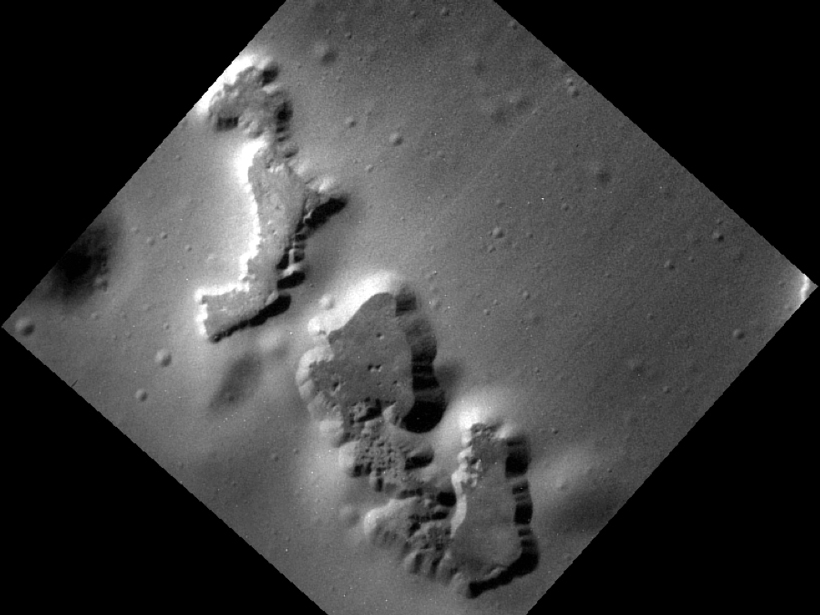
Unprecedented Views of Mercury Constrain Hollow Formation
The consistently shallow depths of the depressions scattered across Mercury's surface suggest their morphology is not determined by the thickness of a volatile-rich outer layer.
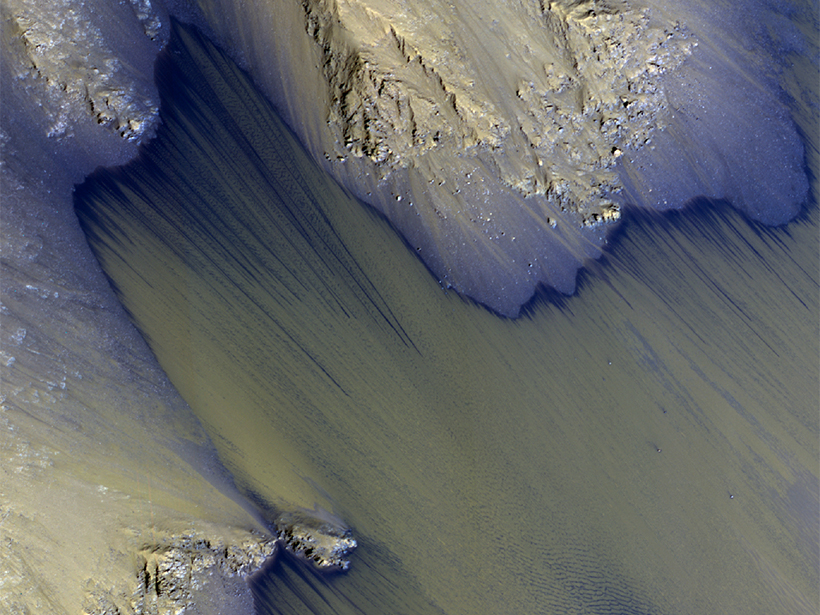
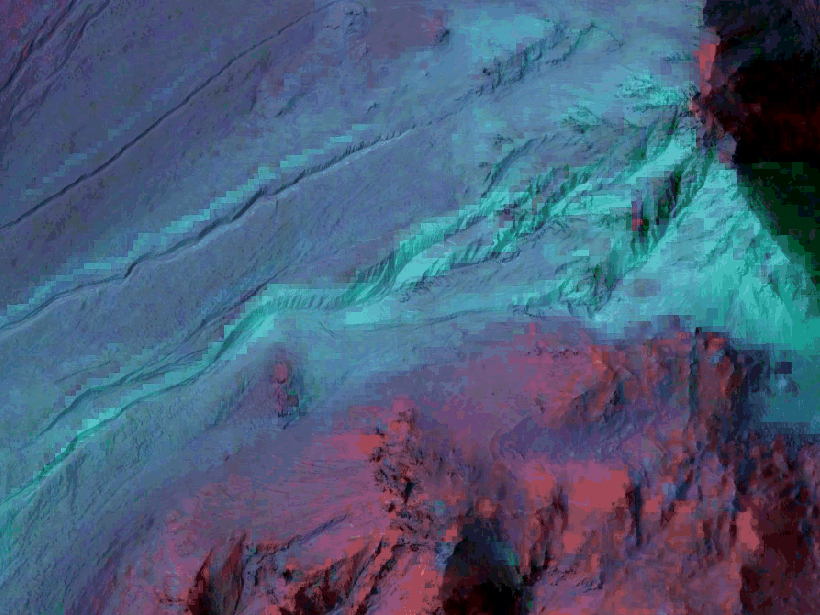
How Do Gullies Form on Mars?
New orbiter data support an important role for seasonal frost—not liquid water—in the formation of Martian gullies.
Minerals Hint at Liquid Groundwater, More Oxygen in Mars's Past
Manganese deposits in Gale Crater fractures are similar to Earth features that usually require flowing water and highly oxidizing conditions.
Reconstructing Catastrophic Floods on Earth and Mars
A new theoretical model suggests that ancient floods that carved canyons on Earth and Mars may have been much smaller but lasted longer than previously thought.
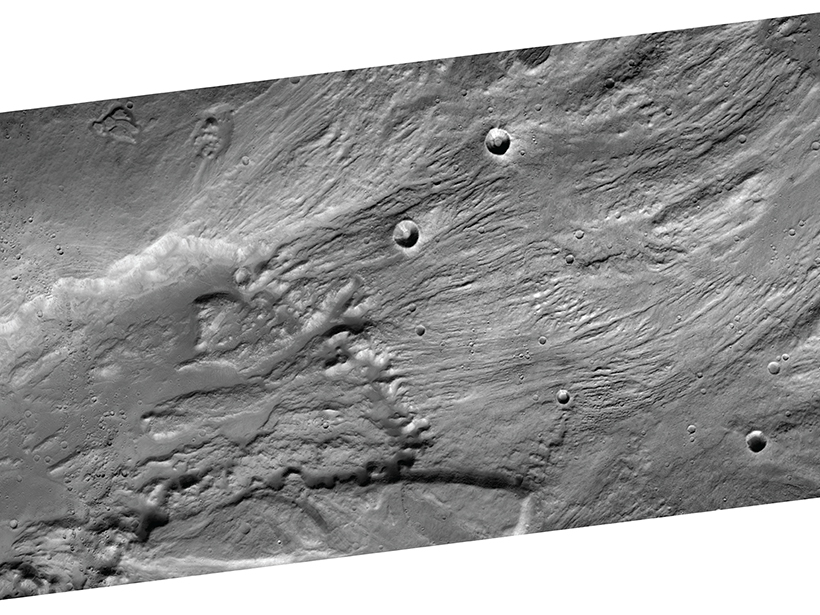
A Cluster of Water Seeps on Mars?
The discovery of dense concentrations of recurring flowlike features in two Valles Marineris chasms could aid in the search for life and influence future exploration of the Red Planet.