Trace elements in coral reefs provide a timeline of how Borneo’s rainforests have been altered by industry.
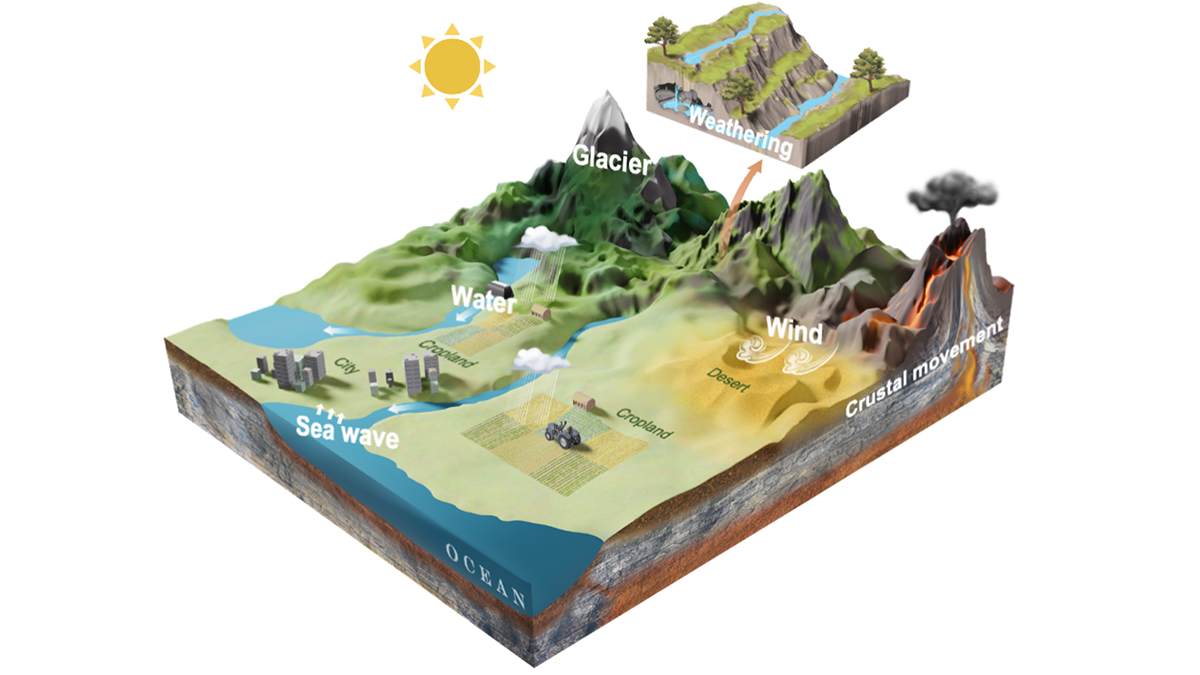
erosion & weathering
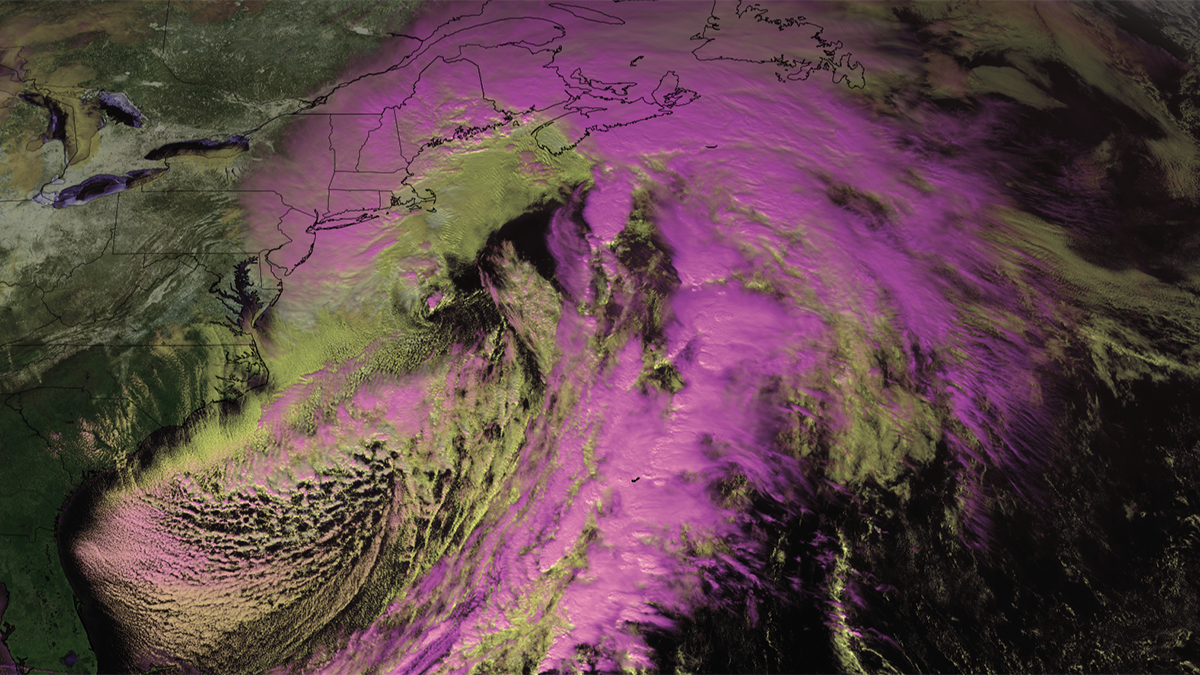
New Research Shows More Extreme Global Warming Impacts Looming for the Northeast
One new study identifies a 17% increase in the destructive potential of the strongest nor’easters, while another bolsters links between Arctic ice melt and dangerous blizzards.
Deep Root Respiration Helps Break Down Rocks
The carbon dioxide that results from respiration in and around deep roots is an essential component in the chemical weathering of sandstone rock soils.
Fallowed Fields Are Fueling California’s Dust Problem
New research shows that unplanted agricultural lands are behind most of the state’s anthropogenic dust events.
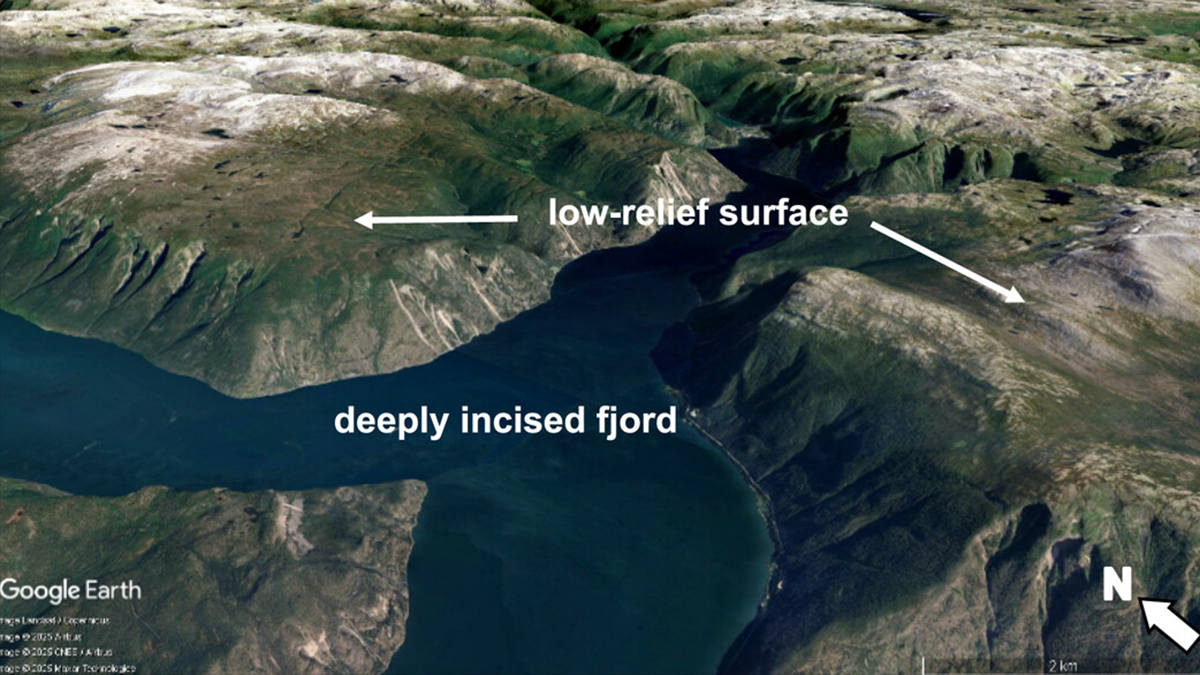
High Relief, Low Relief — Glaciers Do It All
Contrary to conventional wisdom that glaciers just carve landscapes, they can also form low-relief surfaces by sheltering rock from erosion, enriching understanding of how mountain landscapes evolve.
Compost and Biochar Could Boost Carbon Sequestration by Crushed Rock
Crushed rock additives may also help decrease soil emissions of other greenhouse gases, such as nitrous oxide and methane.
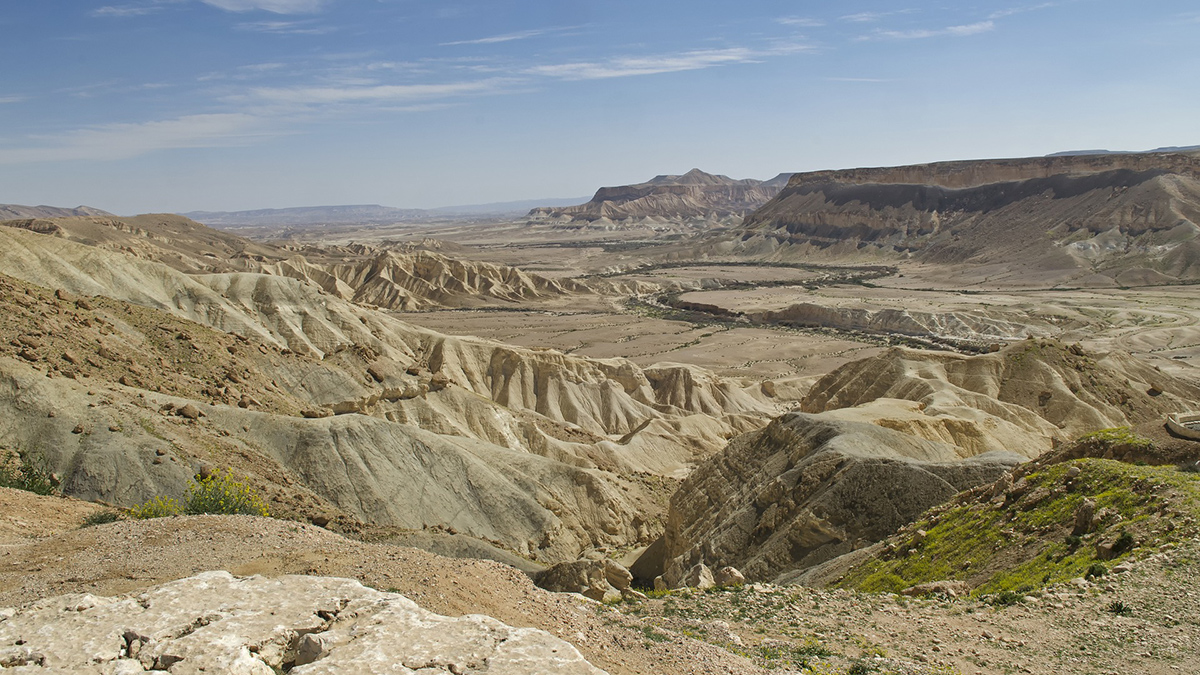
Climate Shifts Drive Episodic Drainage Changes
Drainage divide migration is influenced by tectonics and climate over long periods. New research in Israel shows that even shorter-term wet-dry cycles can move divides.
Erosion: An Overlooked Contributor to the Carbon Cycle
Since physical and chemical erosion yield comparable carbon fluxes, studying both together is essential to avoid biases in erosion-driven carbon flux estimates.
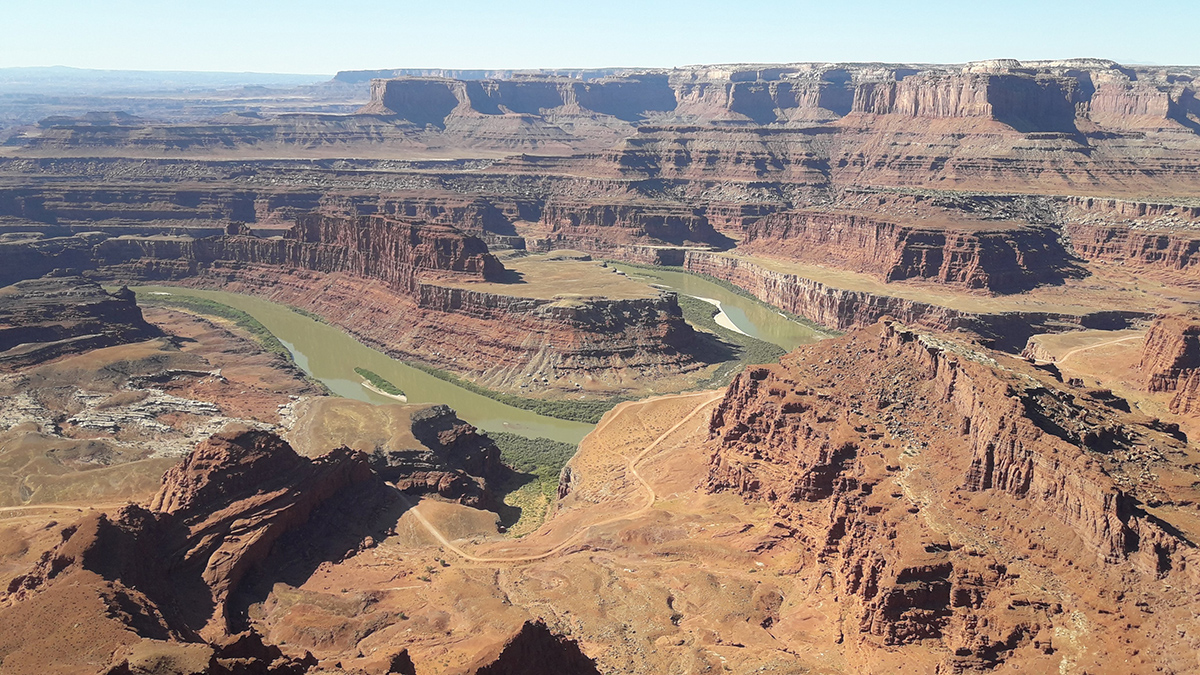
How Rivers Carved the Canyons of the Central Colorado Plateau
A new study offers insights into a puzzling piece of the geological history of the Grand Canyon and surrounding regions.
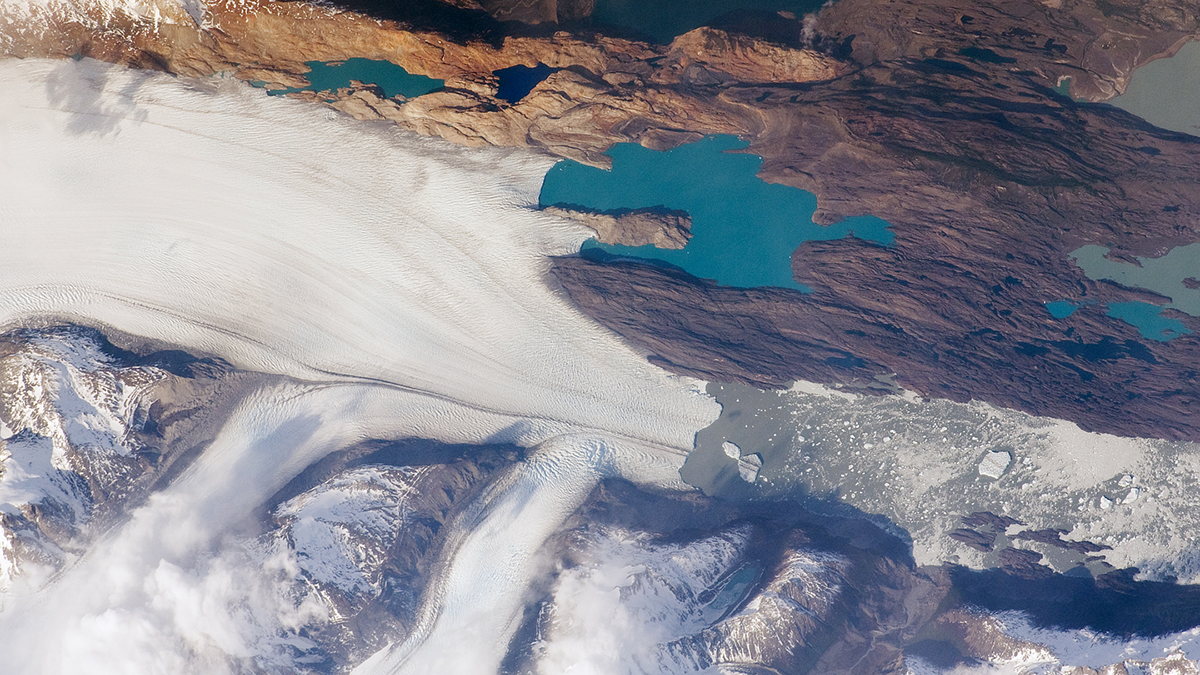
The Pulsed Pace of Glacial Erosion
New data from Lago Argentino, Patagonia reveal that glacial erosion occurs in discrete pulses, which challenges previous ideas that erosion rates have increased over time due to climate change.