Une nouvelle étude, la première dans son genre, suggère qu’il serait possible de recourir à une analyse isotopique pour localiser les sources et les puits de chlorométhane dans l’atmosphère.
everything atmospheric
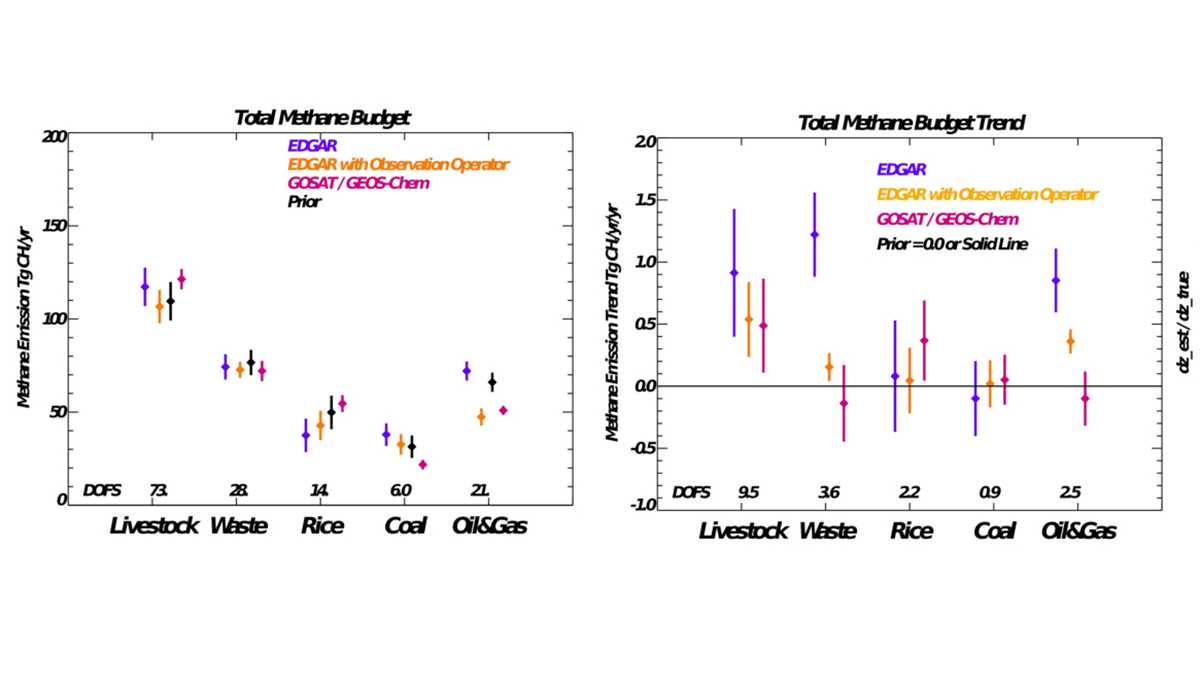
Using Bayesian Estimation to Improve Methane Inventories
A Bayesian, optimal estimation evaluation of state-of-the-art methane inventory with satellite-based emissions from 2009 to 2018 finds substantial differences for livestock, rice, and coal emissions.
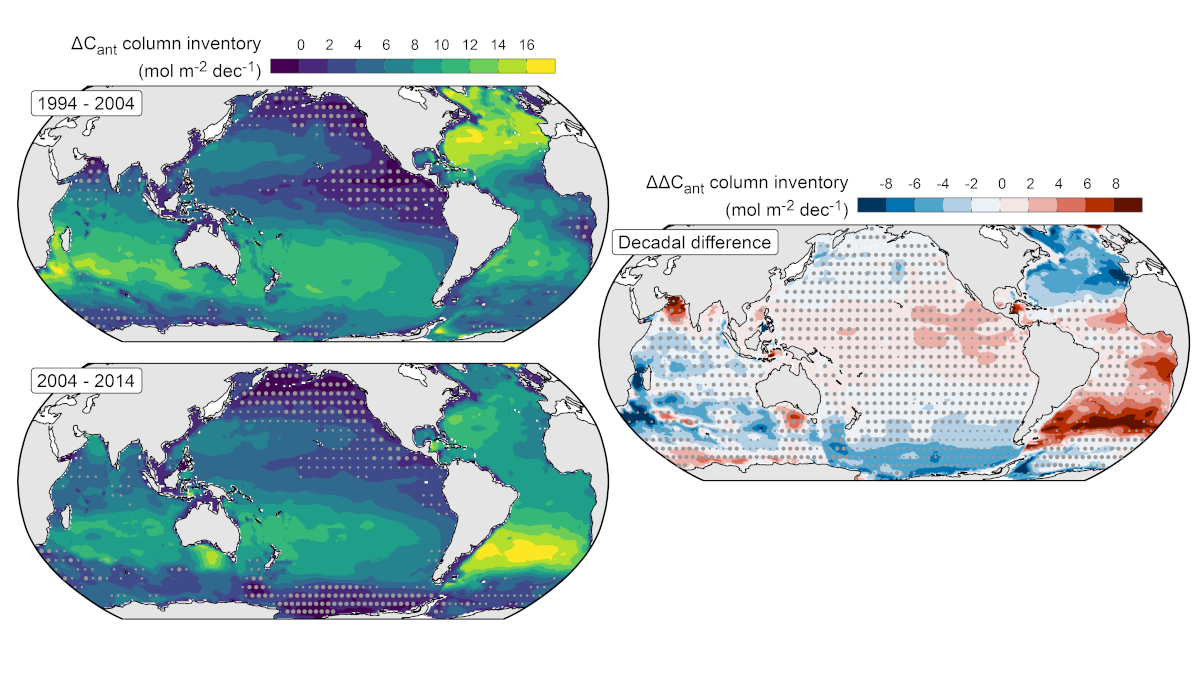
A Multidecadal View of Oceanic Storage of Anthropogenic Carbon
A decline in the ratio of ocean carbon accumulation to atmospheric carbon dioxide growth between 1994-2004 and 2004-2014 suggests a reduction in the sensitivity of the ocean carbon sink.
Lightning-Caused Wildfires are 80 Percent More Likely Under Dry Vegetation
Mimicking a randomized control trial of wildfires, scientists use satellites to uncover the key role of vegetation dryness in wildfire risk, aiding wildfire management and preparedness in California.
Family Trees Clarify Relationships Among Climate Models
A new genealogy based on similarities in the computer codes of different climate models could improve studies that combine projections from multiple models.
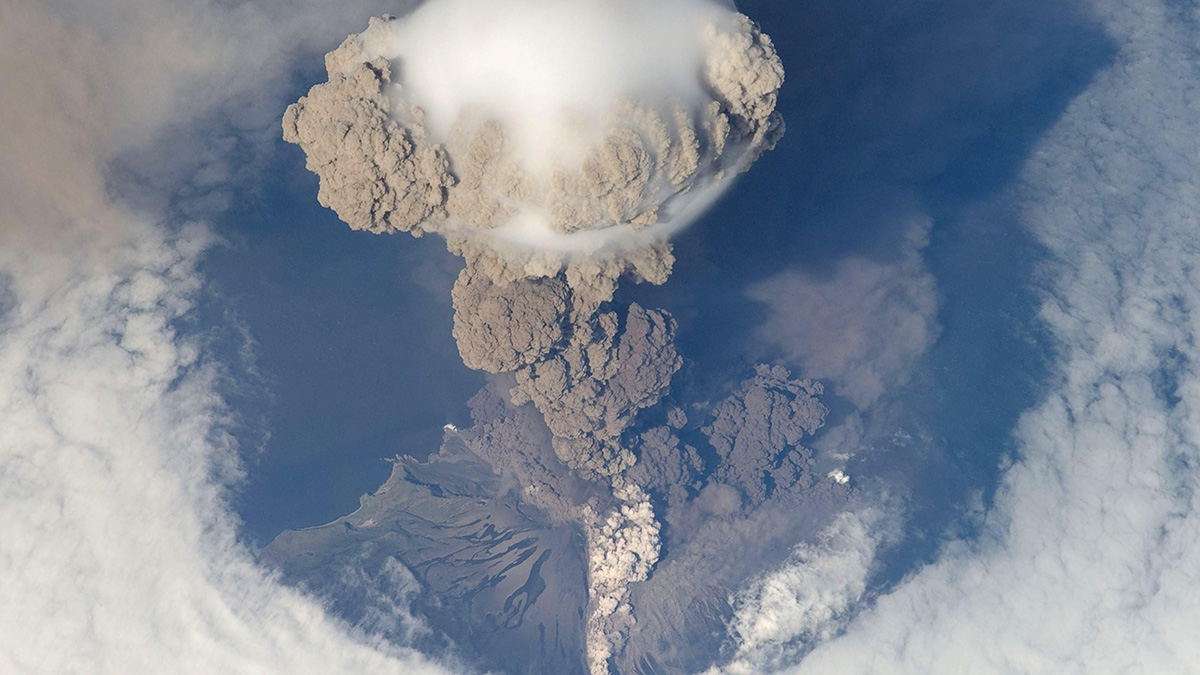
Volcanoes’ Future Climate Effects May Exceed Standard Estimates
Future releases of sulfur dioxide from volcanoes will likely be higher than the reconstructed historical levels currently used for climate predictions.
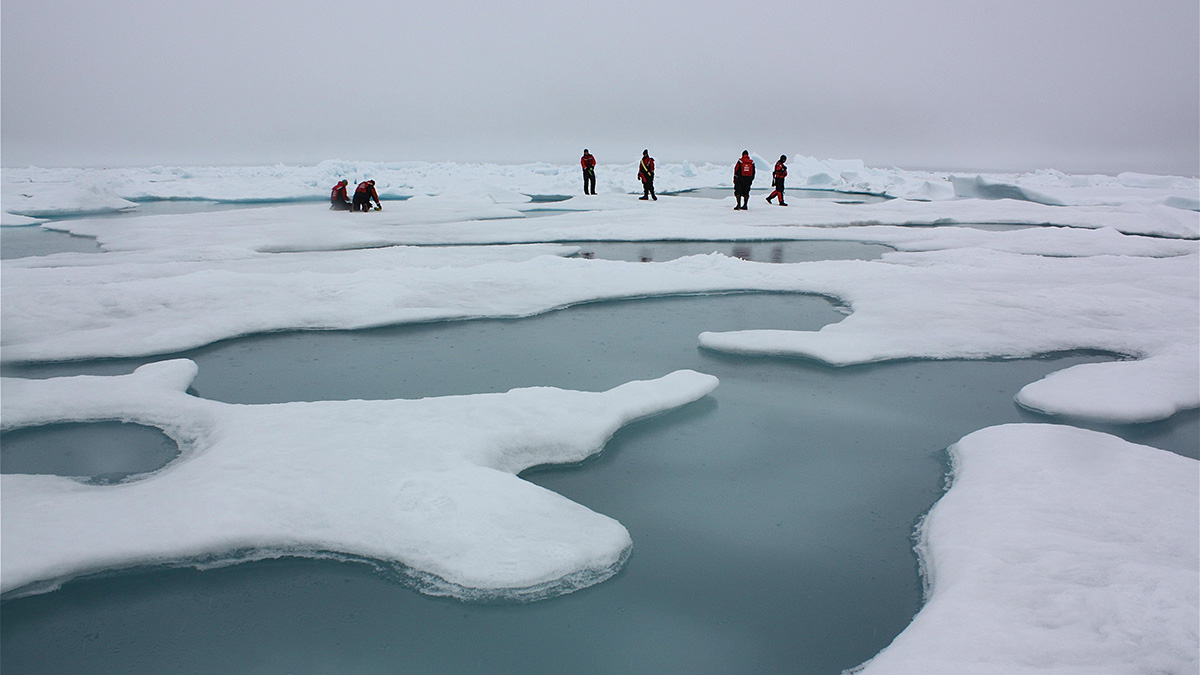
Sea Ice Is Going, but When Will It Be Gone?
A pair of studies demonstrate the uncertainty over when the Arctic will become seasonally sea ice free.
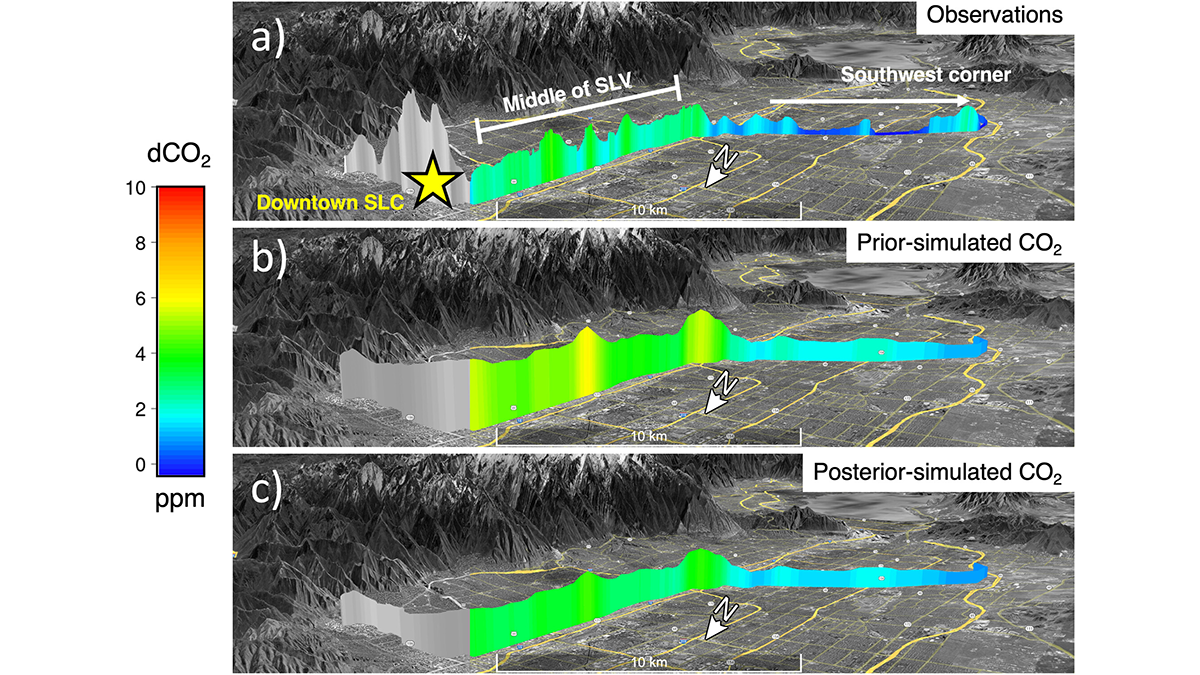
Tracking Human CO2 Emissions from Medium-Sized Cities
Atmospheric inverse models, combined with observations, successfully tracked modest CO2 emission reductions in Salt Lake City during the first COVID-19 lockdown in 2020.
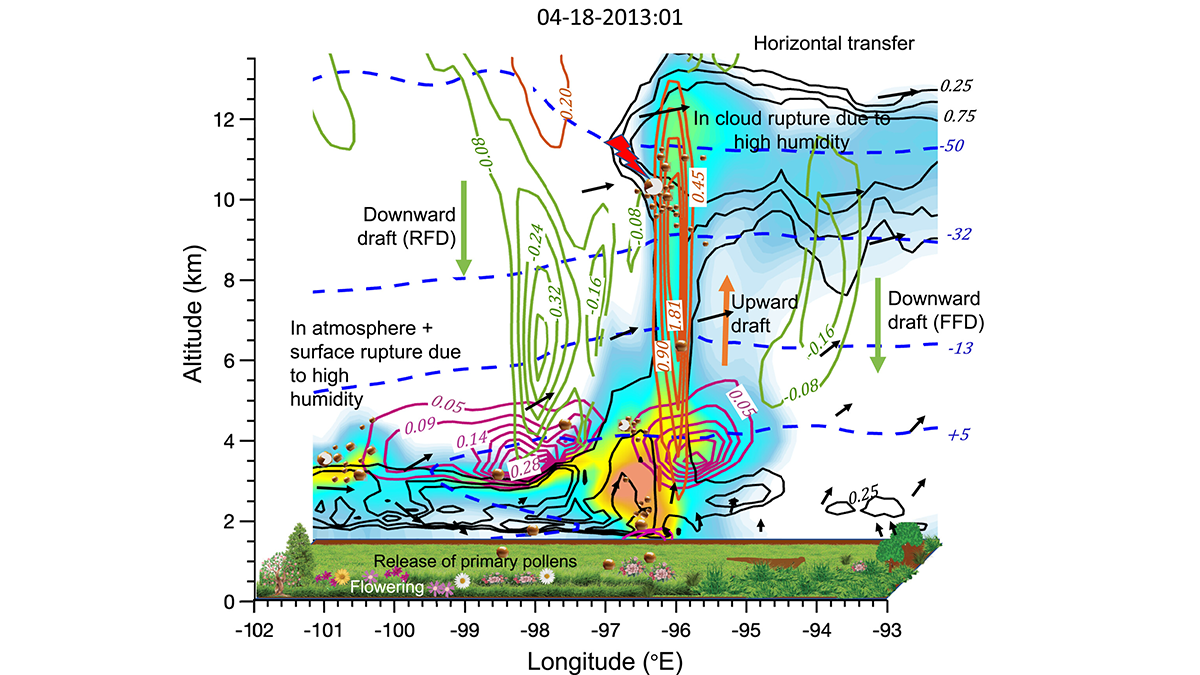
Simulating the Journey of Pollen in the Atmosphere
A new study couples an emission and transport scheme of pollen from vegetation, and explores pollen’s evolution in different atmospheric conditions and its impacts on clouds and precipitation.
The Nitty-Gritty Forces That Shape Planetary Surfaces
Scientists are coming up with ingenious ways to compare terrestrial sand dunes, dust storms, and rain with their counterparts on Mars and Titan.