A study of “weird” Australian rocks suggests stores of niobium rose to the surface during the breakup of the supercontinent Rodinia.
geochronology
Cave Deposit Links Greenland’s and Europe’s Climate Records with a German Volcano
Dating a late Pleistocene eruption has big implications for understanding the Younger Dryas—and current climate change.
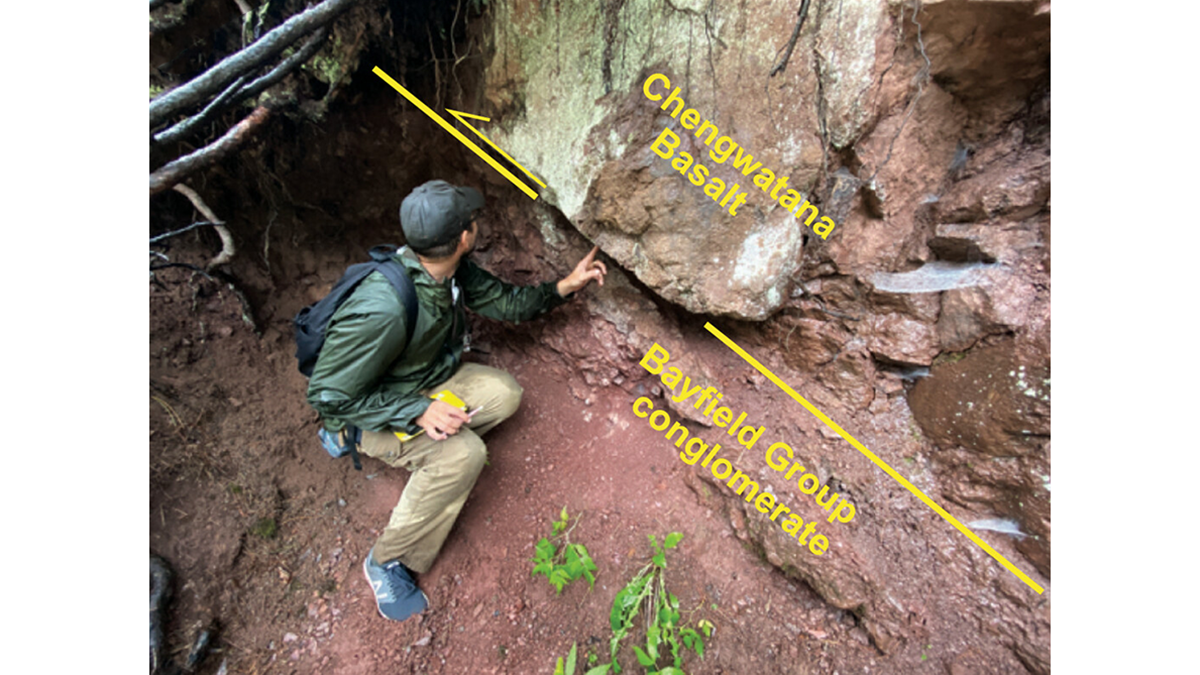
Structural Inversion of an Intracratonic Rift System in Deep Time
A new study reconstructs how an ancient North American rift system was uplifted in space and time due to subsequent continent-continent collision.
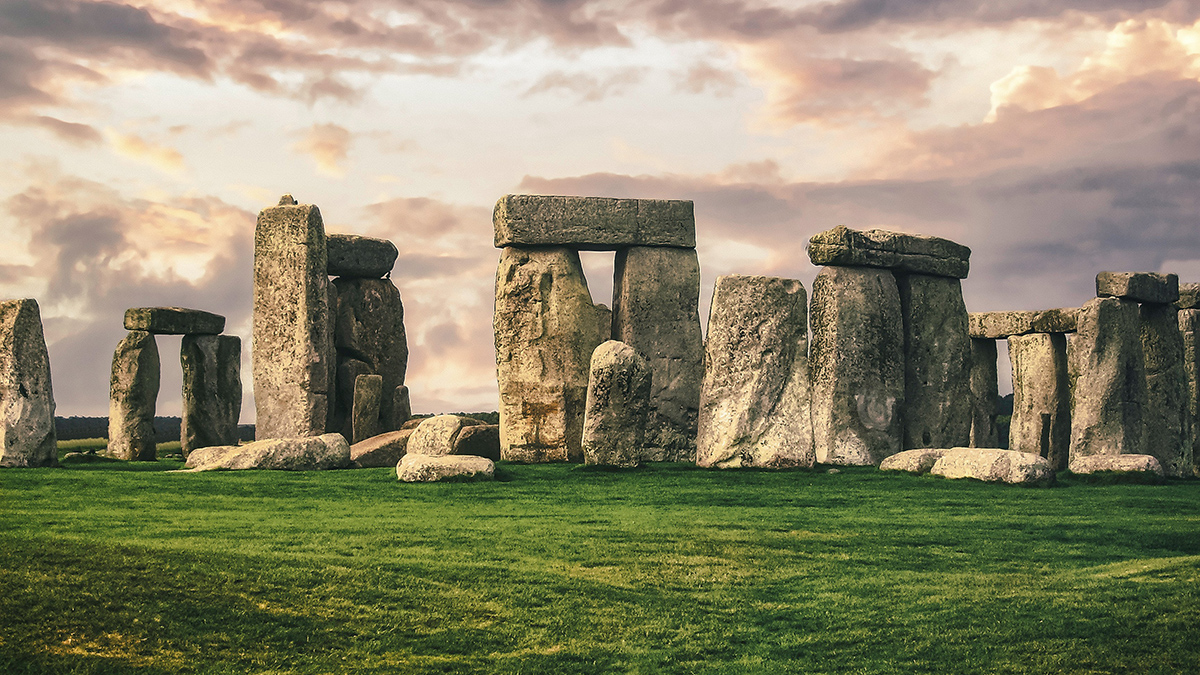
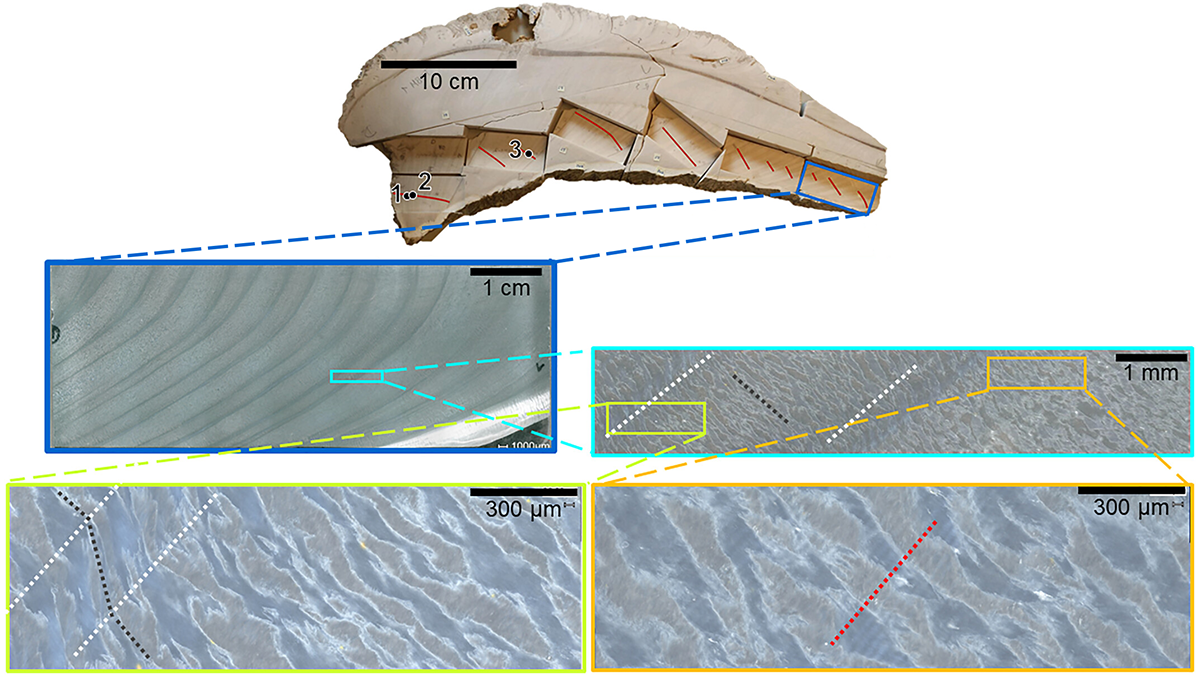
From Sandstone Basin to Stonehenge Altar
New research unearths the Scottish origin of Stonehenge’s Altar Stone and its 750-kilometer journey to Salisbury Plain.
Unlocking Earth’s Terrestrial Sedimentary Record with Paleosols
Harnessing the micro-stratigraphy of pedogenic carbonates, scientists have demonstrated that age determination of fossil soils is possible via uranium-lead dating.
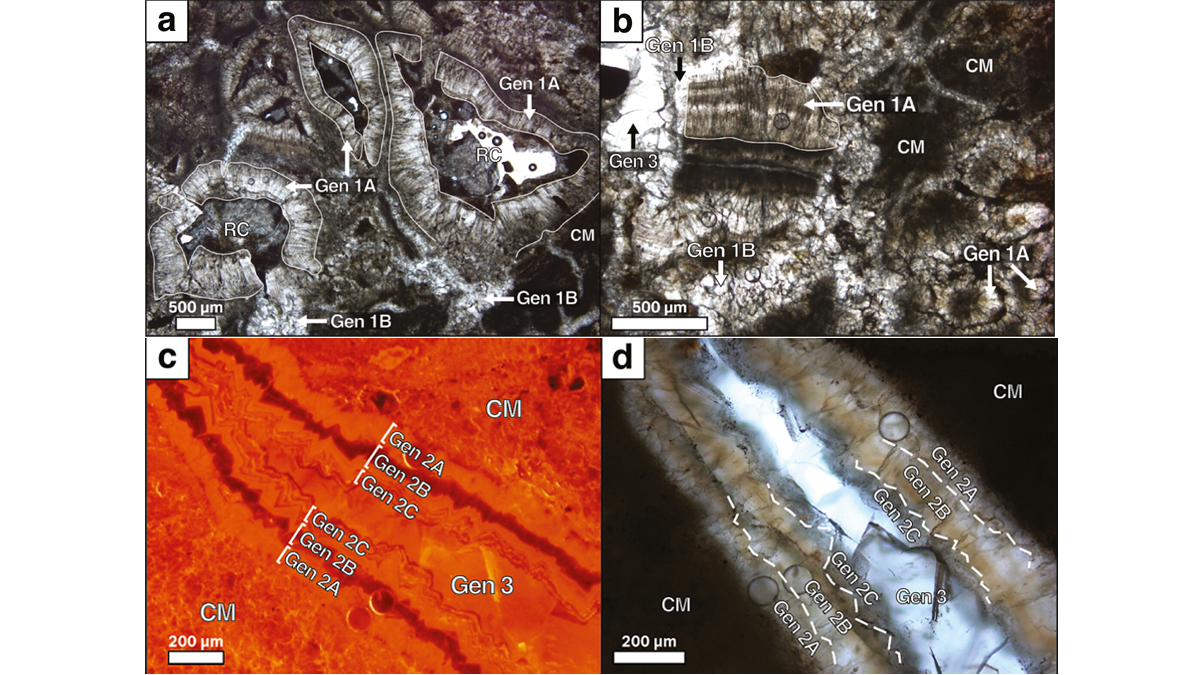
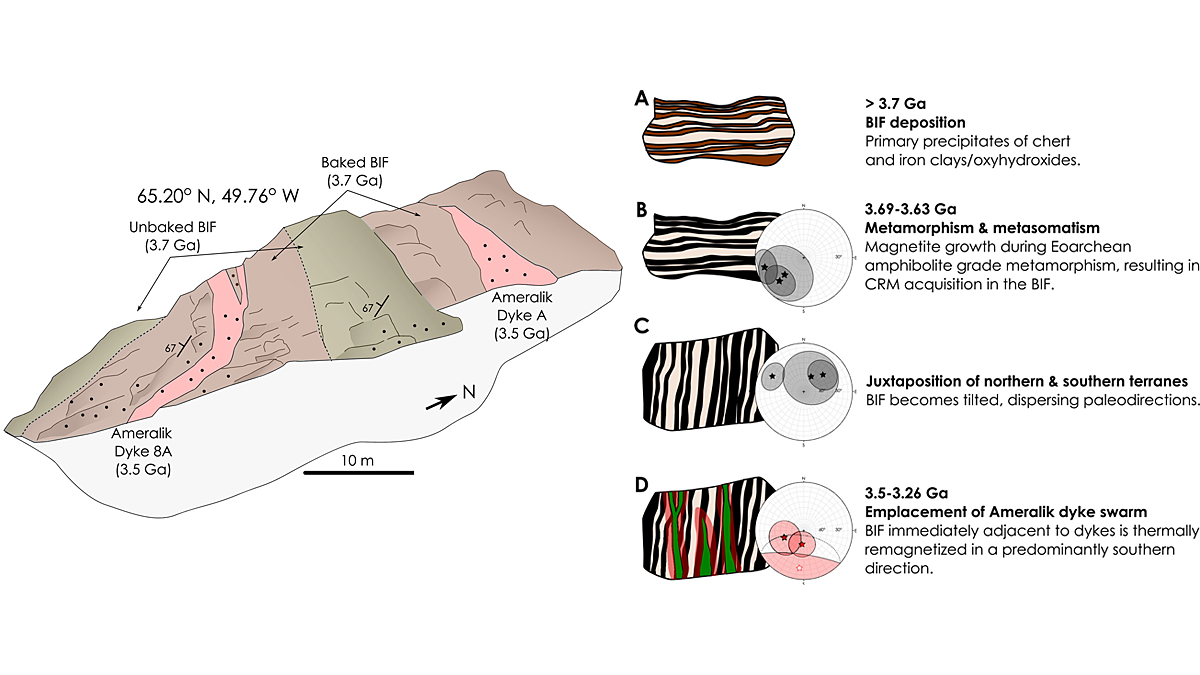
Greenland Could Have Records of 3.7-billion-year-old Geomagnetic Fields
Scientists argue that paleomagnetic field tests preserve a geomagnetic field record acquired as chemical remnant magnetization in banded iron formations in southwest Greenland.
Carbon Dating Reveals the Timing of Puerto Rican Cave Art
New dates from cave art pigment add to evidence that Indigenous Puerto Ricans inhabited the island for millennia.
Ultra-High-Resolution Age Model in Clams Yields Daily Paleo-Data
Using geochemical techniques, scientists identify daily cycles in fossilized giant clams, which permits climate reconstructions at the weather timescale.
Paleostorm Chasers Test a New Detection Tool
A method typically used to date sediments shows promise for documenting tropical storms through history—information needed for future projections of storm activity.
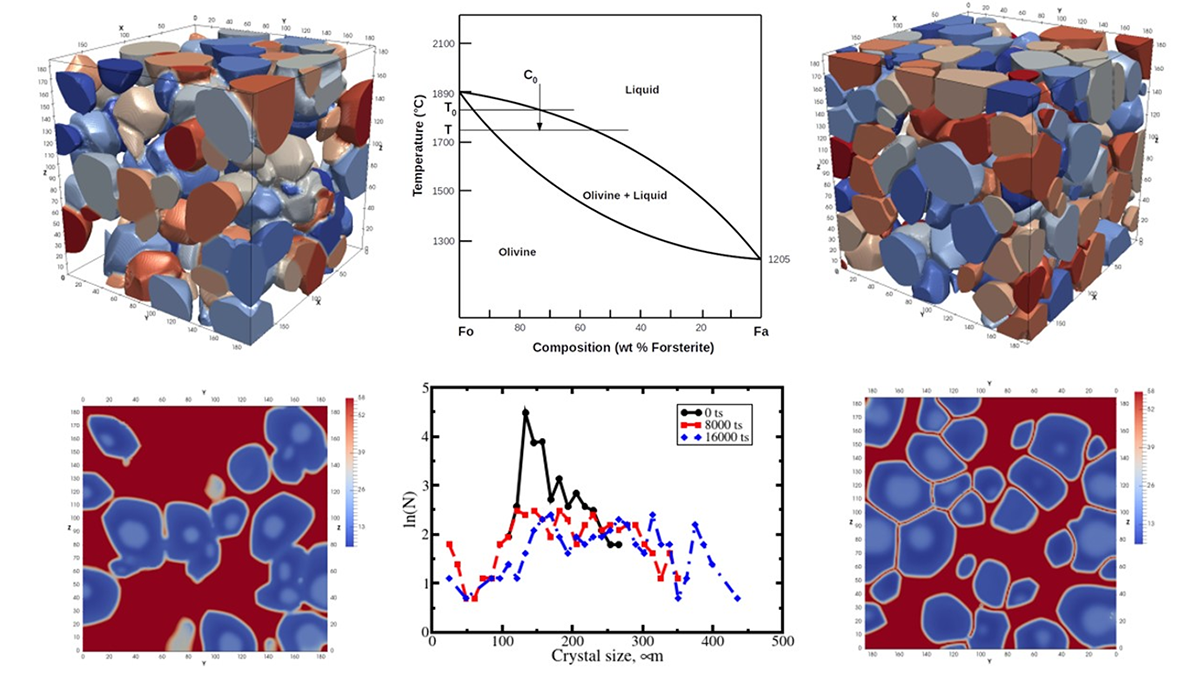
Deciphering the History of a Rock’s Crystallization
By combining a phase field function approach with bulk thermodynamics of mineral phases, the thermal history of a rock can now be deciphered from its distribution of mineral phases.