Microbial genomics techniques came of age following the Deepwater Horizon spill, offering researchers unparalleled insights into how ecosystems respond to such environmental disasters.
Gulf of Mexico
Modeling Under Pressure
At a critical moment in the effort to end one of the world’s worst oil spills, one scientist holed up in his office and pulled an all-nighter to calculate the well’s aquifer support.
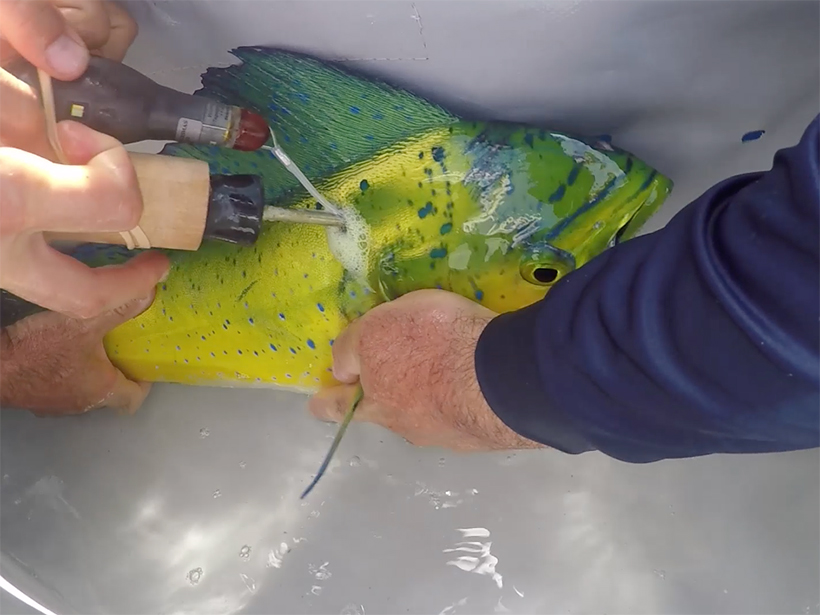
Oil-Exposed Mahi-Mahi More Likely to Lose Oil-Avoidance Behavior
Contact with oil may make it harder for the fish to avoid additional exposure, creating a vicious cycle following offshore oil spills.
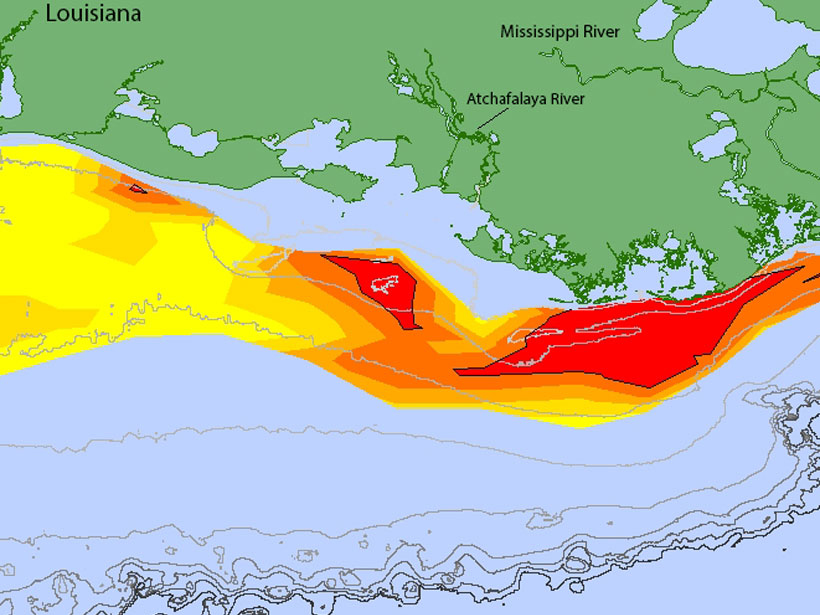
Gulf Dead Zone Looms Large in 2019
A new forecast predicts widespread hypoxia after a wet Midwest spring.
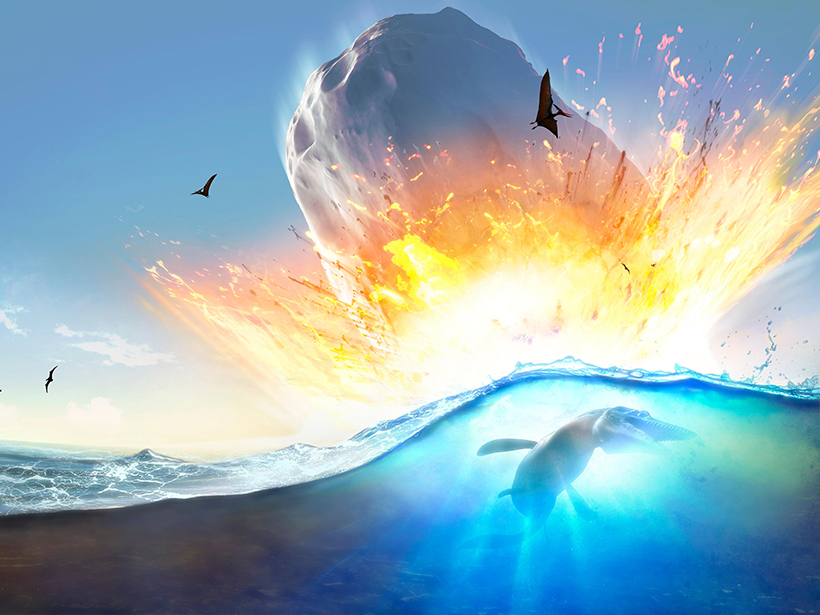
Huge Global Tsunami Followed Dinosaur-Killing Asteroid Impact
The cataclysmic Chicxulub impact roughly 66 million years ago spawned a tsunami that produced wave heights of several meters in distant waters, new simulations suggest.
Deep Floats Reveal Complex Ocean Circulation Patterns
Acoustically tracked floats drift far below the ocean’s surface, providing fresh discoveries about deep-sea currents. A new archive gathers decades’ worth of float data into a central repository.
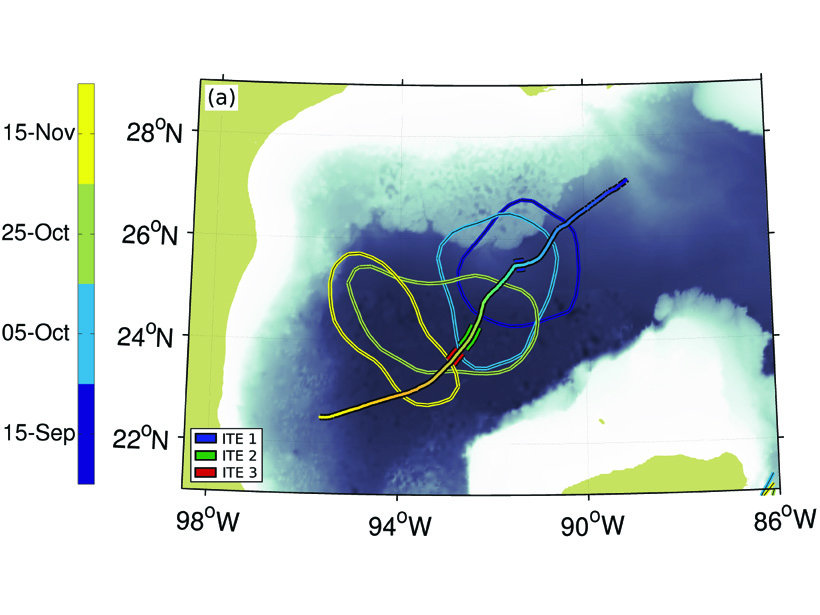
Smaller Eddies Found Within Eddies
A glider survey observed three small eddies embedded within a larger scale eddy associated with the Loop Current in the Gulf of Mexico.
Improving Tropical Cyclone Predictions in the Gulf of Mexico
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s newest High Resolution Atmospheric Model captures the influence of intraseasonal oscillations on tropical cyclone activity.
Acoustic Imaging of Oceanic Mixing in the Gulf of Mexico
Detailed analysis of acoustic reflections suggests that vertical mixing of oceanic water is enhanced at greater depths, thanks to weak stratification and the roughness of the seabed.
Deepwater Horizon Dispersant Cleared the Air, New Model Shows
A simulation of oil and gas leakage during the Deepwater Horizon disaster finds that the main chemical dispersant used improved air quality for emergency responders.