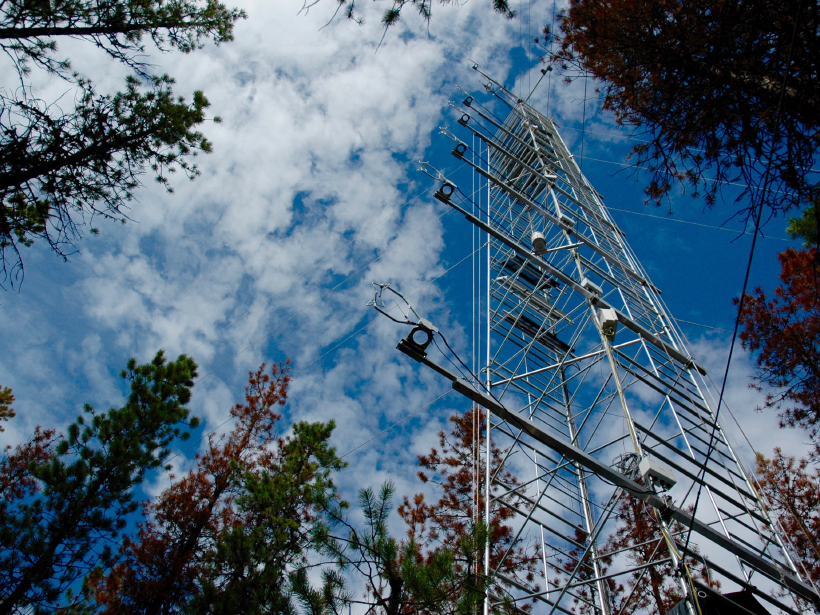
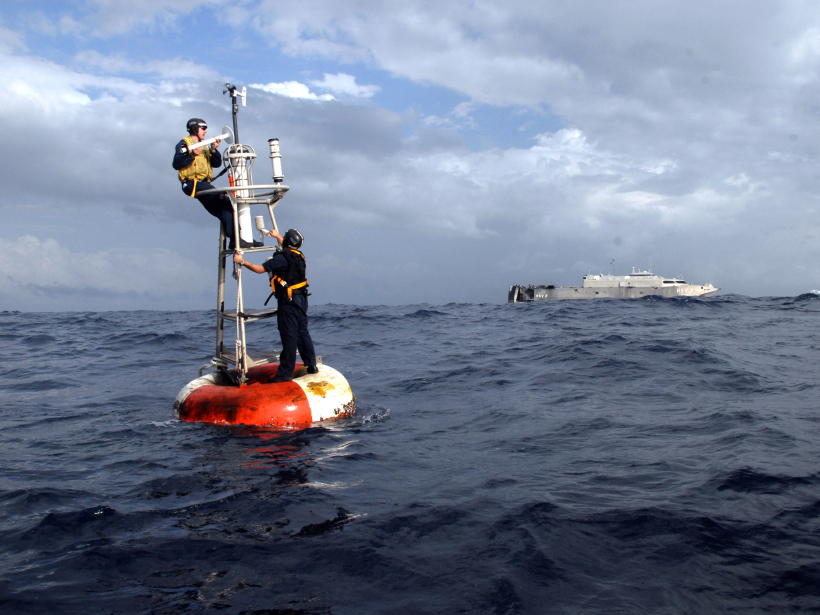
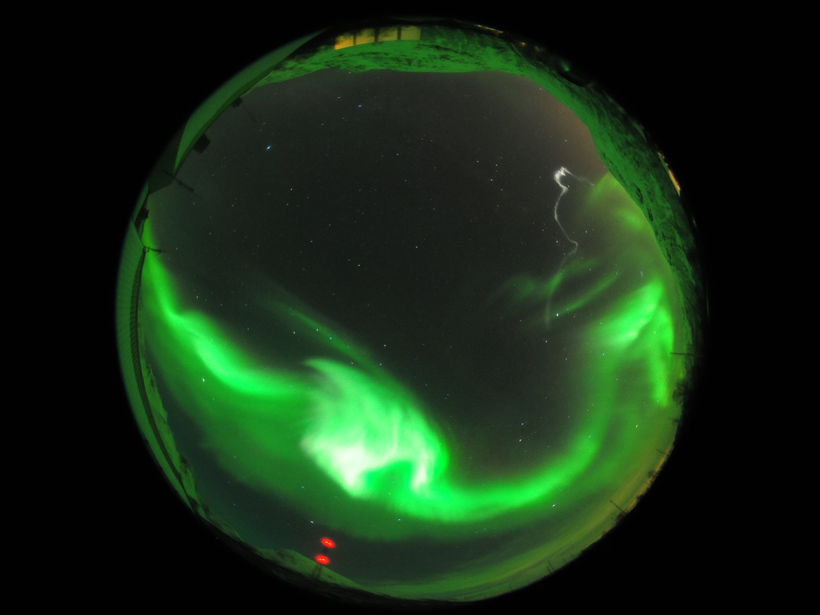
Scientists measure how the aurora affects winds in the upper atmosphere.
hardware & infrastructure
Recording Belgium’s Gravitational History
Instruments at Belgium’s Membach geophysical station set a new record for monitoring gravitational fluctuations caused by storm surges, groundwater fluctuations, and the Moon’s tidal pull.
Urban Sewers Evolve Similarly to River Networks
Like river systems, engineered drainage networks become increasingly fractal as they grow.
Sea Level Rise May Swamp Many Coastal U.S. Sewage Plants
Cities typically build wastewater treatment facilities in low-lying areas. A new national study identifies which plants are most vulnerable to coastal flooding.
Hurricanes Expose Vulnerabilities in Puerto Rico Seismic Network
Could overreliance on cell networks to transmit data leave instruments in the dark after the next storm hits?
Exact Moonlight Measurements Could Aid Earth-Observing Missions
A new telescope’s unprecedented study of subtle variations in lunar light could finally give Earth-facing satellites a common reference point for their observations.
U.S. Weather Alert Systems Must Modernize, Say New Reports
To reduce risks, including loss of life, national weather alert systems must incorporate social and behavioral sciences and new technology, according to two federally sponsored reports.
Global Atmospheric Observations May Need Tweaking for Turbulence
A new study that overturns an 80-year-old assumption about atmospheric turbulence may finally resolve discrepancies in observations of atmospheric heat, water vapor, and carbon.
Antenna Towers Attract Additional Lightning Strikes
Atmospheric scientists evaluate the influence of human-made structures on lightning data.
Deep Trouble! Common Problems for Ocean Observatories
Ocean Observing Infrastructure and Sensing – Technical Lessons Learned and Best Practices; Moss Landing, California, 23–25 September 2016