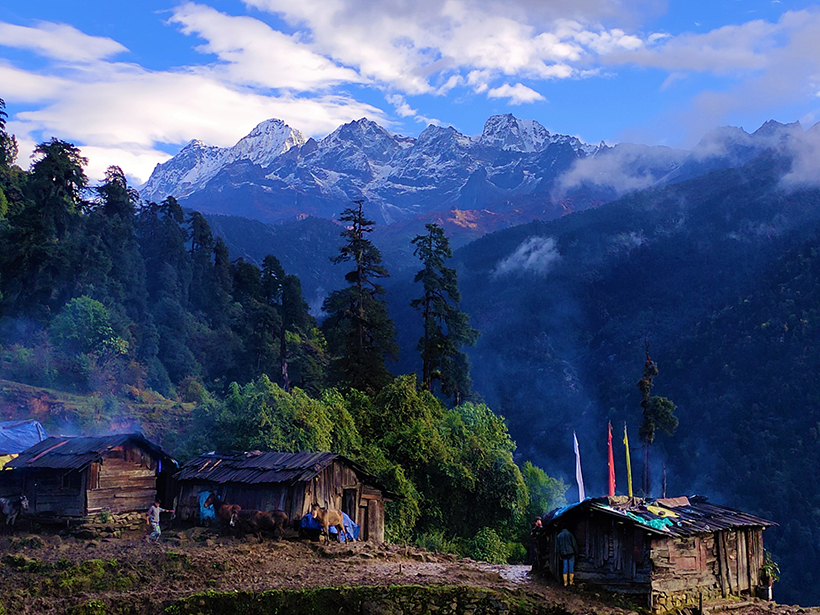
A dense seismic network in operation since 2019 will provide new insights into the tectonics of seismically active Himalayan regions.
Himalayas
El Monte Everest a veces puede sentirse más bajo que el K2
Las variaciones de la presión atmosférica en la cima del Everest afectan a la disponibilidad de oxígeno, modificando la percepción de la elevación de la cumbre unos cientos de metros.
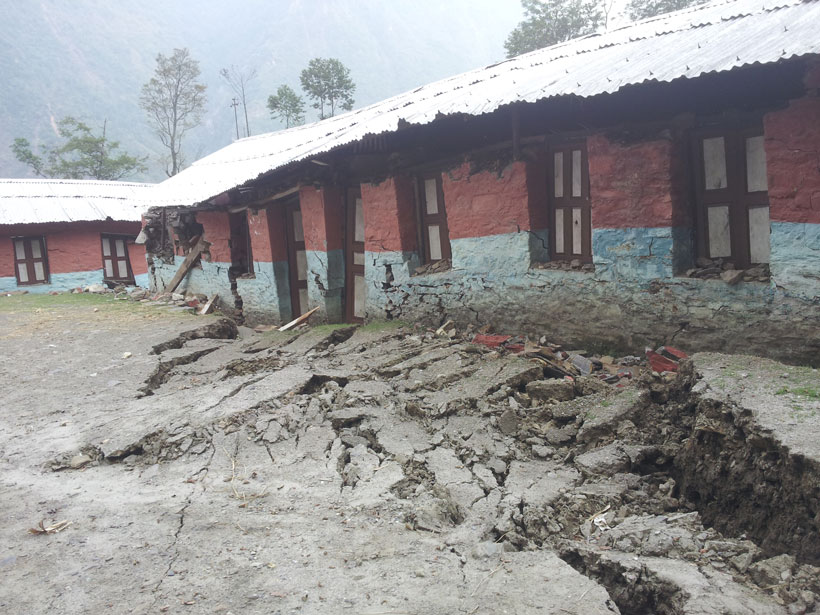
Development and Climate Change Contribute to a Himalayan Tragedy
Infrastructure projects like roads and dams destabilize slopes and compound the effects of glacial floods and avalanches, scientists say.
Mount Everest Can Sometimes Feel Lower Than K2
Variations in air pressure on the top of Mount Everest affect oxygen availability, changing the perceived elevation of the summit by hundreds of meters.
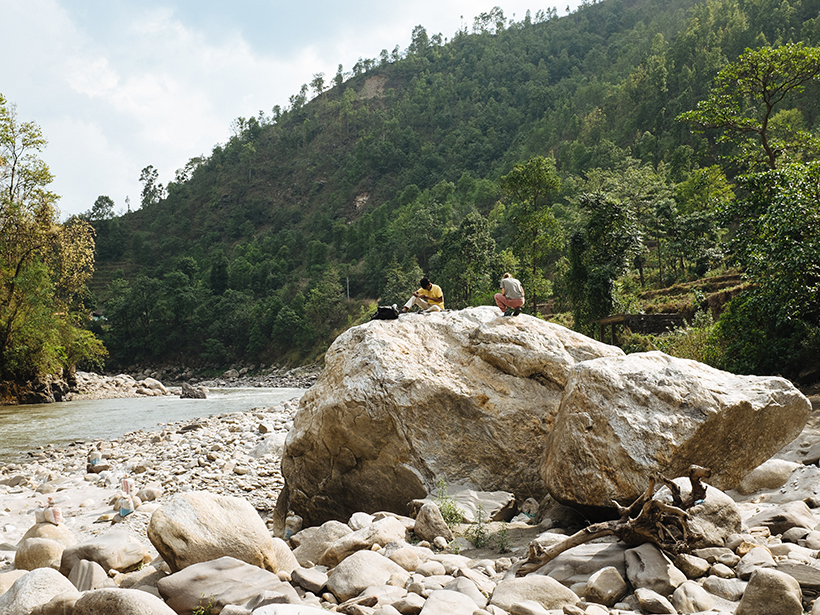
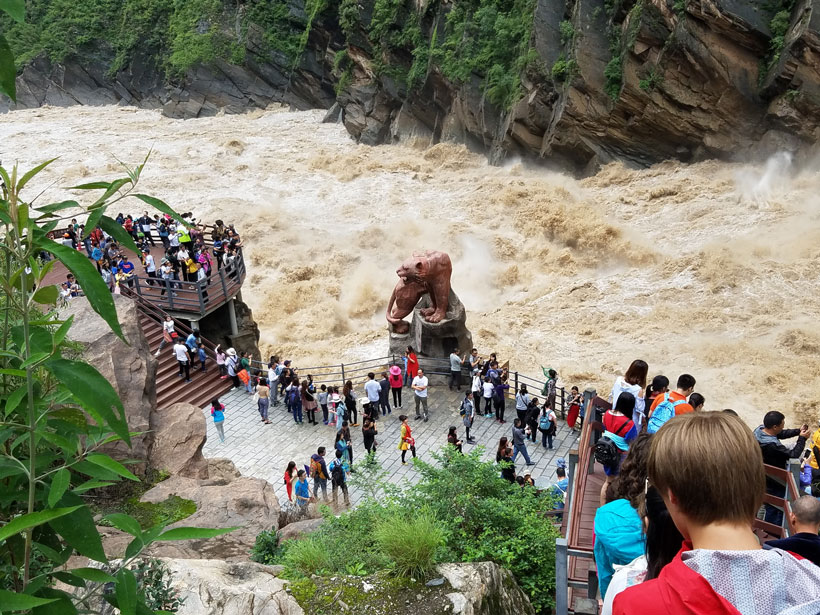
Powerful Glacial Floods Heave Himalayan Boulders
Many of the house-sized boulders that litter Himalayan river channels were transported thousands of years ago by glacial lake outburst floods, new observations suggest.
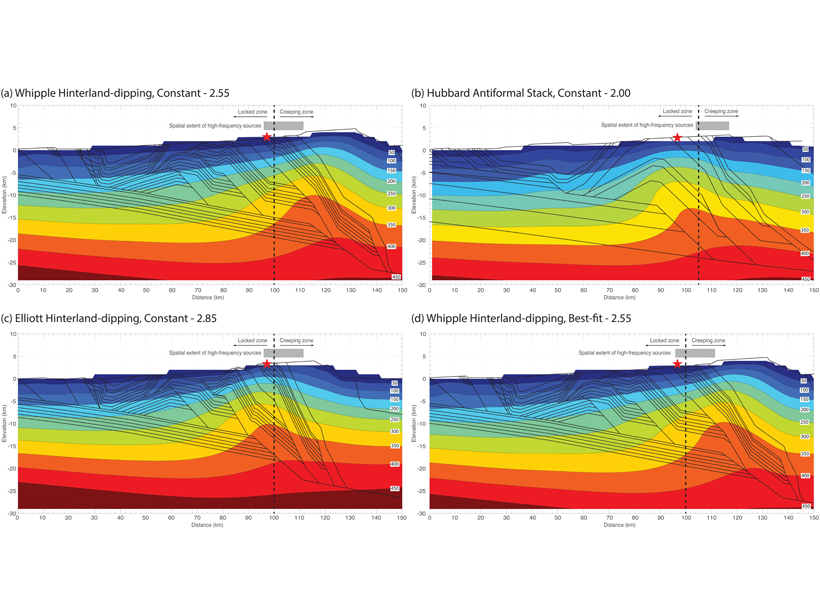
Deconvolving What Lies Beneath the Himalaya
A new study that combines constraints from the 2015 Gorkha earthquake, forward models of deforming crust, and thermochronology data gives new insights into the structure of the Himalaya.
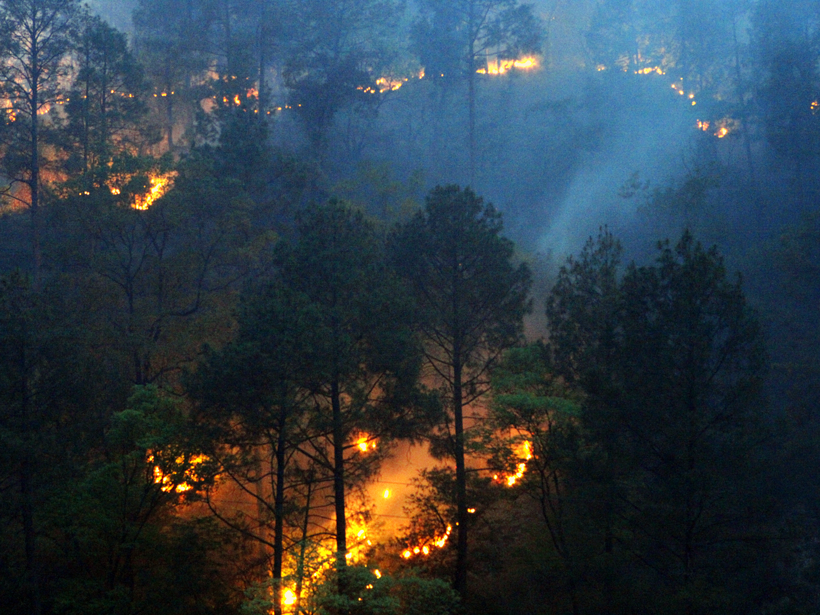
COVID-19 Lockdown Reduces Forest Fires in the Western Himalayas
The overlap between peak fire season and pandemic response has made for a serendipitous experiment in forest fires in two Indian states. Humans, not lightning, seem to be the likeliest culprit.
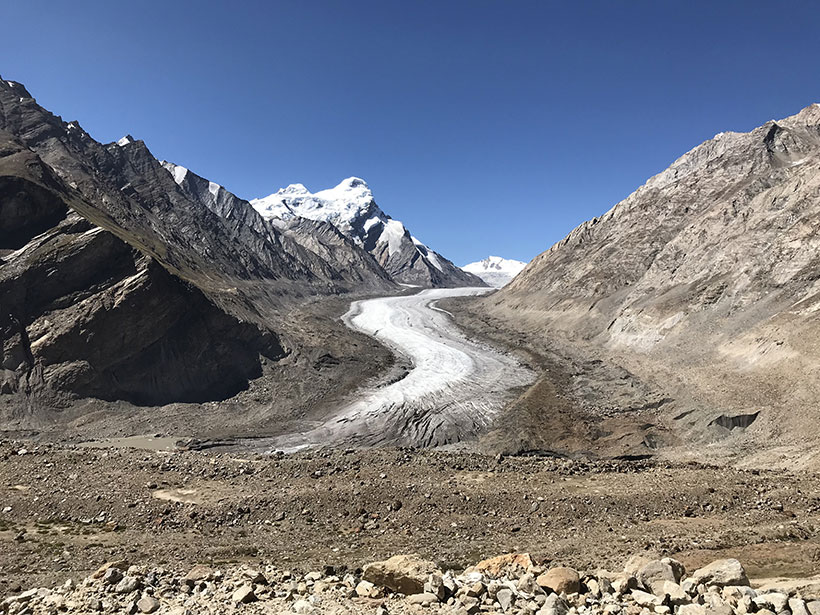
A Future of Retreating Glaciers in the Himalayas
India’s first regional climate change assessment warns of accelerated glacier melt.
Asia’s Mega Rivers: Common Source, Diverse Fates
How do humans affect the ways that Asia’s mega rivers deliver sediment and dissolved matter to farms, river deltas, and, eventually, the sea? A proposed study would construct an integrated picture.
Geodetic Data Pinpoint Earthquake-Prone Regions of the Himalayas
GPS measurements of the Indian and Eurasian plates reveal four locked segments most likely to produce large earthquakes.