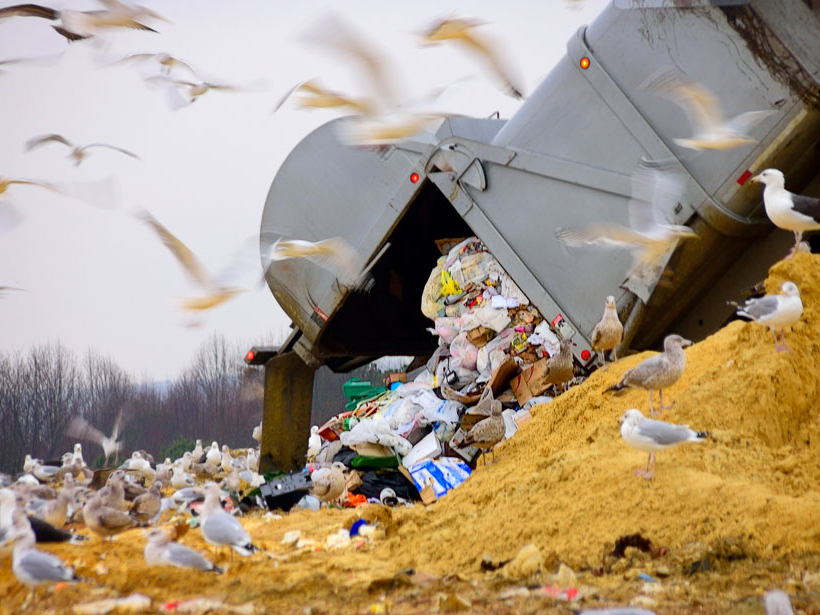
A new study in the Baltimore-Washington metropolitan area reveals prior estimates may significantly underrepresent methane emissions, particularly from landfills and natural gas systems.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
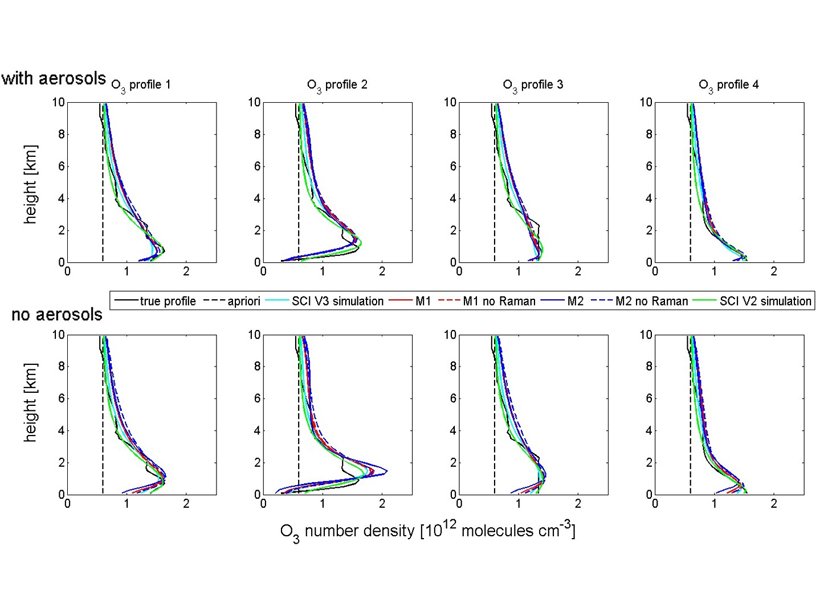
Retrieving Tropospheric Ozone from Ground-based Spectroscopy
A new technique can retrieve the profile of ozone from surface to tropopause by MAX-DOS ground-based measurements.
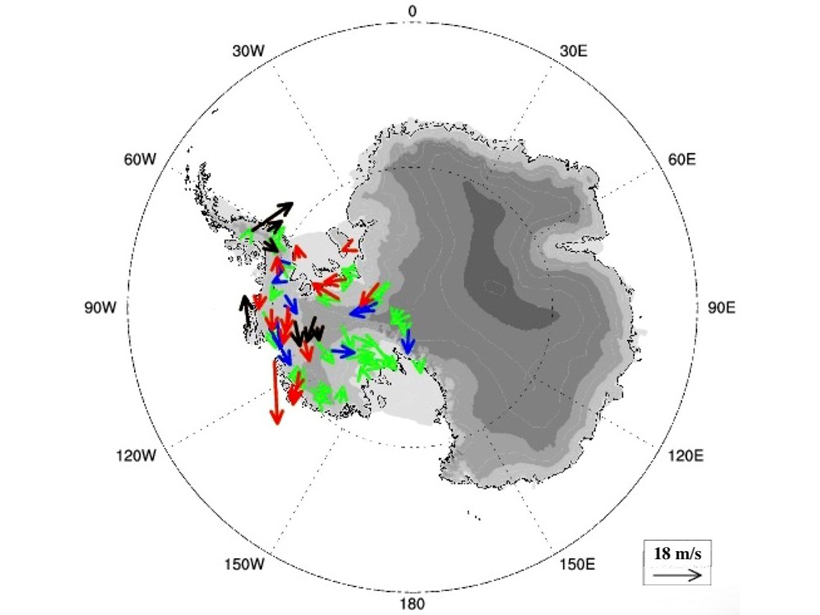
Dropsondes Reveal Atmospheric Boundary Layers Over Antarctic
636 high-resolution dropsondes reveal four types of atmospheric boundary layer over the Antarctic, including well-mixed and convective types.
Polarization Measurements Probe the Physics of Lightning
A new measurement capability can detect the polarization of the radio frequency wave of lightning sources, which reveals different forms of lightning breakdown processes.
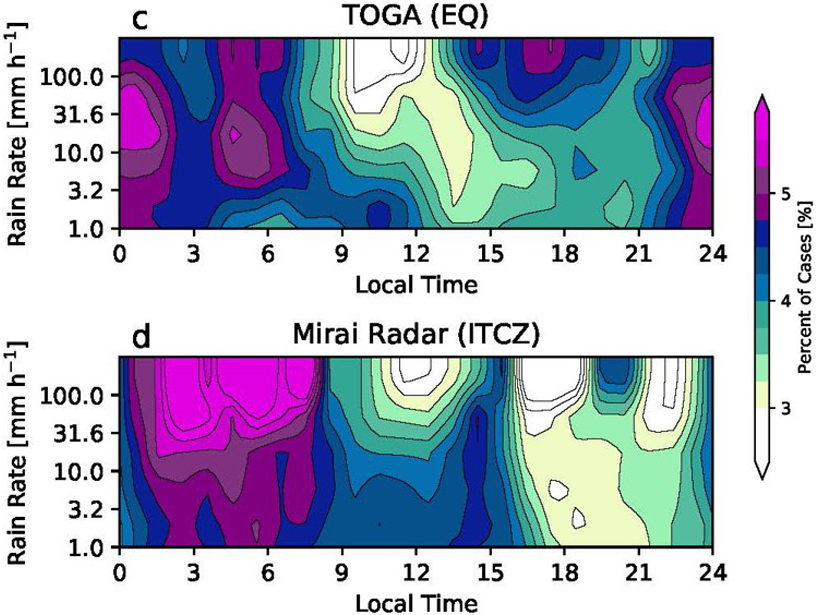
Diurnal Variation of Rainfall over the Equator Revisited
Radar data show an afternoon precipitation maximum in the equatorial Indian Ocean in addition to the nocturnal maximum; this occurs under light surface winds and suppressed large-scale convection.
New Lidar Comparisons of Temperatures Near the Mesopause
For the first time, simultaneous measurements of upper atmosphere temperatures over altitudes 80 to 110 kilometers have been made by two complementary lidar techniques.
Observing Winter Mixing and Spring Bloom in the Mediterranean
A new special issue of JGR: Oceans and JGR: Atmospheres presents new insights into the dynamics of dense water formation in the western Mediterranean Sea and its biogeochemical consequences.
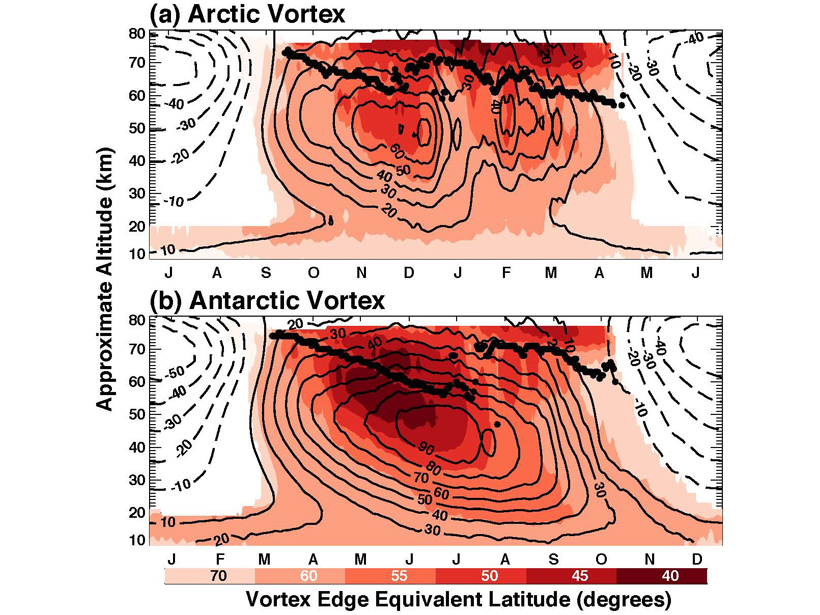
New Characterization of the Mesospheric Polar Vortices
Polar vortices play a central role in coupling the atmosphere from the ground to the middle atmosphere. New satellite diagnostics describe mesospheric polar vortices and coupling to lower altitudes.
Wind Speed Governs Turbulence in Atmospheric Inversions
Measurements made during a field campaign in Idaho indicate that the speed of winds 2 meters above Earth’s surface determines the type of turbulence present in nighttime inversions.
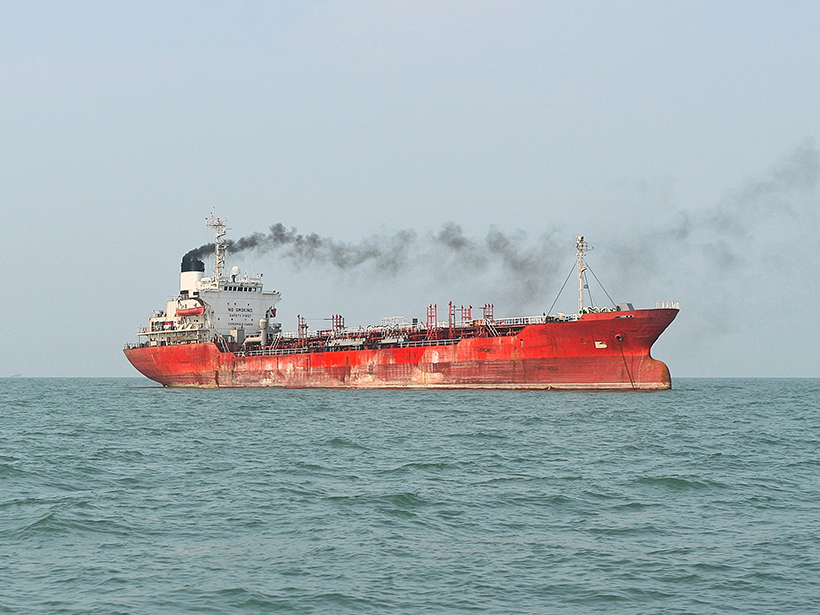
Brown Carbon from Increased Shipping Could Harm Arctic Ice
Emission from a ship’s engine gives clues to how much light-absorbing molecules may build up on and above snow and sea ice. Such emissions are likely to increase as more ships venture into the Arctic.