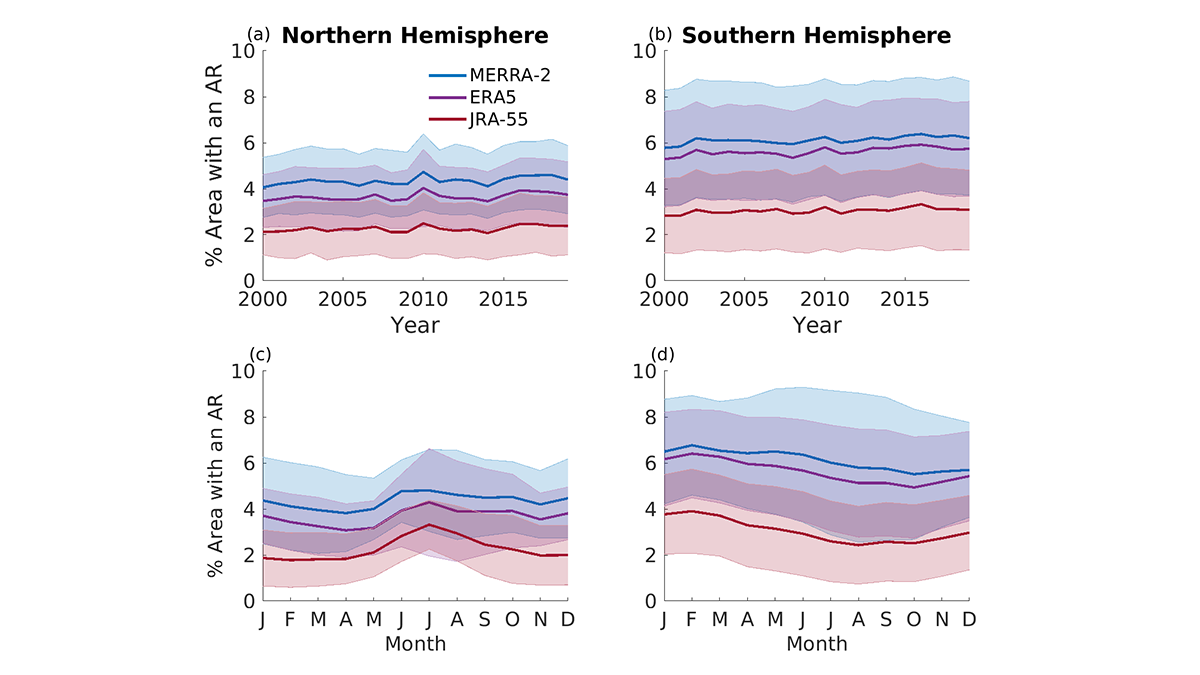
Results from the Atmospheric River Tracking Method Intercomparison Project (ARTMIP) describe the similarity and difference of using eleven detection algorithms and three reanalysis products.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
Radar Diagnosis of the Thundercloud Electron Accelerator
Altitude-resolved S-band radar observations of graupel are used to decipher thunderstorm ground enhancements in surface electric field and gamma ray flux.
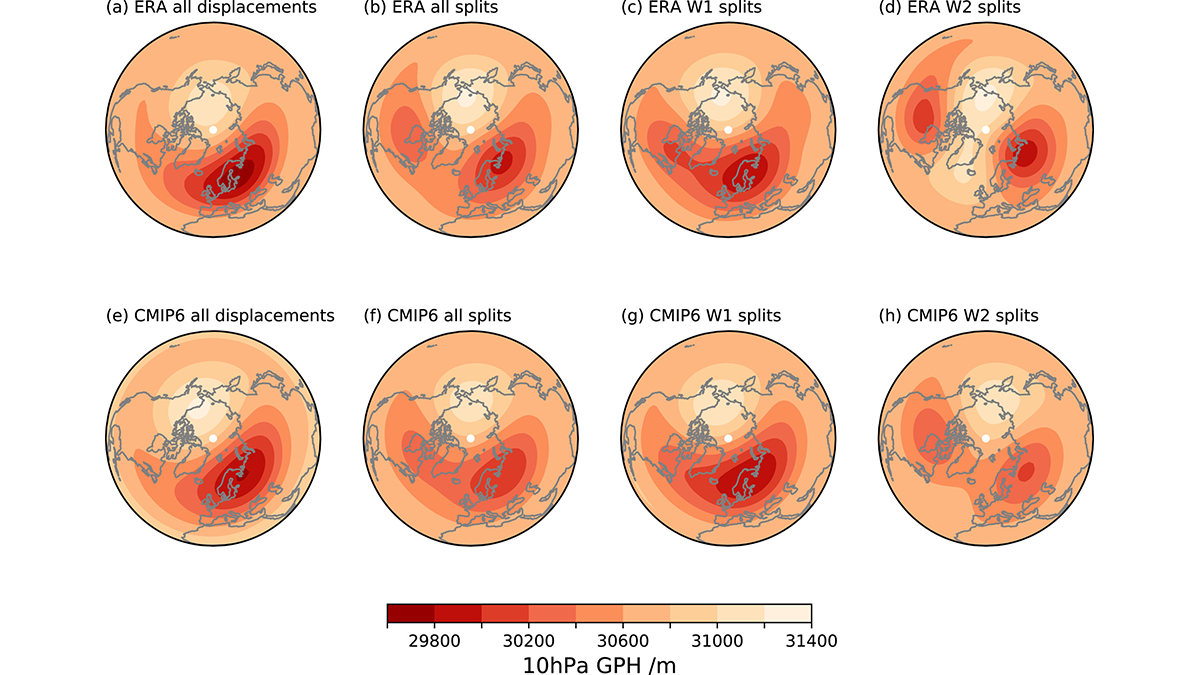
Simulating Surface Impacts of Stratospheric Sudden Warmings
New evaluations of climate model simulations show how the stratosphere polar vortex couples to surface weather.
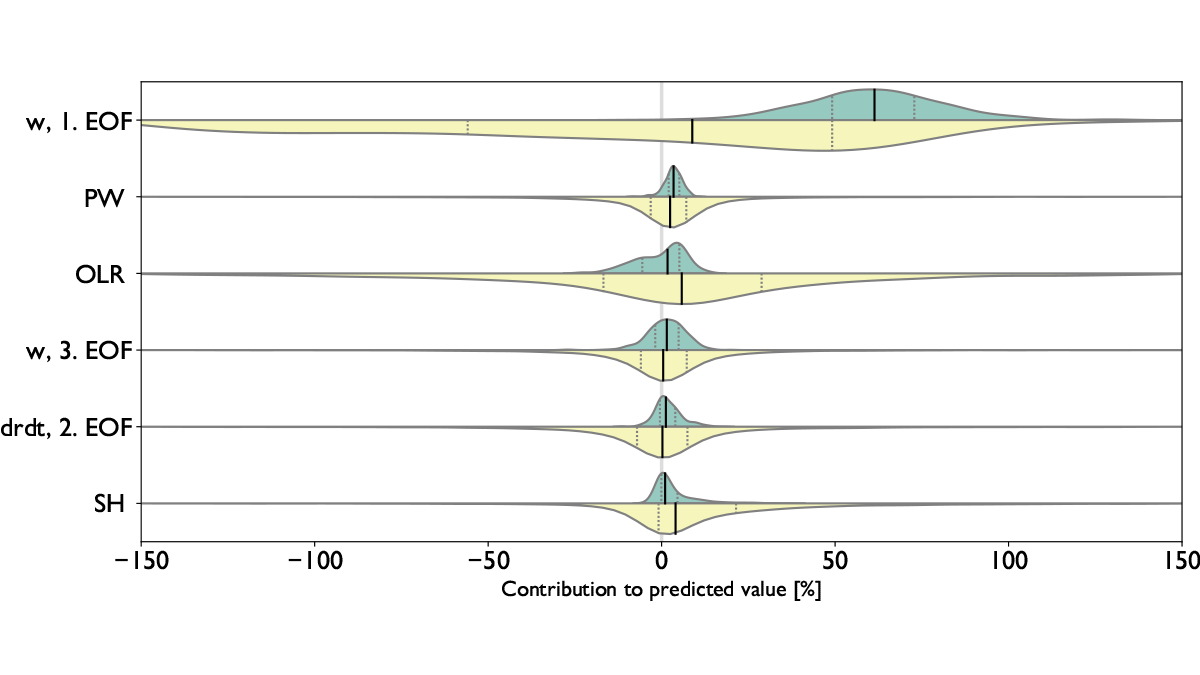
Using Artificial Intelligence to Study Convection
Machine learning techniques are used to examine relationships between the large-scale state of the atmosphere, the convection total area, and the degree of organization in northern Australia.
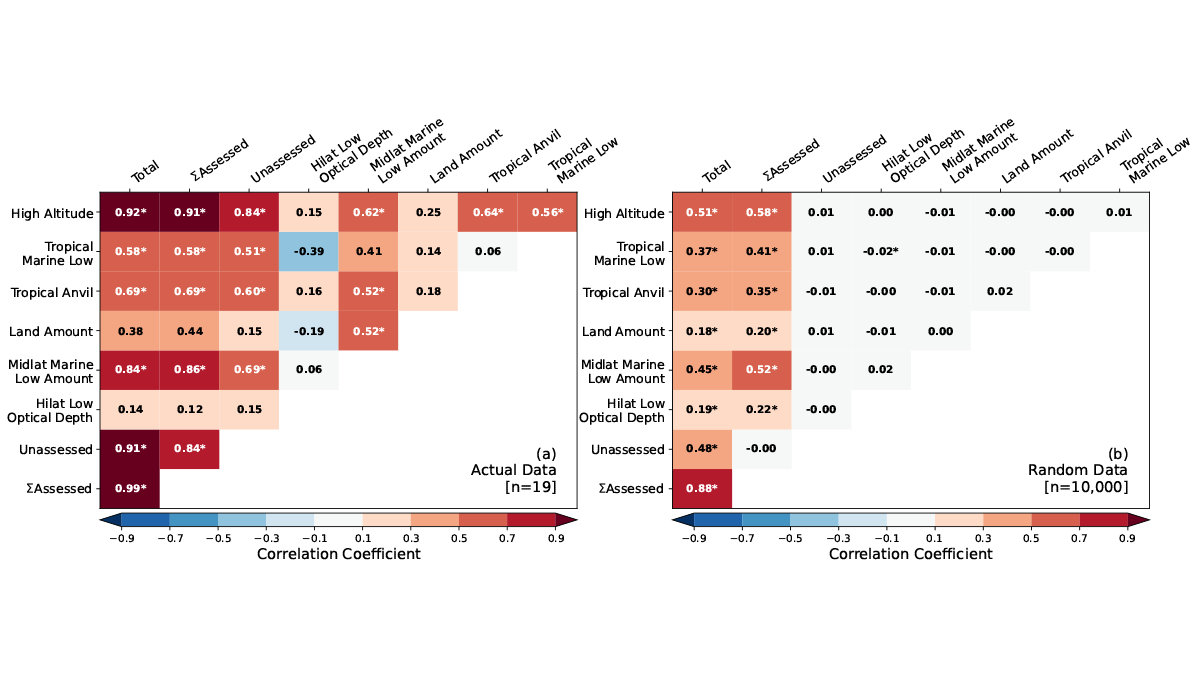
Cloud Feedbacks in CMIP6 Models Versus Expert Synthesis
Models with smallest feedback errors are found to have moderate cloud feedbacks and equilibrium climate sensitivity of 3 to 4 degrees of warming when the concentration of carbon dioxide is doubled.
Arctic Sea Ice is Crucial for Forecasting Ural Blocking
By solving the nonlinear optimization problem, sea ice concentration in Greenland, Barents and Okhotsk Seas is found crucial for prediction of strong and long-lasting Ural blocking formation.
¿Cuánto tiempo permanecen las partículas de carbono negro en la atmósfera?
Investigadores descubren cómo el carbono negro evoluciona de partículas hidrofóbicas a sitios de nucleación de nubes, removiendo eventualmente las partículas que absorben calor del cielo.
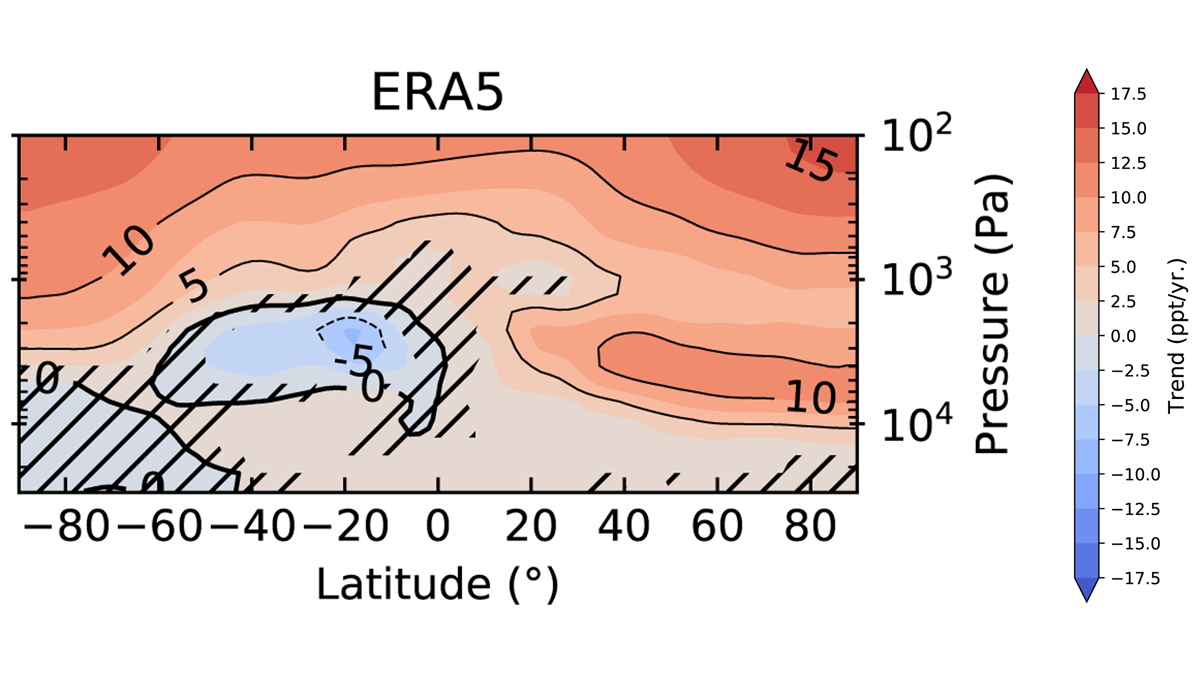
New Insights on Stratospheric Circulation from Fluorine Tracers
Stratospheric fluorine species have accumulated faster in the Northern Hemisphere over the past two decades reflecting interhemispheric differences in the Brewer-Dobson transport circulation.
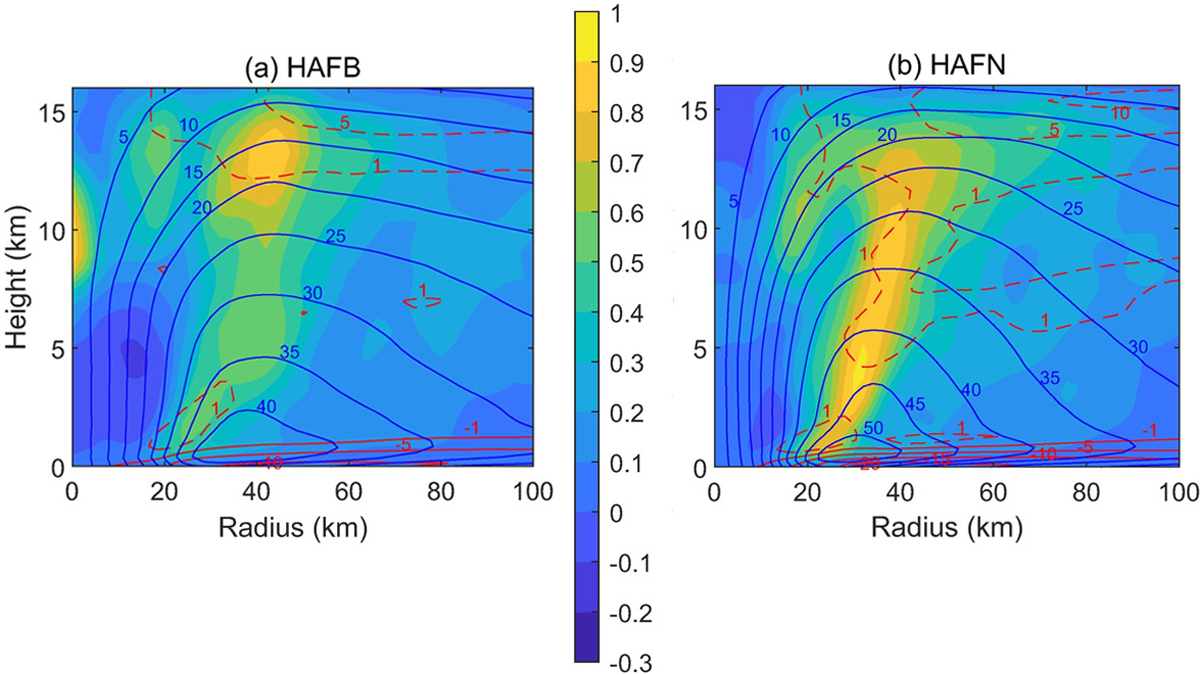
Hurricane Forecast Improvement with Better Turbulent Processes
A new look at turbulent processes has improved the prediction of hurricane rapid intensification by properly accounting for the unique environment of a hurricane eyewall.
How Long Do Black Carbon Particles Linger in the Atmosphere?
Researchers uncover how black carbon evolves from hydrophobic particles to cloud nucleation sites, eventually removing the heat-absorbing particles from the sky.