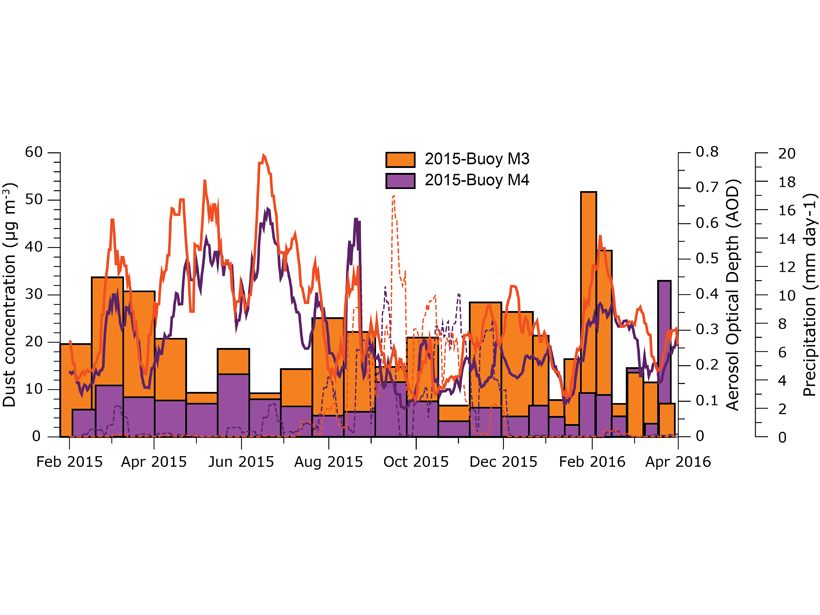
The first time series of bi-weekly dust concentrations measured in-situ across the remote Atlantic Ocean.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
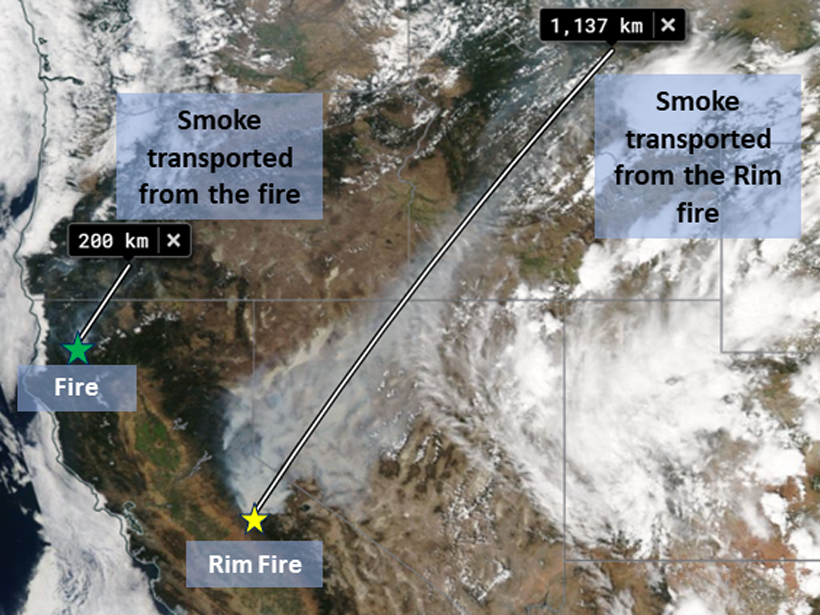
Satellite Sensor EPIC Detects Aerosols in Earth’s Atmosphere
Aerosol observations from EPIC—a sensor aboard a satellite—align well with ground- and aircraft-based data, including measurements of smoke plumes produced by recent megafires.
Modeling Volcanic Debris Clouds
How does a large volcanic cloud get into the stratosphere? Scientists model how volcanic debris injected into the lower stratosphere can be lofted high into the middle stratosphere.
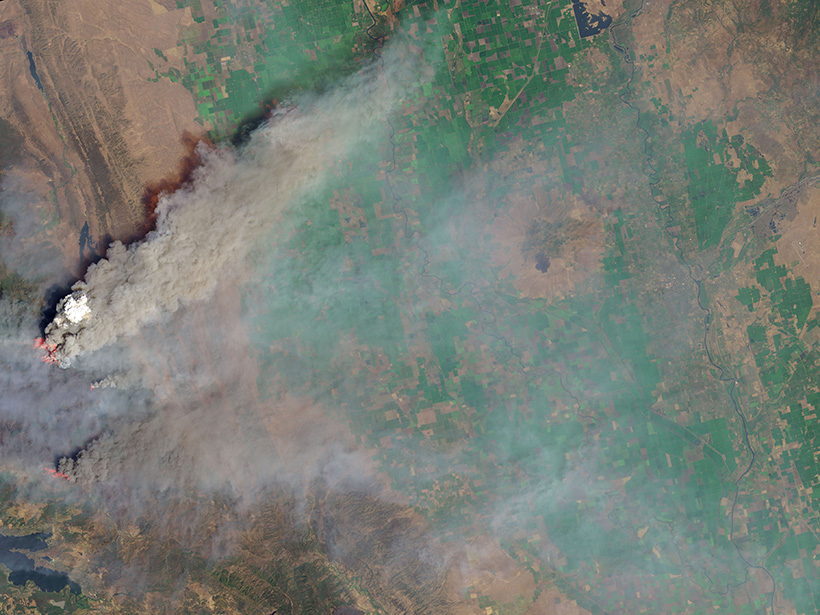
Improved Algorithms Help Scientists Monitor Wildfires from Space
Wildfires release pollutants that harm human health. Quality satellite monitoring can help track these pollutants and predict where they may become health hazards.
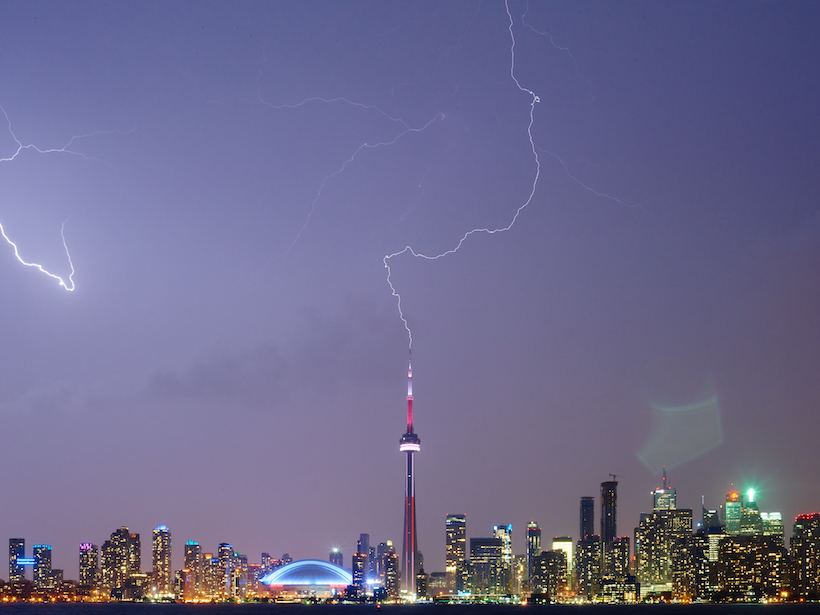
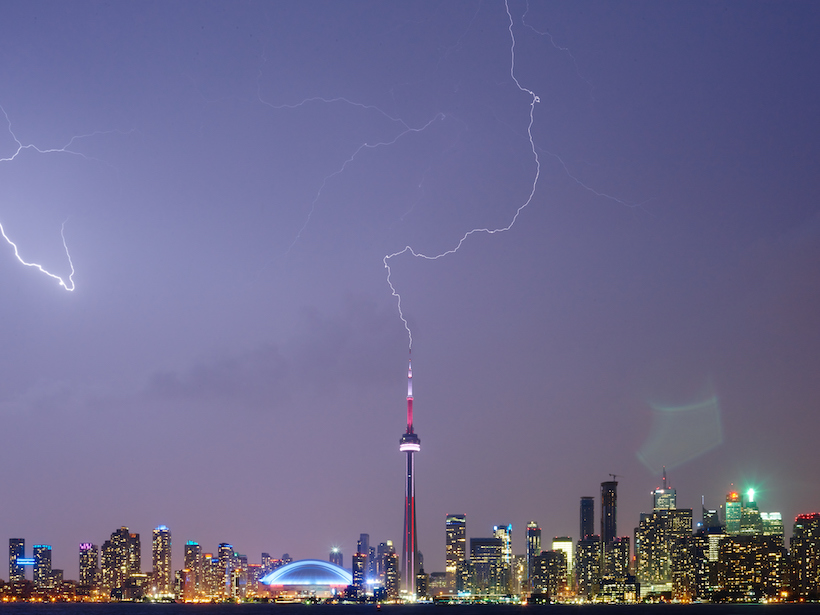
Observations from Space and Ground Reveal Clues About Lightning
In a coordinated monitoring effort, scientists have uncovered the timing and triggering of high-energy lightning events in the sky.
Mejorando el presupuesto mundial para el metanol atmosférico
Nuevos datos de exploración con aeronaves muestran que aunque la química atmosférica sobre regiones oceánicas remotas es una fuente considerable de producción de metanol, la emisión neta de metanol del océano es menor.
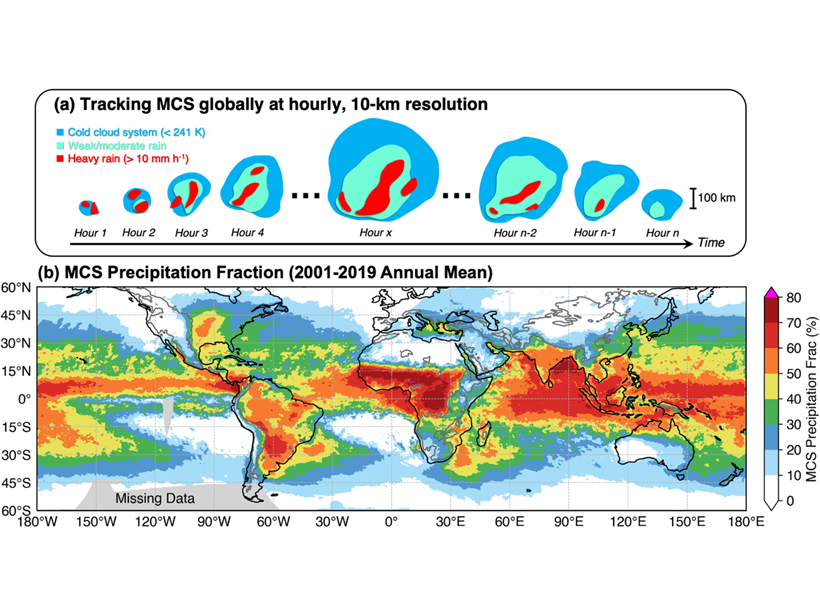
New Global Mesoscale Convective System Tracking Database
A 20-year high-resolution global mesoscale convective system tracking database reveals the characteristics of mesoscale convective systems and their significant contributions to global rainfall.
Upward Lightning Takes Its Cue from Nearby Lightning Events
Lightning in a thunderstorm changes the electromagnetic field in a way that sparks upward lightning from tall structures.