New aircraft survey data show that although atmospheric chemistry above remote ocean regions is a considerable source of methanol production, the ocean’s net methanol emission is minor.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres
Atmospheric Turbulence May Promote Cloud Droplet Formation
Turbulence causes local variations in relative humidity, which can push particles past a critical saturation threshold for droplet nucleation.
New Land Surface Air Temperature Global Dataset
The fifth major update of land surface air temperature data from the Climatic Research Unit and the Met Office has extended the time series, included more stations, and used better processing methods.
New Global Surface Temperature Dataset Spans 170 Years
HadCRUT5, the new version of the Met Office Hadley Centre/Climatic Research Unit global surface temperature dataset from 1850 to 2018, has extended and improved the previous temperature record.
Seeding Ice Clouds with Wildfire Emissions
Wildfires create airborne plumes of organic and inorganic matter as they burn. These particles can nucleate cloud-forming ice crystals and affect cloud dynamics, precipitation, and climate.
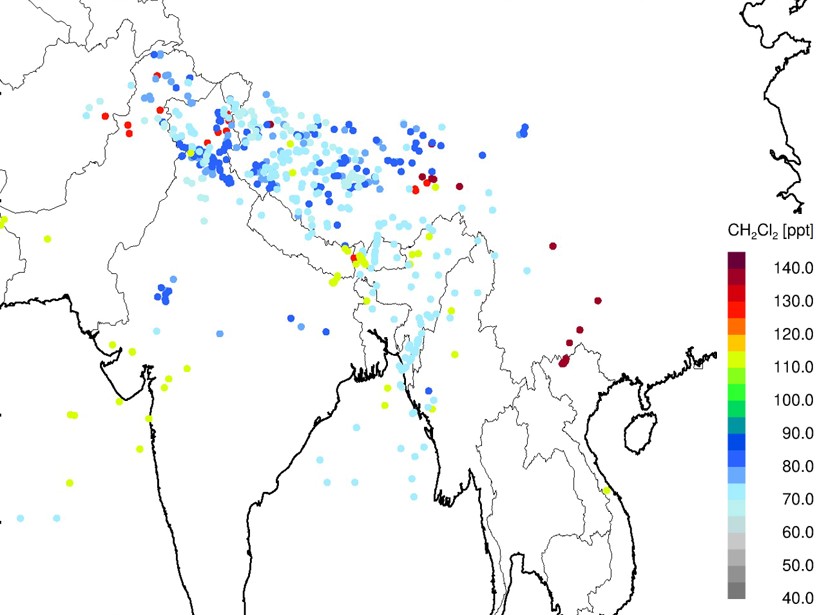
Measurements of Ozone-Depleting Chemicals in the Asian Monsoon
New high-altitude aircraft observations identify unexpected high levels of halogen-containing species entering the stratosphere above the summertime Asian monsoon.
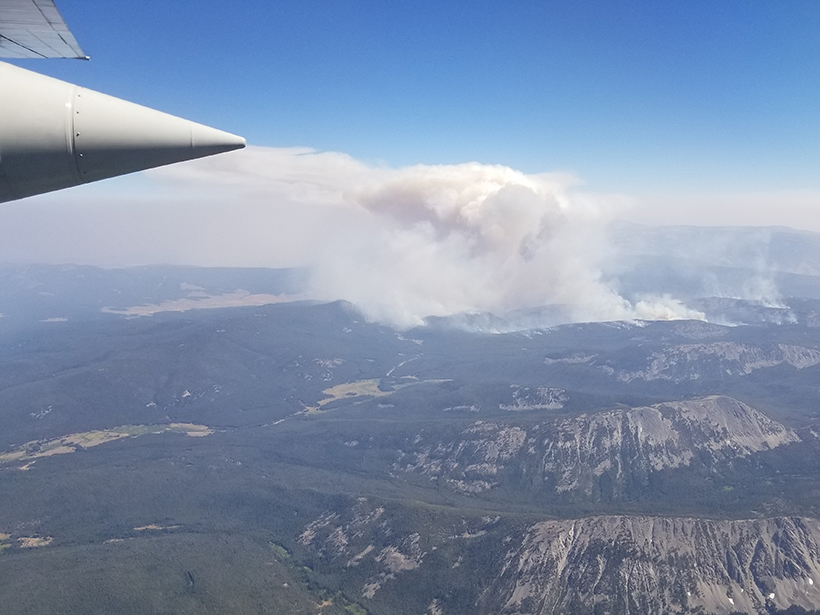
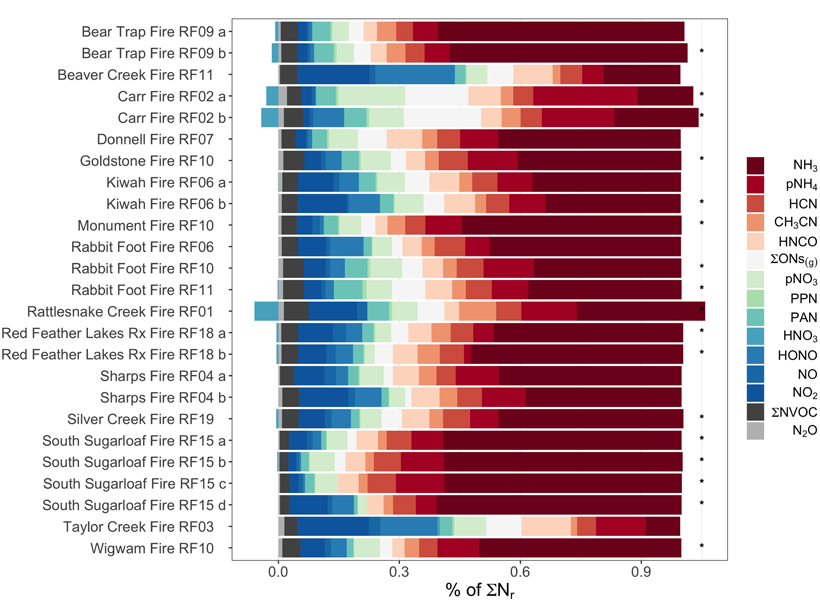
Deciphering Reactive Nitrogen Emissions from Wildfire Smoke
In-situ data gathered from an aircraft flying over 23 western US wildfires in 2018 reveal the importance of reduced nitrogen, shedding insights on ozone and aerosol formation from wildfires.
Devastation of Hurricane Maria to Puerto Rican Landscape
The destructive winds and rain of Hurricane Maria in 2017 caused a dramatic transformation to Puerto Rico’s landscape and altered the characteristics of land-air interaction.
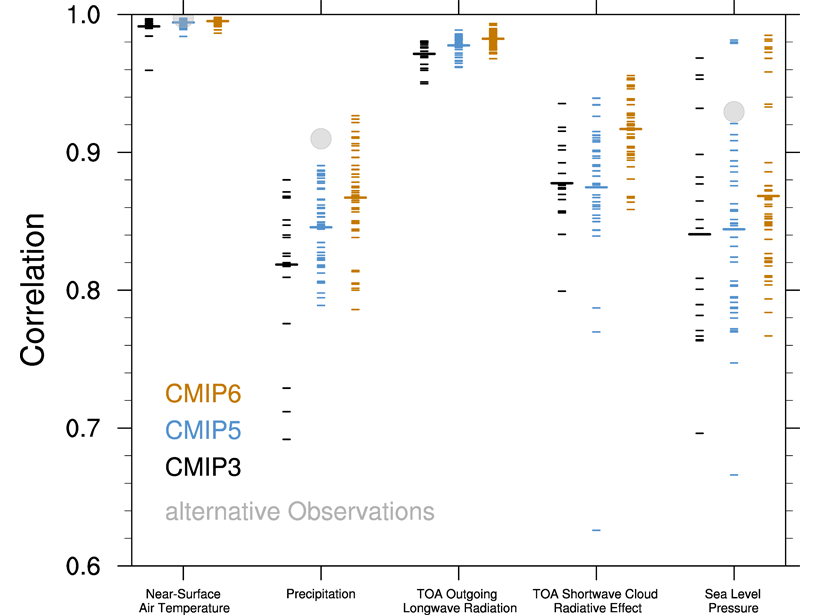
Climate Modeling Progress in the Past 15 Years
An assessment and comparison of the performances of climate models participating in three phases of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project (CMIP3, CMIP5 and CMIP6).
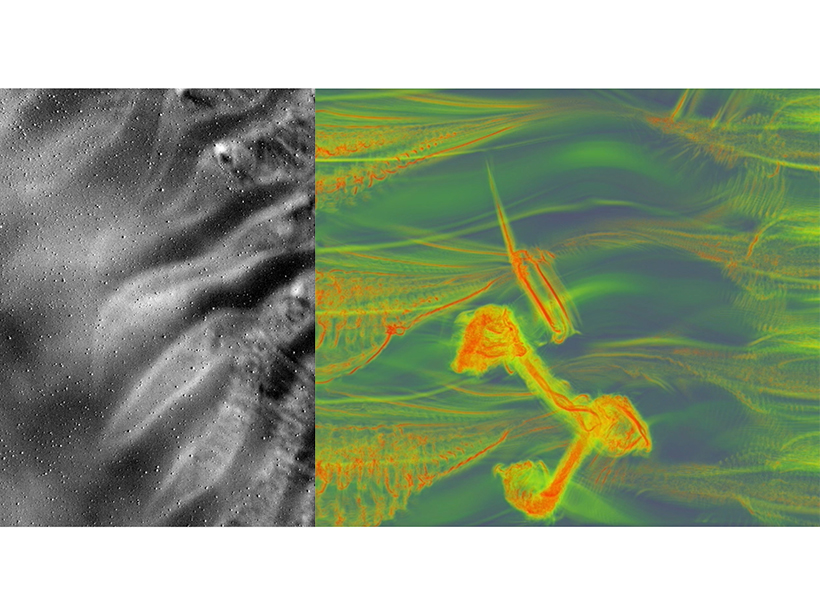
Newly Identified Instabilities Enhance Atmospheric Turbulence
New high-resolution imaging and modeling reveal the first evidence of enhanced turbulence due to gravity wave modulation of Kelvin-Helmholtz instabilities.