The low density of Kuiper Belt Object Arrokoth sheds light on the formation of planetesimals in the early solar system.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets
Pushing the Limits of IR Spectra: Using Nano-FTIR on Meteorites
A new method, nano-FTIR, is used to examine microstructures and processes on grains, displaying its benefit for examining asteroid returned samples through a meteorite.
Dynamics of Ocean Worlds Likely Controlled by Their Rotation
New simulations suggest that subsurface oceans on icy moons with small natural Rossby numbers may be dominated by rotational effects.
An Impact Basin Thermometer for the Moon
Large impact basins on the near side of the Moon lack the annulus of thickened crust that far-side basins have. The difference can be linked to the thermal structure of the lunar crust.
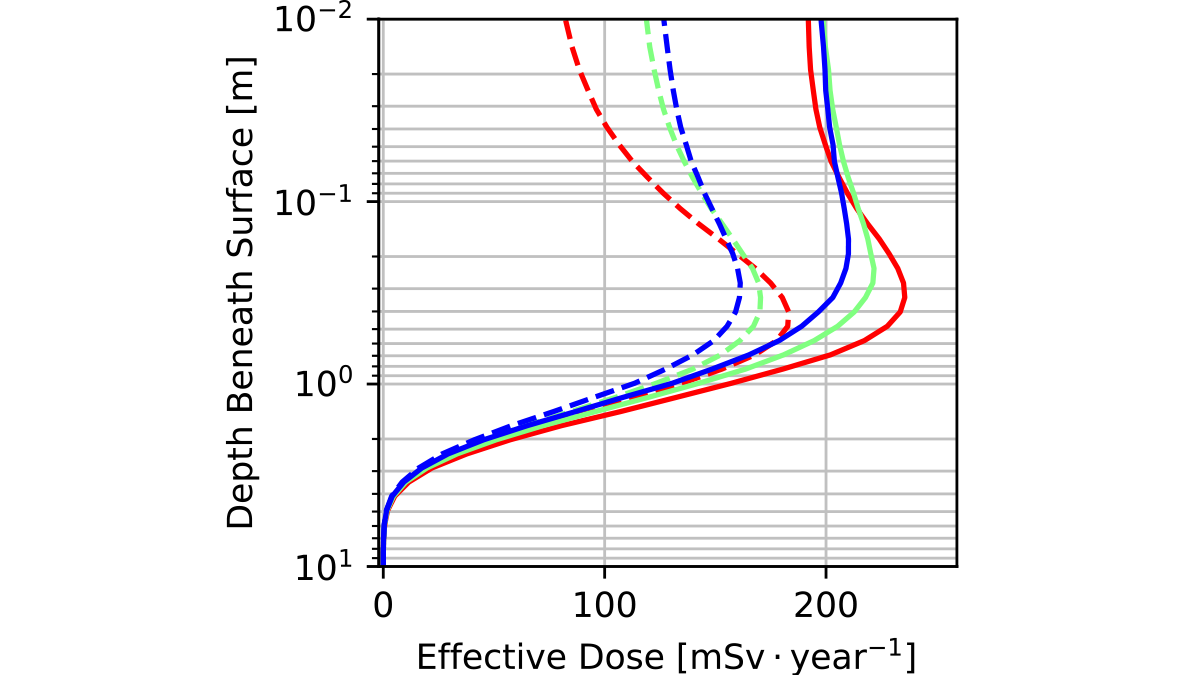
Life on Mars? Estimating Radiation Risks for Martian Astronauts
New research suggests that to minimize radiation risk for human exploration of Mars, astronauts will need to dig deep for safety.
The Mystery of Methane on Mars Thickens
Two recently published papers zoom in on the mystery source of methane in the Martian atmosphere.
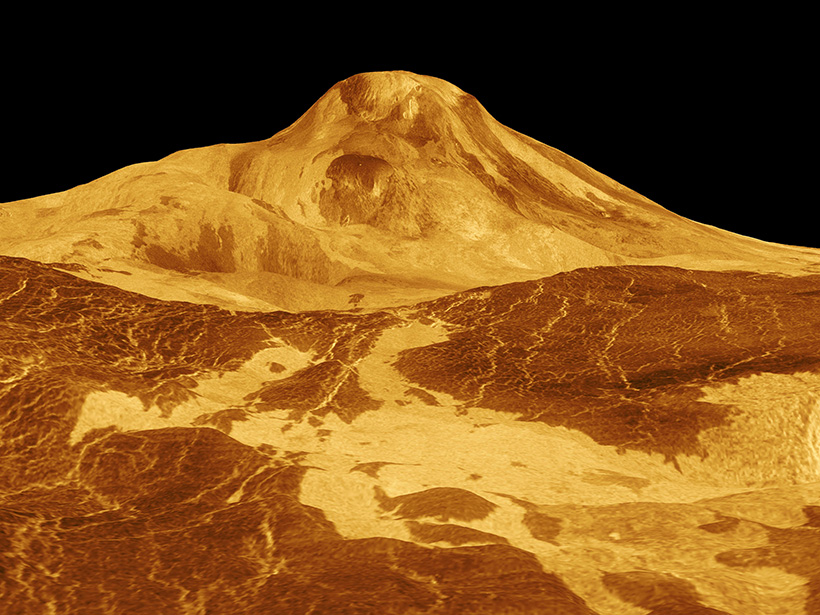
¿Es Venus volcánicamente activo? Nuevo enfoque podría proporcionar una respuesta
Una estrategia que combina la cartografía geológica con datos sobre cómo la superficie del planeta emite y absorbe la radiación de microondas podría potencialmente identificar flujos de lava recientes.
Clues to Pluto’s History Lie in Its Faults
Studying geological features on Pluto’s surface can illuminate the ancient history of how the dwarf planet formed.
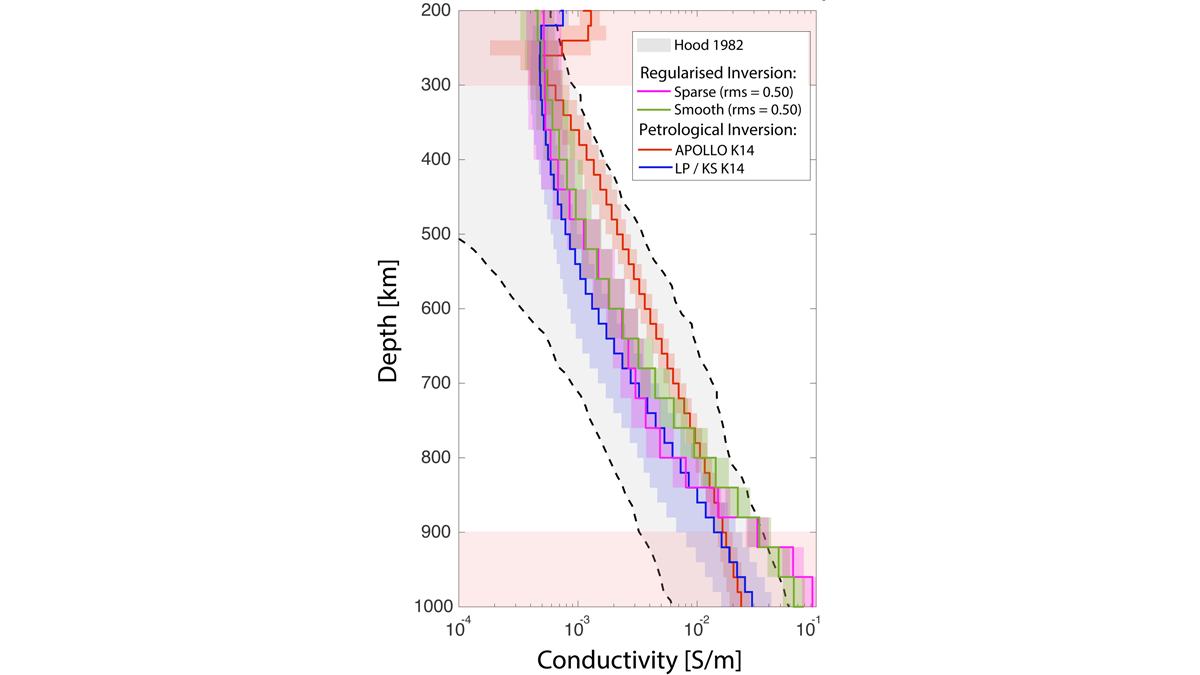
A Better Look at the Moon’s Middle Mantle
A new analysis strategy sheds new light on the electrical conductivity of the lunar mantle between 300 and 900 km depth.
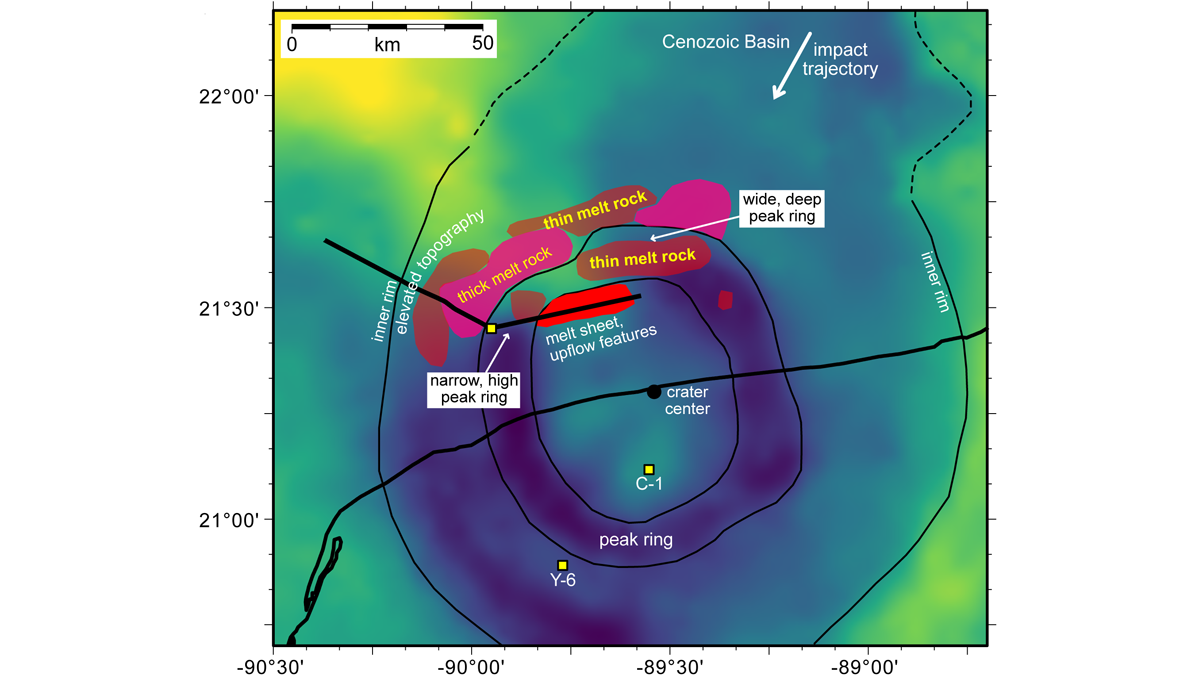
Shining a Spotlight on the Chicxulub Impact Crater
A new seismic survey of the Chicxulub impact crater reveals the structure of its peak ring and the sediments that cover it.