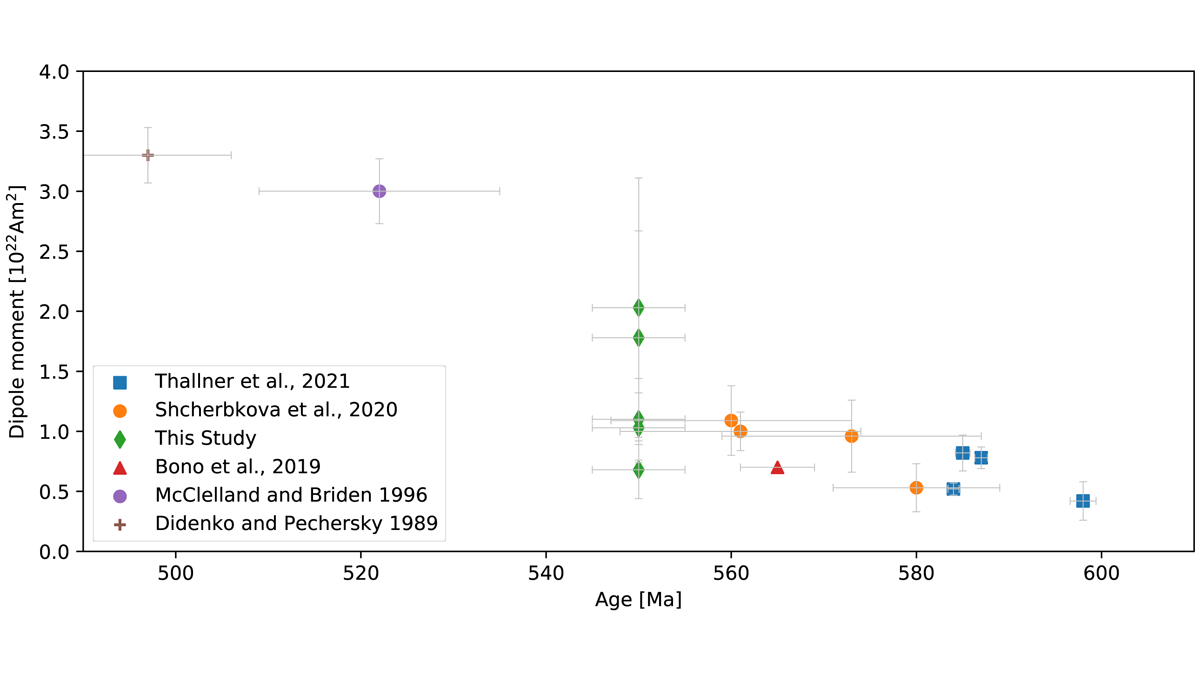
The Ediacaran features an instable magnetic field complicating paleogeographic reconstructions; a new paleointensity study on late Ediacaran rocks indicates a weak but stable dipolar field.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
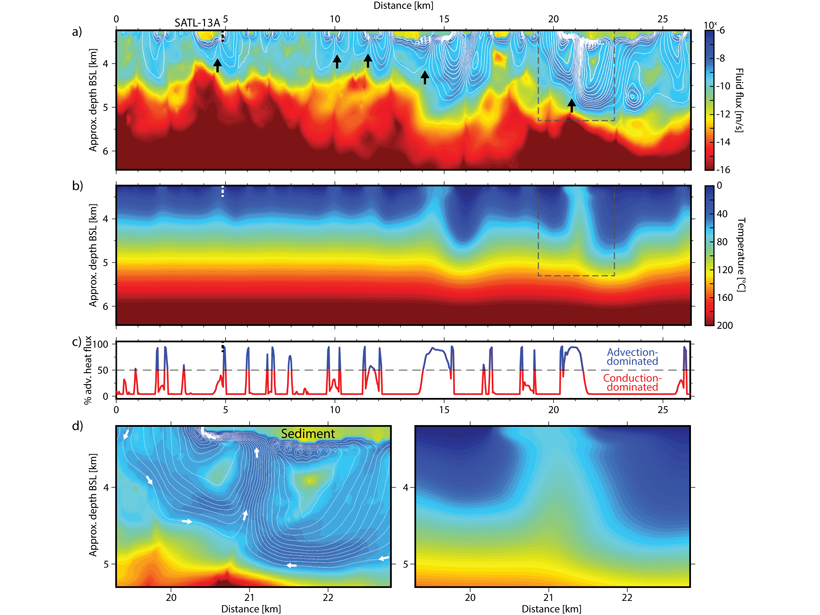
Mechanisms of Hydrothermal Ocean Plate Cooling Revealed
A combination of waveform tomography and hydrothermal modelling allows characterizing the mechanisms and reach of fluid flux and ocean plate cooling near mid-ocean ridges with unprecedented detail.
Long-Term Sea Level Cycle Affects Predictions of Future Rise
New research confirms the existence of a regular, long-term fluctuation in sea level, perhaps caused by processes in Earth’s core.
A Novel Thermobarometer to Infer Mantle Melting Conditions
The algorithm RevPET automatically reverses the complex multi-phase fractional crystallization path of oceanic basalts and offers new perspectives for advancing mantle thermobarometry.
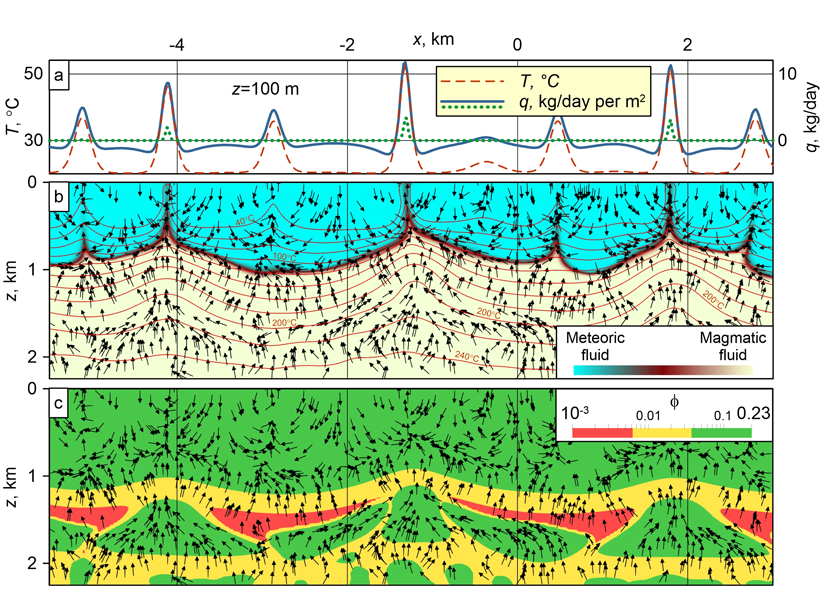
Coupled Mechanisms of Fluid Transport Across the Crust
Magmatic fluid moves up in the ductile zone through porosity waves, accumulates in high-porosity lenses, and migrates across the brittle zone in a convection pattern involving also meteoric fluid.
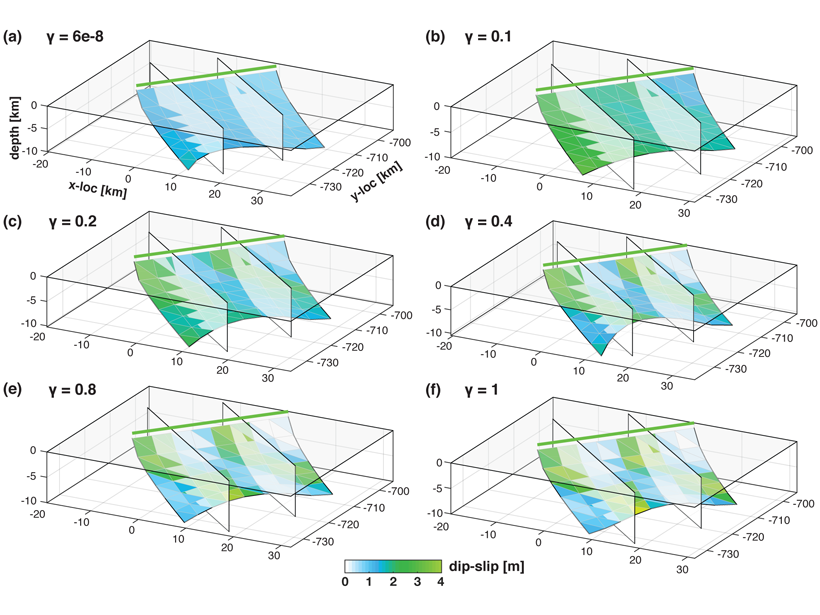
New Inversion Method Improves Earthquake Source Imaging
A new method uses Bayesian inference to jointly invert for non-planar fault geometry and spatially variable slip (with associated uncertainties) in earthquake source modeling, based on geodetic data.
La primera mirada de la meteorización a escala angstrom
Investigadores observan cómo el vapor de agua y el líquido alteran las rocas sedimentarias a través de procesos físicos y químicos.
Volcanic Tremor and Deformation at Kīlauea
Two new studies investigate activity at Hawaii’s Kīlauea leading up to and following the 2018 eruption to better understand the volcano’s plumbing and behavior.
Understanding and Anticipating Induced Seismicity
A new special collection in JGR: Solid Earth and Earth and Space Science seeks papers from across disciplines that provide insights into induced seismicity at different spatial and temporal scales.
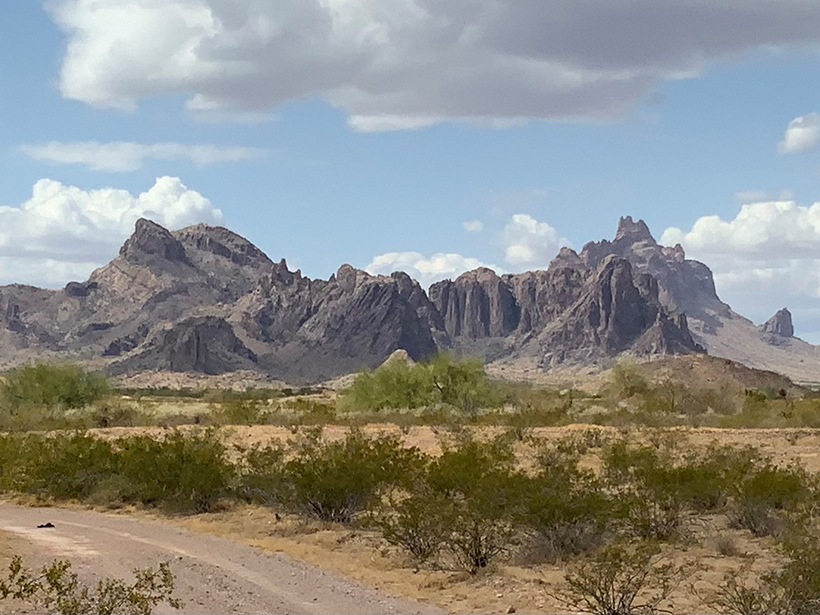
Crustal Motion and Strain Rates in the Southern Basin and Range Province
New research teases out variations in strain rates and explores potential earthquake hazards across the southern Basin and Range and Colorado Plateau.