Based on an extended stress database, scientists observe systematic changes in the tectonic stress state and a reduction in fault reactivation potential near salt walls in the Paradox Basin.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth
Microbes Likely Form Magnetite in the South China Sea
Researchers sampled sediment cores and found that where magnetite was abundant, methane-producing bacteria were as well.
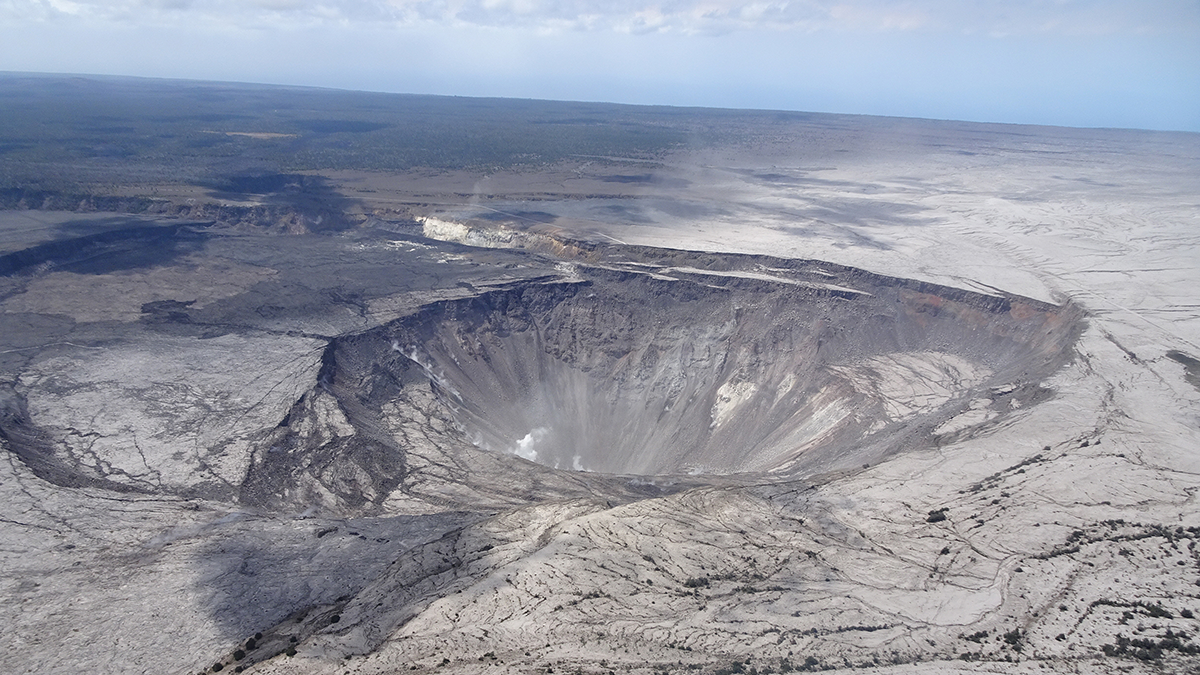
Caldera Collapse as a Natural Example of Rock Friction
Recurrent slips on the caldera wall of the Kīlauea Volcano are a natural experiment not only to understand the mechanics of caldera formation but also to gain more insights into fault friction.
Cómo los movimientos del manto dan forma a la superficie terrestre
Dos nuevos conjuntos de datos ayudan a los investigadores a separar las influencias de la tectónica de placas y el movimiento del manto en la topografía de la superficie.
¿El secreto para imitar fallas naturales? Plexiglás y teflón
Investigadores encontraron una manera eficaz para producir un comportamiento de fallas natural en el laboratorio.
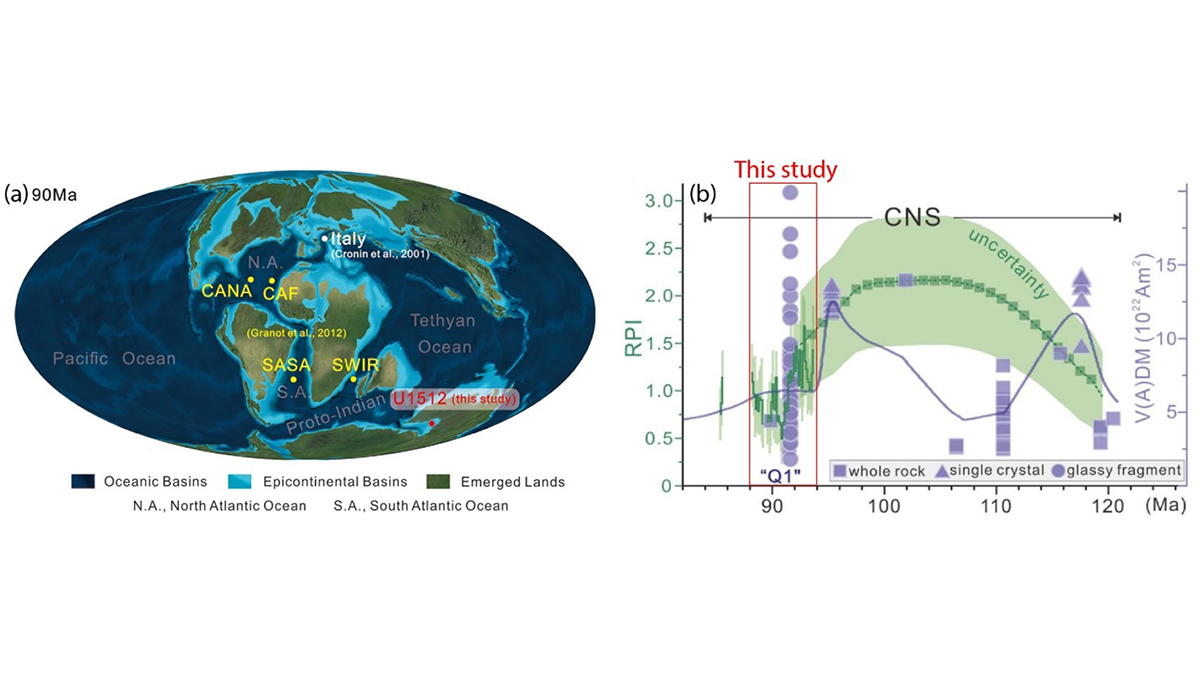
The Not-So-Quiet Cretaceous Quiet Zone
A new study finds that Earth’s magnetic field intensity varied significantly during the Cretaceous Normal Superchron, providing insights into the operation of the geodynamo during superchrons.
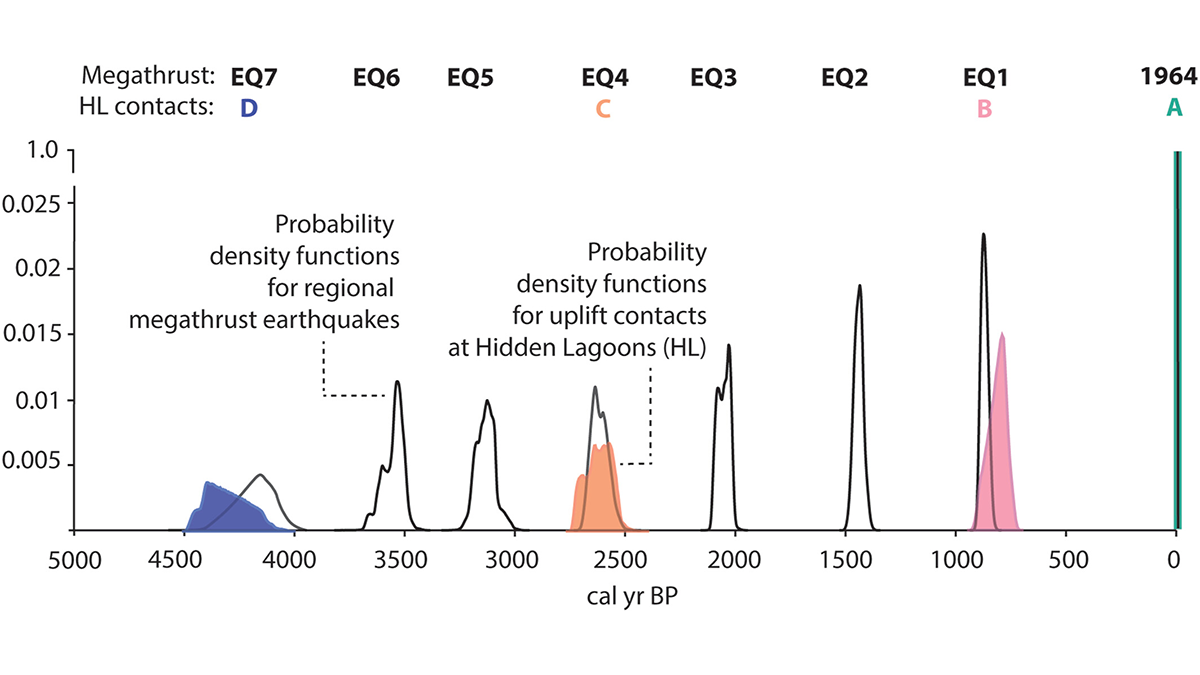
Repeated Coseismic Uplift Above the Patton Bay Splay Fault, Alaska
Stratigraphic and diatom analyses suggest ruptures of the Patton Bay splay fault occurred together with half of the documented great Alaskan megathrust earthquakes during the past 4,200 years.
The Secret to Mimicking Natural Faults? Plexiglass and Teflon
Researchers found an effective way to produce natural fault behavior in the laboratory.
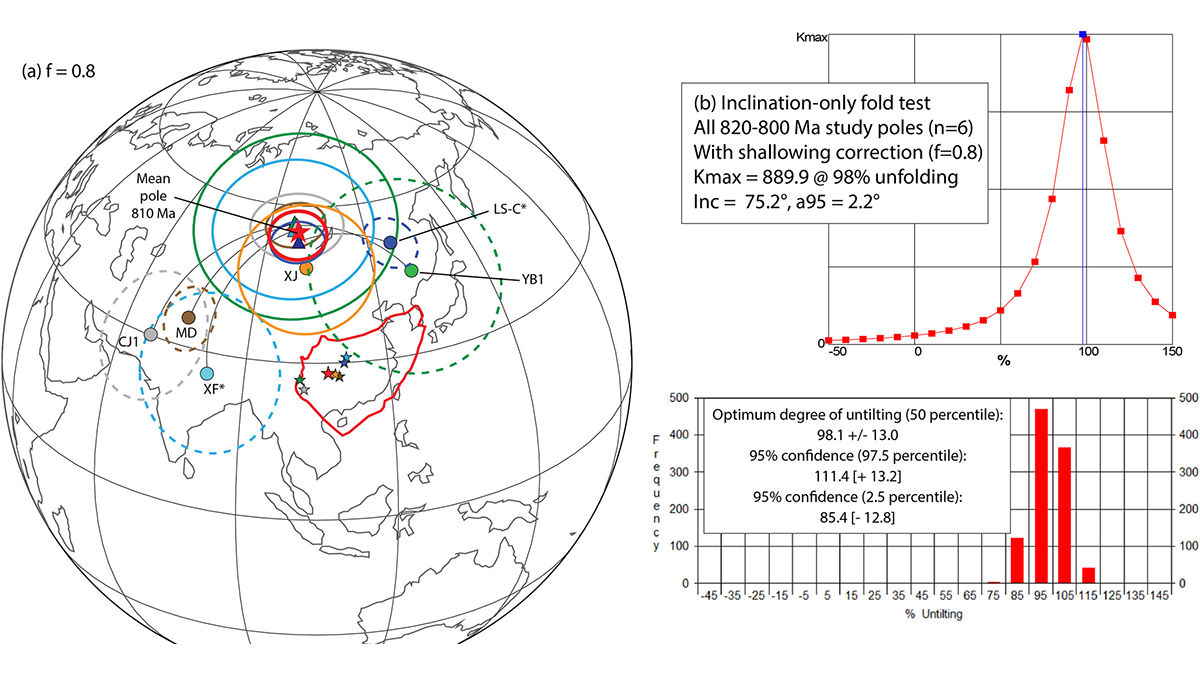
GAD is Enough!
An exhaustive study in China finds no need to invoke extreme true polar wander nor anomalous geomagnetic fields in the early Neoproterozoic.
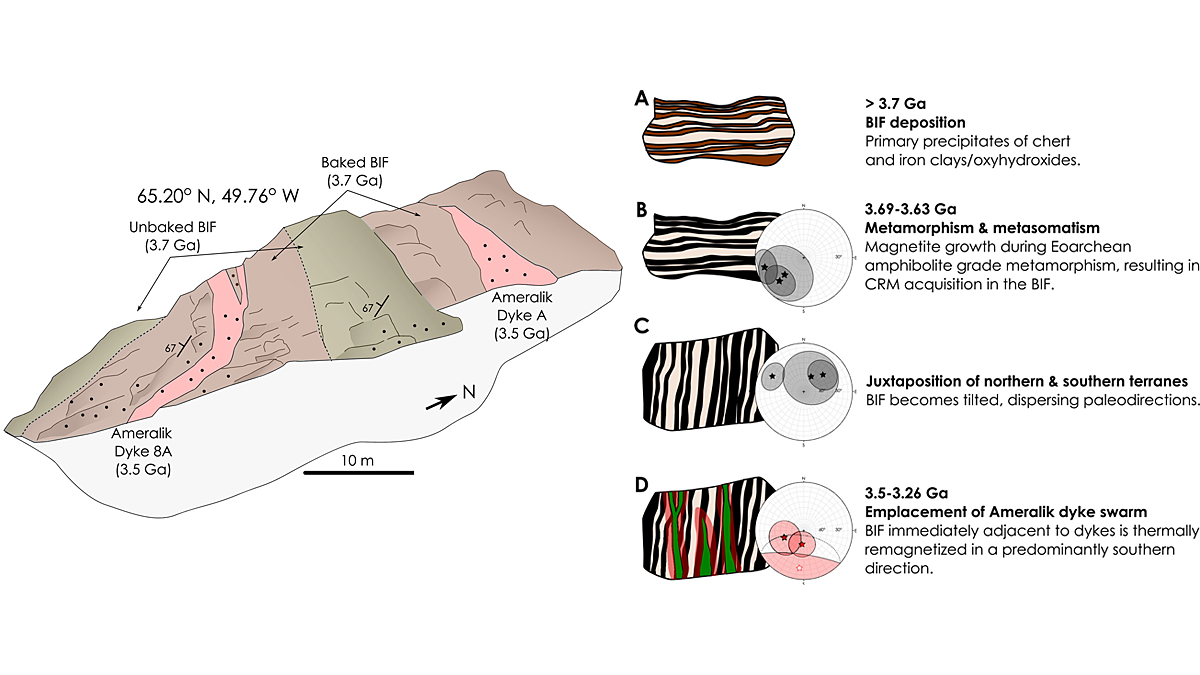
Greenland Could Have Records of 3.7-billion-year-old Geomagnetic Fields
Scientists argue that paleomagnetic field tests preserve a geomagnetic field record acquired as chemical remnant magnetization in banded iron formations in southwest Greenland.