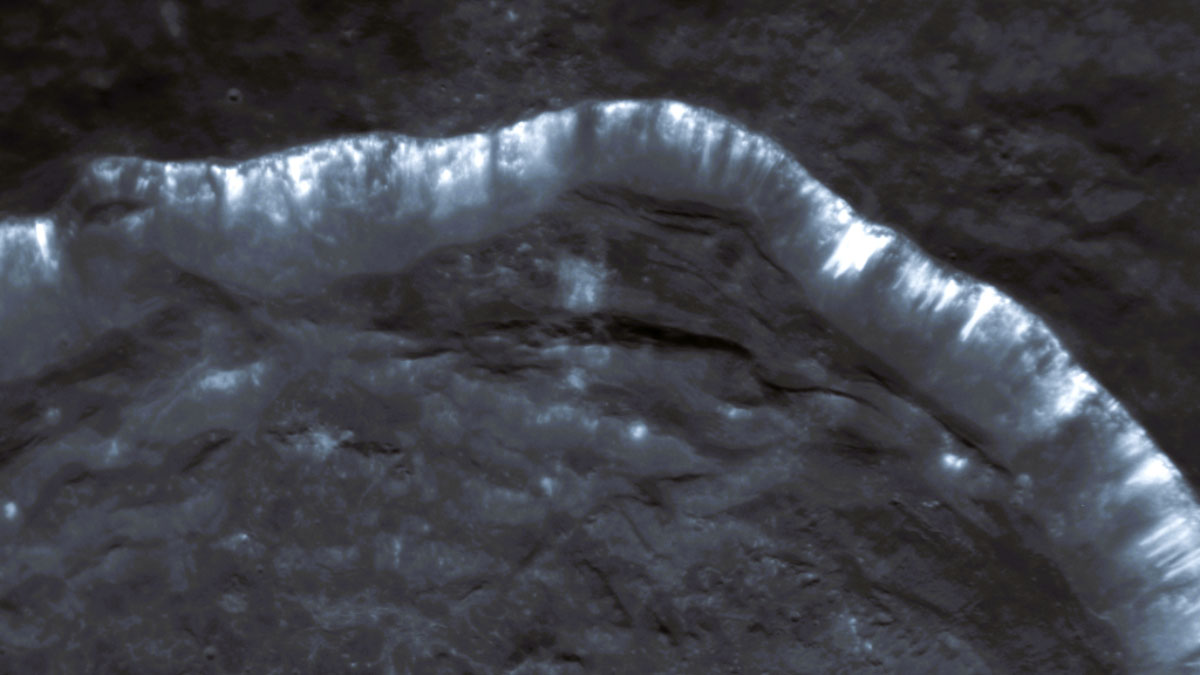
Scientists are using new computational tools to analyze troves of old spacecraft data to better understand one of Mercury’s unsolved mysteries.
machine learning & AI
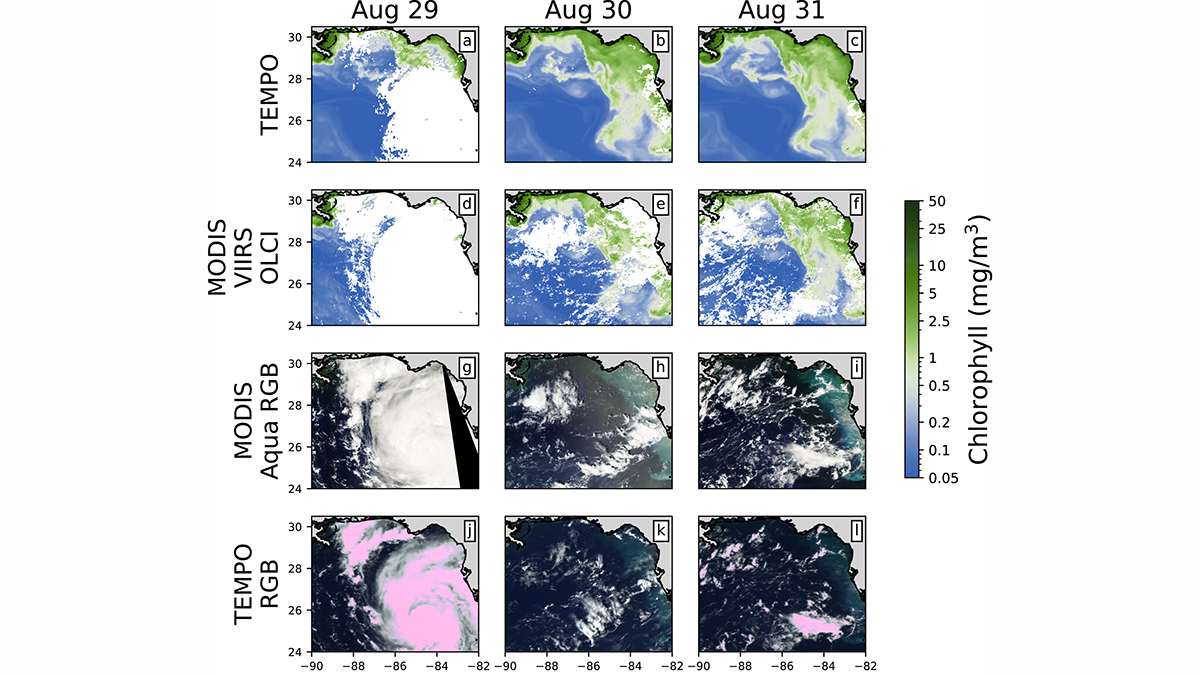
Monitoring Ocean Color From Deep Space: A TEMPO Study
Scientists apply machine learning to demonstrate that geosynchronous satellites can be used to assess the health of oceans from deep space.
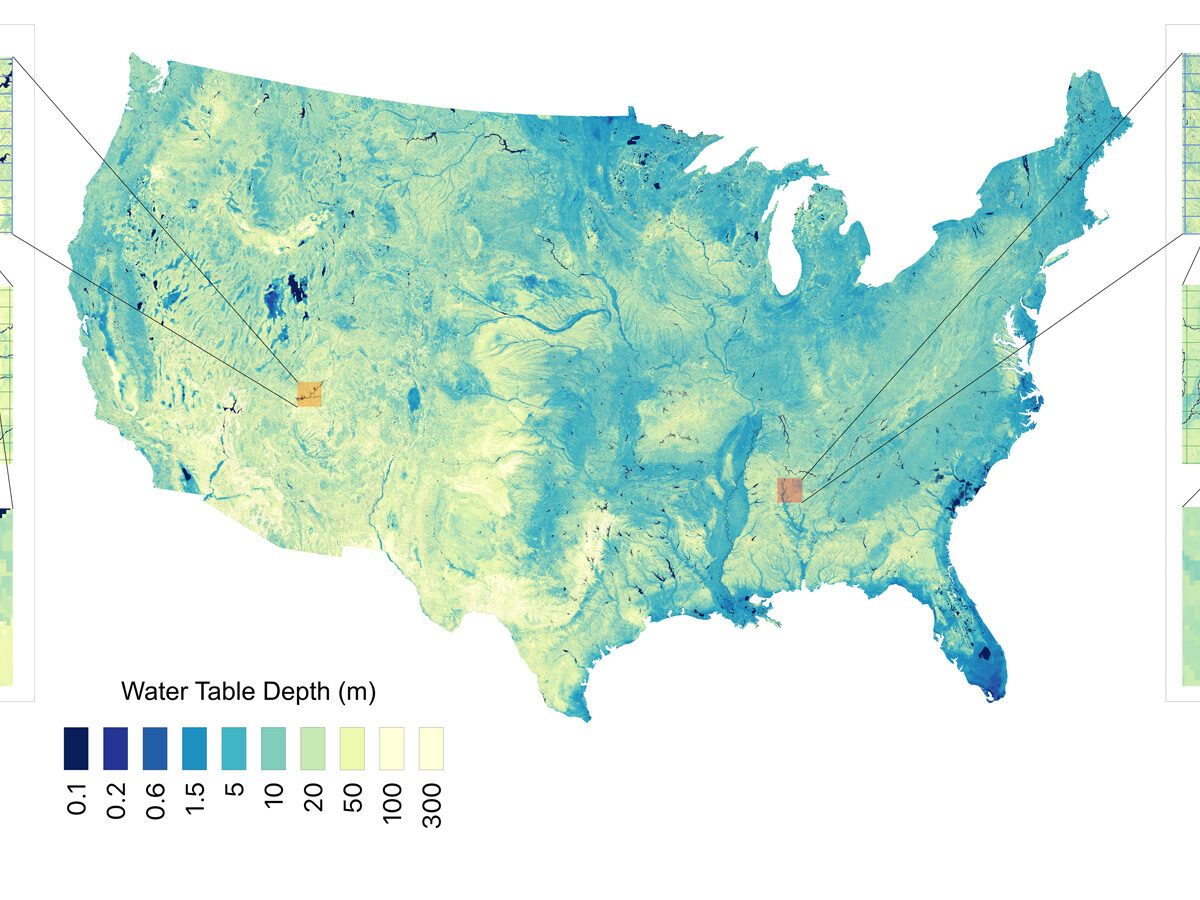
Report: 13 Great Lakes’ Worth of Water Underlies the Contiguous United States
Researchers used 1 million data points and a machine learning algorithm to estimate groundwater stores with higher resolution than ever before.
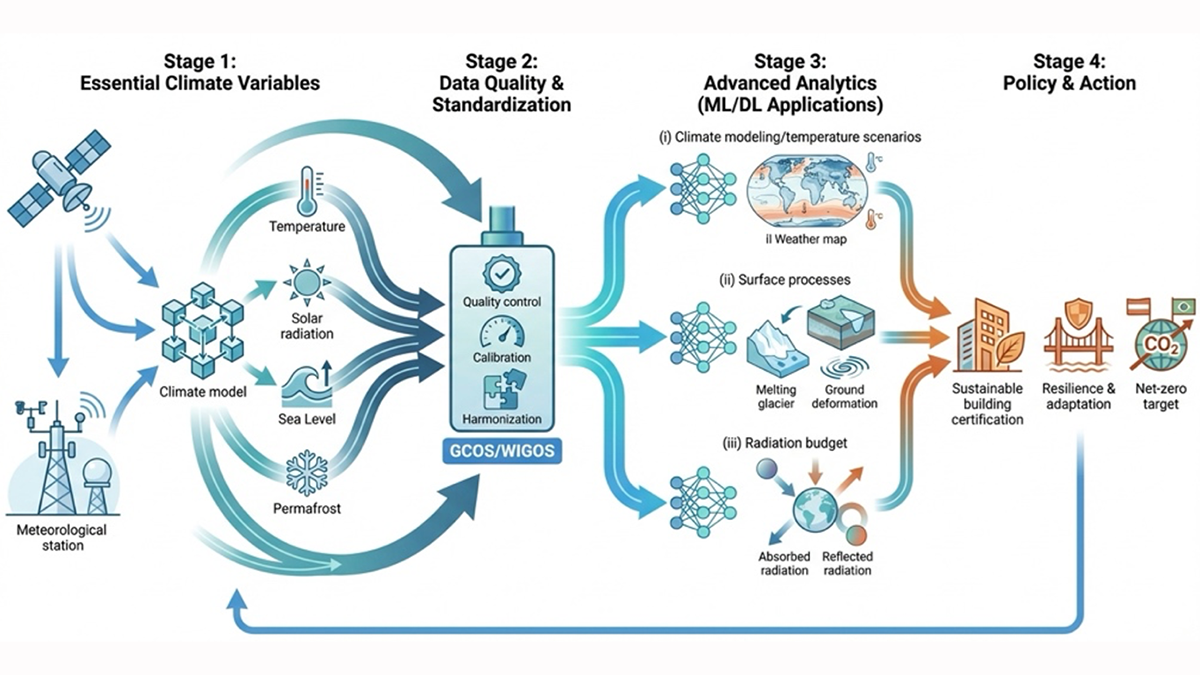
Bridging the Gap: Transforming Reliable Climate Data into Climate Policy
A new special collection welcomes research that bridges the gap between rigorous Essential Climate Variable (ECV) monitoring, AI analytics, and climate policy.
AI Sheds Light on Hard-to-Study Ocean Currents
The Maluku Strait is a key predictor of conditions in the Indonesian Throughflow, modeling shows.
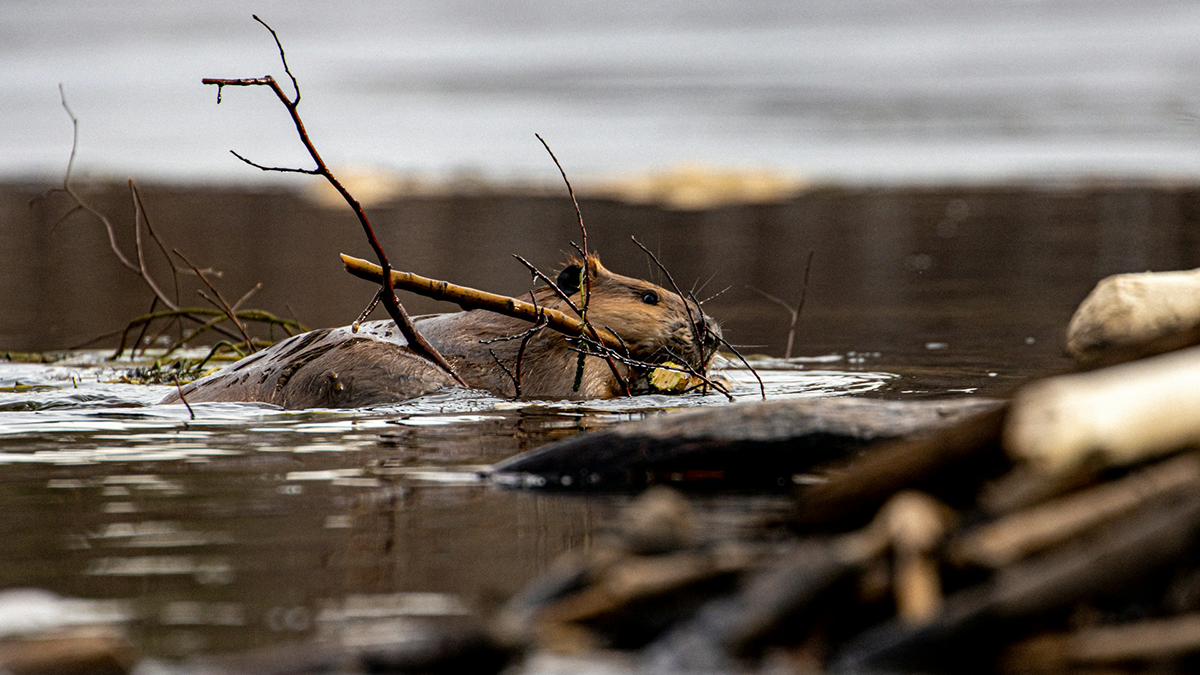
Beavers are Not Concerned About Groundwater
But, scientists are! A new study illuminates the complex interactions of beaver dam induced ponding and floodplain inundation with shallow groundwater storage and flow patterns.
AI is Changing our Understanding of Earthquakes
Machine learning is expanding scientists’ catalogs of quakes and refining maps of underground faults. It also promises to improve quake forecasts.
Martian Dust Devils Reveal Dynamic Surface Winds
A new wind map covering the whole of Mars includes some of the fastest winds ever detected on the Red Planet.
A Step Toward AI Modeling of the Whole Earth System
Coupling an AI-driven model of the atmosphere with a model of the ocean could help scientists create highly efficient emulations of the entire Earth system.
The AI Revolution in Weather Forecasting Is Here
The past decade has seen explosive growth in forecasting research and applications using AI. Sophisticated new approaches show vast potential to support public safety, health, and economic prosperity.