The lack of bird records in formerly redlined areas creates an inaccurate picture of urban biodiversity, leading to gaps in conservation efforts.
mapping
A Lunar Mission Spots Its Failed Brethren
Data from NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter have been instrumental in pinpointing where other Moon-bound spacecraft have crashed.
Natural Floodplains Are Quickly Vanishing
From 1992 to 2019, 600,000 square kilometers of natural floodplains were lost globally due to land conversion.
Where the Ground Gives Way
Sinkholes are a significant hazard, but where are they most likely to happen? A new study identifies hot spots in the contiguous United States.
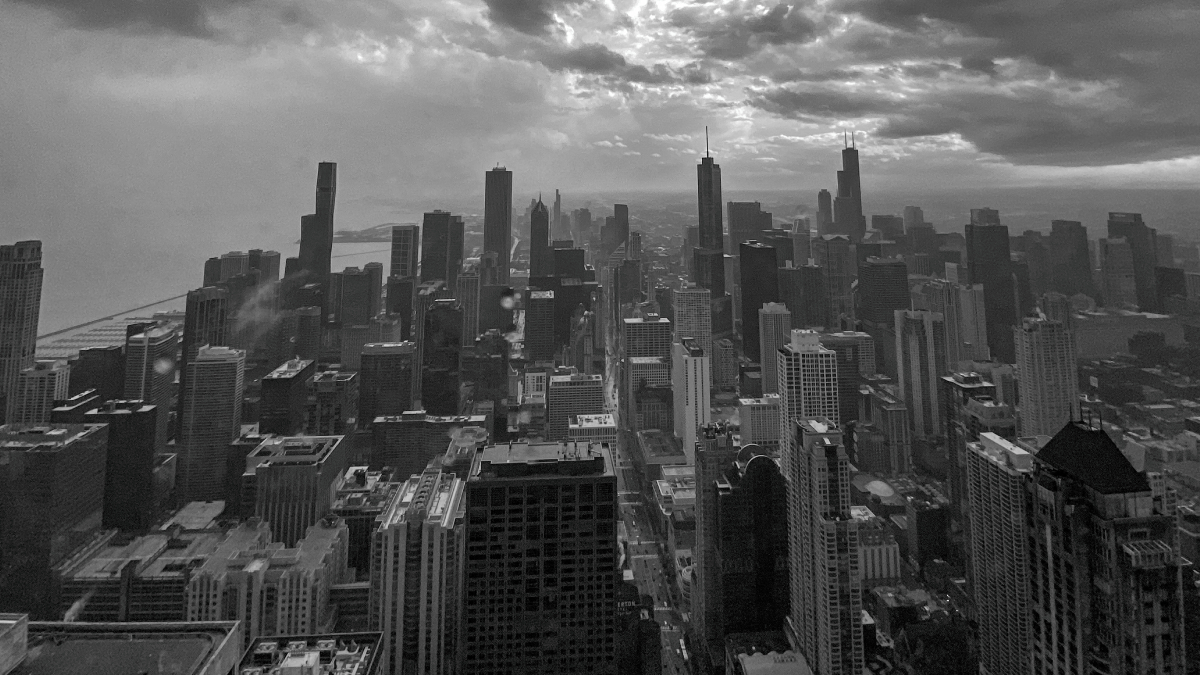
Underground Heat Could Be a Problem, or a Perk, for Chicago Buildings
Heat released by old and inefficient Chicago buildings could, if harnessed, be an energy solution.
A New, Underground Atlas of Subduction Zones
Submap merges graphic design with geodynamics, providing a fast, free, and user-friendly resource to map subduction zones.
Cee Nell: Making Data Visual
Nell turns vast columns of data into beautiful and understandable graphics.
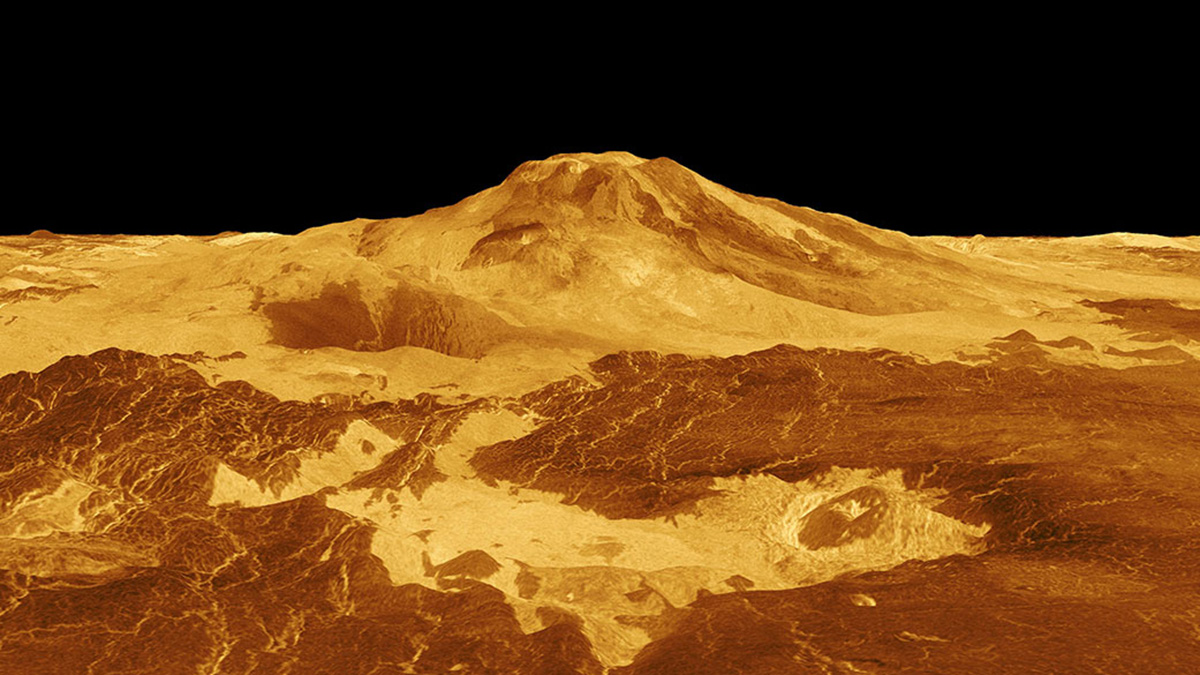
Active Volcanoes on Venus?
With a new look at old imagery, scientists may have found evidence of volcanic activity on Venus.
Mapping Wetland Loss Across Three Centuries
Millions of square kilometers of wetlands have been drained or converted to make room for crops, pastures, or development. In some places, up to 80% are gone.
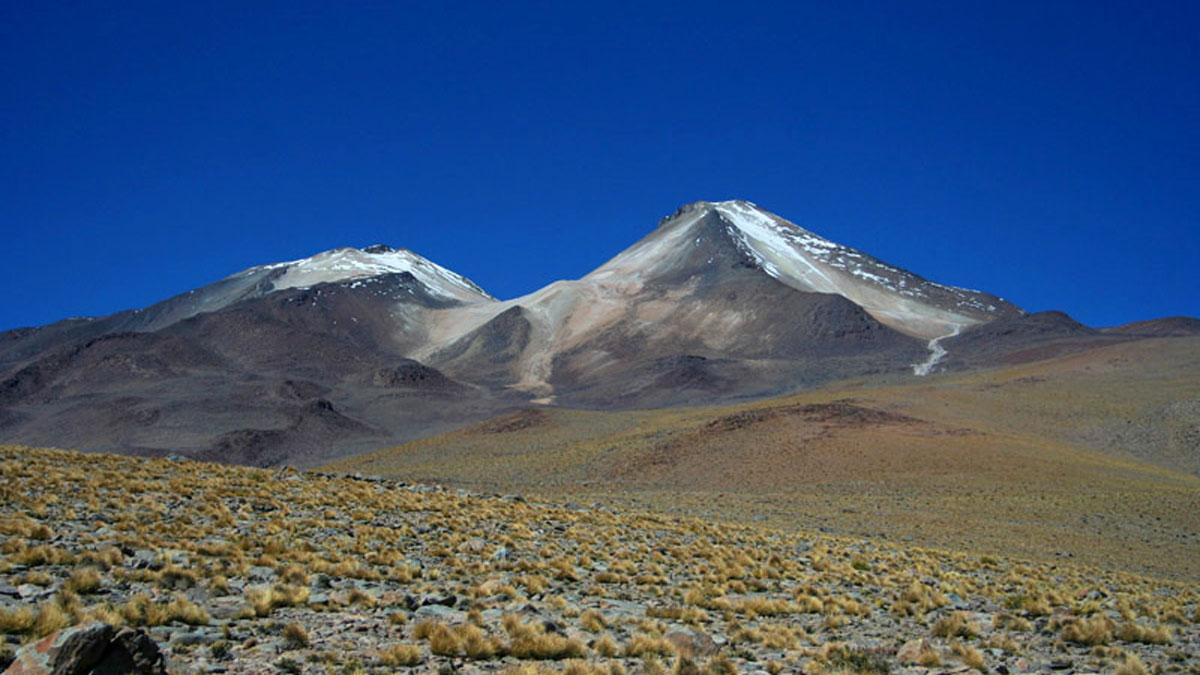
Mapping the Fizzy Brines and Fluid-Filled Fractures Below a Volcano
Seismic tools reveal where hydrothermal fluids lie beneath the Uturuncu volcano in Bolivia and hint at their composition.