From a simple set of in situ or synthetic data, a general unified model has been developed to calculate turbulent fluxes and evaporation rates on any rocky body with an atmosphere.
Modeling
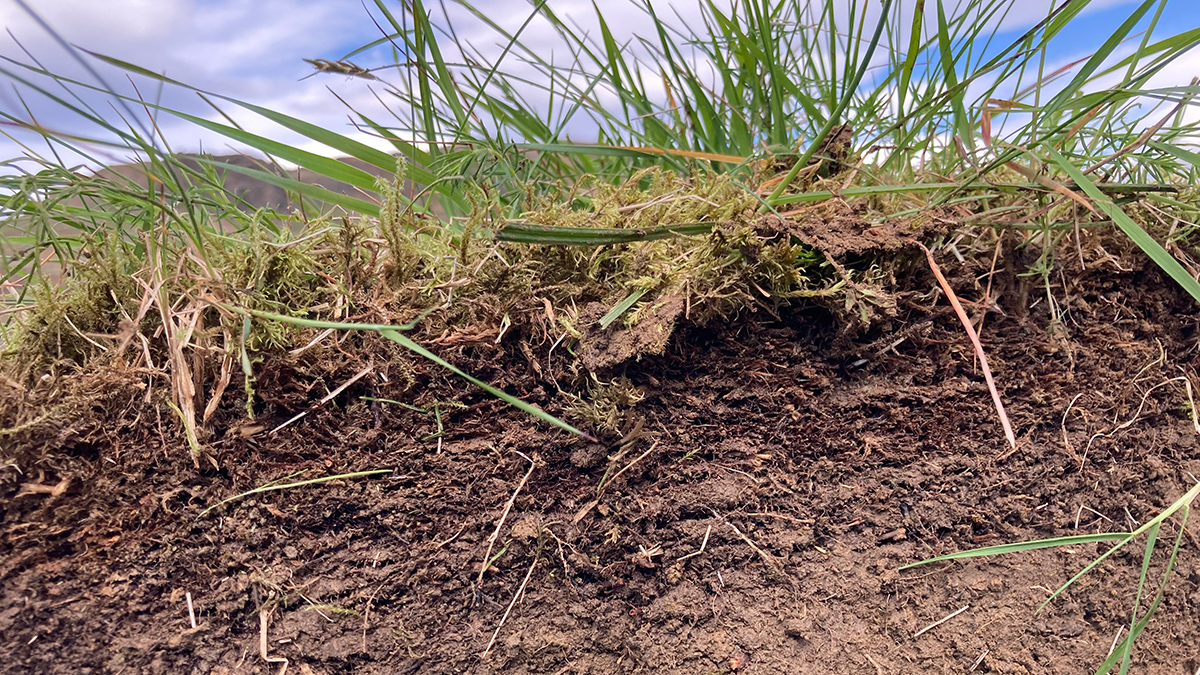
How Are Deep Soils Responding to Warming?
Scientists aim to integrate observations from deep-soil-warming experiments worldwide to better understand how ecosystems vital to food security and environmental health will react to climate change.
Animals Deserve to Be Included in Global Carbon Cycle Models, Too
Because they are far less plentiful than plants and microbes, animals have typically been excluded from examinations of carbon exchange in the atmosphere. But new research shows they may have a considerable influence on carbon cycle dynamics.
Learning Data Assimilation Without the Help of the Gaussian Assumption
Major Earth system processes are non-linear and non-Gaussian, and so should be our data assimilation approaches.
Barrier Islands Are at the Forefront of Climate Change Adaptation
Coastal evolution modeling sheds light on the impacts of coastal development and adaptation decisions on barrier islands in the era of sea-level rise.
Verifying the Mathematics Behind Ocean Modeling
A series of test cases designed to confirm the accuracy of ocean models could help improve our understanding of large-scale climate processes.
Forecasters Expect Slow Start to U.S. Wildfire Season
A wet spring in the United States will dampen early fires, but some regions will see elevated risk this summer.
When It Rains, It Pours!
Water that falls on a forest canopy during rainfall events reaches the ground at focused locations called “pour points”. This insight has a major impact on how we view hydrologic processes on the ground.
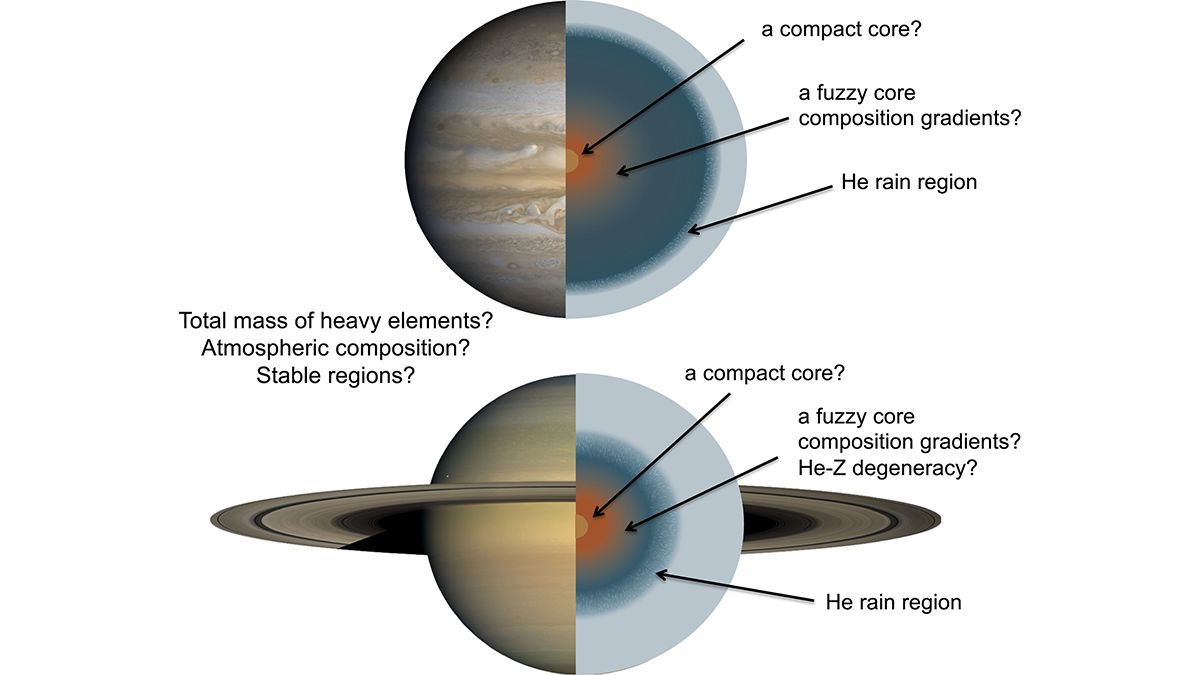
Gas Giants with Fuzzy Cores
New measurements of Jupiter and Saturn show that both planets have dense cores that are gradational (fuzzy) and large, rather than small and compact.
When You’re a Wet(land), You’re A Wet(land) All the Way
Wetlands and their methane emissions require careful consideration for incorporation in Earth system models with many advances made over the past 30 years.