The #GreatAntarcticClimateHack; La Jolla, California, 9–12 October 2017
Modeling
Life and Death in the Deepest Depths of the Seafloor
Lacking light and energy, under-seafloor microbes rely on ancient organic materials to survive.
New Paths for Plankton in Warming Arctic?
Water flowing from the Pacific to the Atlantic could find new shortcuts, enabling plankton to survive the trip through the cold polar region.
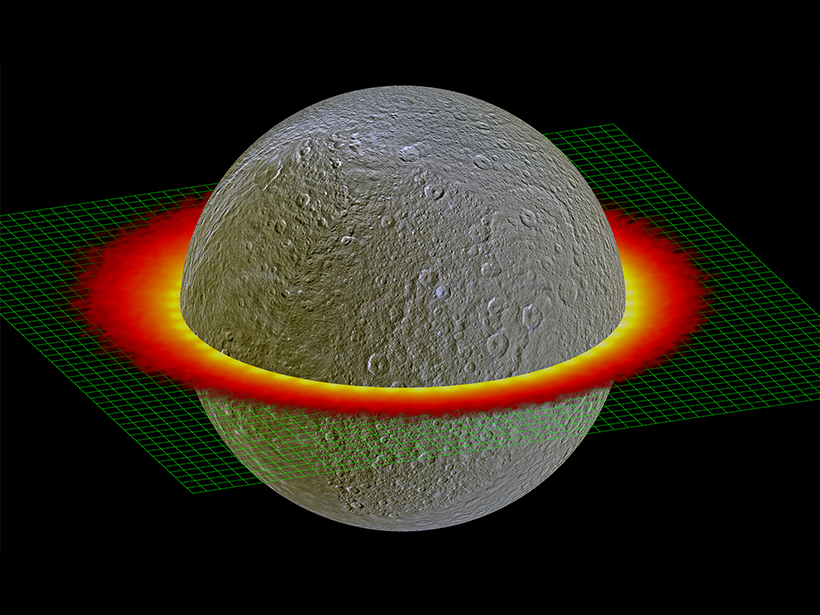
A Consistent Model of Ice Dissociation on Celestial Bodies
A model based on decades of experimental results can now quantify the products of water ice dissociation caused by radiation and predict the products expelled into an icy body’s outer atmosphere.
A Near-Real-Time Tool to Characterize Global Landslide Hazards
By fusing susceptibility information with precipitation data, a new model generates “nowcasts” to predict the potential for rainfall-triggered landslides in steep terrain between 50°N and 50°S.
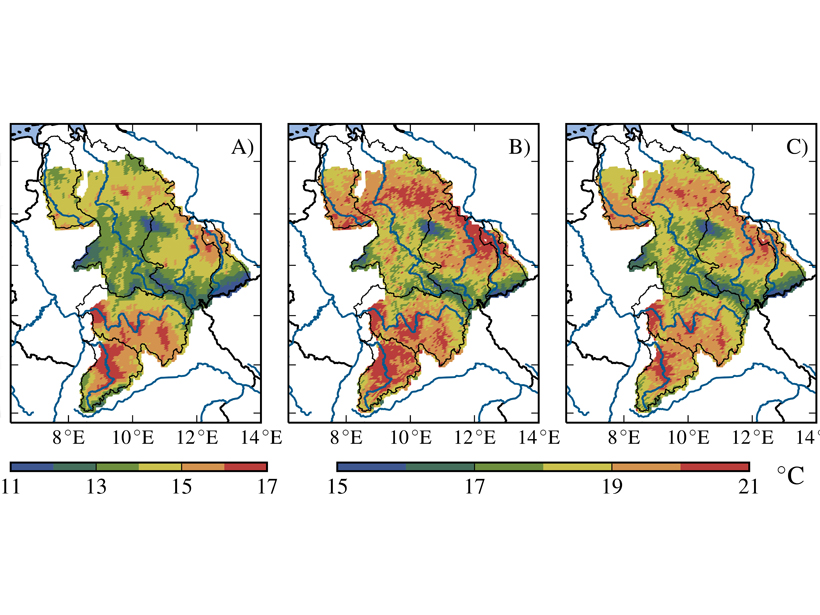
A Better Way to Predict the Indian Monsoon
A new study finds that including Himalayan topography and land-atmosphere interactions improves climate models.
Toward More Realistic Modeling of the Mesosphere
New study reveals complex behavior of gravity waves in the atmosphere.
Improving Tropical Cyclone Predictions in the Gulf of Mexico
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s newest High Resolution Atmospheric Model captures the influence of intraseasonal oscillations on tropical cyclone activity.
Calibrating Hydrological Models by Satellite
Hydrological models are usually calibrated using observations of streamflow, but a new method uses remotely sensed land surface temperature for this purpose.
How Space Storms Affect the Satellite Superhighway
A powerful numerical model reveals how space weather disturbs magnetic field at geosynchronous orbit.