Information is lost when researchers combine statistical models and remote sensing data, but just how much is often unclear. A new study offers a framework to measure the inefficiency.
Modeling
First Multi-Decade Simulation of the Earth’s Radiation Belt
A new simulation of the Earth’s electron radiation belts captures large-scale variations over nearly three solar cycles, and replicates primary cyclical features and extreme behaviors.
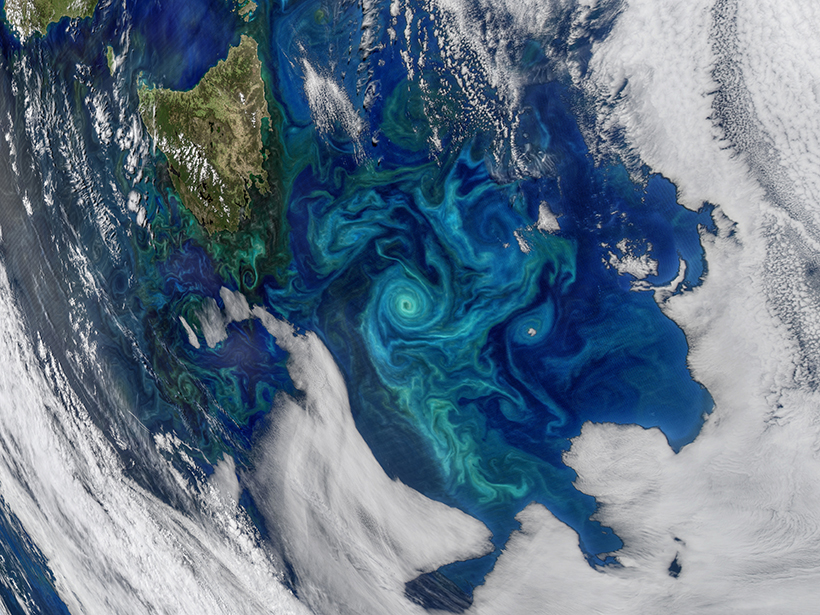
Interpreting Mosaics of Ocean Biogeochemistry
Advances in technology and modeling capabilities are driving a surge in progress in our understanding of how ocean ecosystems mix and mingle on medium to small scales.
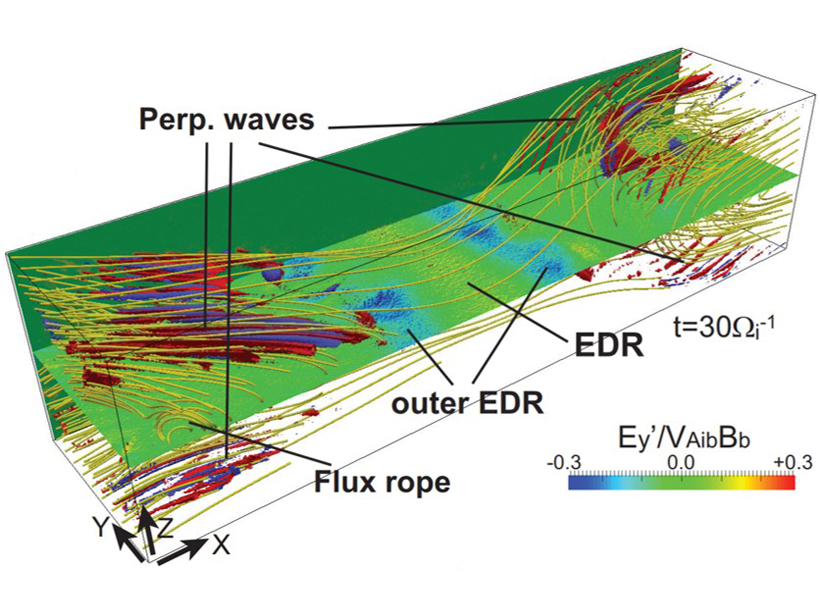
Measuring the Magnetic Reconnection Rate in the Magnetotail
Both simulations and observations are used to measure the magnetic reconnection rate in the Earth’s magnetotail, suggesting that the rate is correlated with the intensity of a magnetic substorm.
Facilitating Field-Scale Experiments in Volcano Hazards
Multidisciplinary Volcano Hazards Experiments at the Geohazards Field Station; Amherst and Springville, New York, 24–27 July 2018
The ILAMB System for Benchmarking Land Surface Models
An evolving set of tools helps land surface model developers optimize the realism of their parameterizations for the next generation of weather and climate models.
Satellite Observations Validate Stratosphere Temperature Models
Since the 1970s, the stratosphere has cooled as ozone levels dropped and carbon dioxide levels increased. Chemical models of the temperature decline conflicted with satellite observations—until now.
Using Information Theory in Earth Sciences
Second Workshop on Information Theory and the Earth Sciences; Santander, Spain, 16–19 May 2018
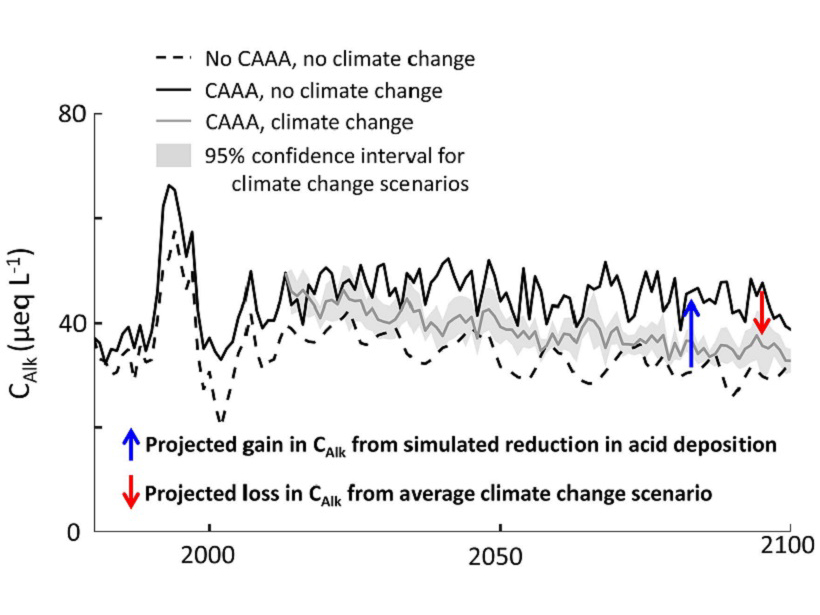
The Acid Tongue of Climate Change Strikes Our Streams
Clear air policies have led to dramatic reductions in acid rain and improved ecosystem health, but it now appears that climate change could counteract those gains.
Congress Throws Tropical Forest Research Program a Lifeline
Climate researchers and ecologists laud the continuation of effort to fuse data from tropical forests with modeling.